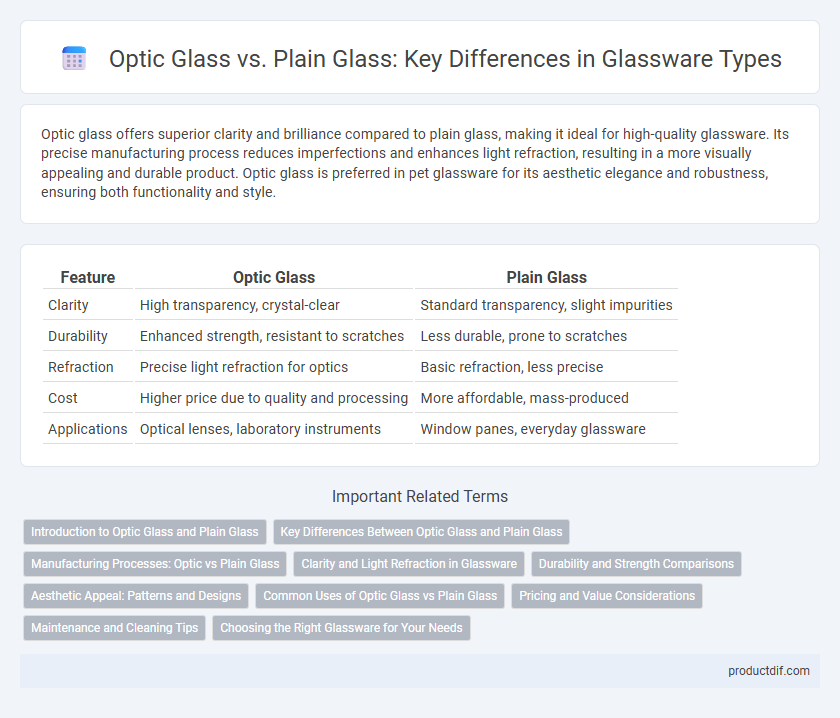
Optic glass offers superior clarity and brilliance compared to plain glass, making it ideal for high-quality glassware. Its precise manufacturing process reduces imperfections and enhances light refraction, resulting in a more visually appealing and durable product. Optic glass is preferred in pet glassware for its aesthetic elegance and robustness, ensuring both functionality and style.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Optic Glass | Plain Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Clarity | High transparency, crystal-clear | Standard transparency, slight impurities |
| Durability | Enhanced strength, resistant to scratches | Less durable, prone to scratches |
| Refraction | Precise light refraction for optics | Basic refraction, less precise |
| Cost | Higher price due to quality and processing | More affordable, mass-produced |
| Applications | Optical lenses, laboratory instruments | Window panes, everyday glassware |
Introduction to Optic Glass and Plain Glass
Optic glass is specially formulated with precise optical properties, offering high clarity, low distortion, and excellent light transmission, making it ideal for lenses and precision instruments. Plain glass lacks these refined characteristics, featuring general-purpose clarity and strength suitable for everyday items like windows and containers. The key distinction lies in optic glass's enhanced purity and controlled refractive index, which enable superior visual performance compared to the more basic and versatile plain glass.
Key Differences Between Optic Glass and Plain Glass
Optic glass offers superior clarity and minimal distortion due to its precise refractive index control, making it ideal for lenses and high-quality optical instruments. Plain glass lacks the optical precision of optic glass, resulting in lower light transmission and higher visual distortion. The manufacturing process of optic glass involves strict purity and composition standards, whereas plain glass is produced with less stringent controls, affecting its durability and performance in specialized applications.
Manufacturing Processes: Optic vs Plain Glass
Optic glass manufacturing involves a precise cutting and polishing process to achieve superior clarity and consistency, often requiring annealing to reduce internal stresses and enhance optical properties. Plain glass production typically employs a simpler float glass method, where molten glass is floated on molten metal to create flat sheets with minimal surface distortion but less emphasis on optical precision. The specialized techniques in optic glass processing result in higher-quality lenses and prisms used in scientific and photographic instruments compared to the more general-purpose applications of plain glass.
Clarity and Light Refraction in Glassware
Optic glass exhibits superior clarity compared to plain glass due to its higher purity and precise manufacturing process, resulting in fewer impurities and distortions. The enhanced light refraction in optic glass creates sharper, more vibrant reflections and increased brilliance, making it ideal for premium glassware. Plain glass typically has lower clarity and less controlled refraction properties, which can dull the appearance and reduce the visual appeal of glassware.
Durability and Strength Comparisons
Optic glass exhibits superior durability and strength compared to plain glass due to its precise manufacturing process and high-quality raw materials, resulting in enhanced resistance to scratches and impact. The molecular composition of optic glass minimizes internal stresses, making it less prone to cracking under pressure, unlike plain glass which often has uneven stress distribution. These properties make optic glass the preferred choice for applications requiring long-lasting clarity and mechanical toughness.
Aesthetic Appeal: Patterns and Designs
Optic glass features intricate patterns and raised ridges that enhance light refraction, creating a visually dynamic and elegant appearance compared to plain glass's smooth and minimalistic surface. The textured design of optic glass adds sophistication and depth, making it a preferred choice for decorative tableware and glassware collections. Plain glass offers a clean, understated look that emphasizes simplicity but lacks the ornate detailing found in optic glass.
Common Uses of Optic Glass vs Plain Glass
Optic glass is commonly used in precision instruments such as microscopes, cameras, and telescopes due to its superior clarity and ability to minimize light distortion. Plain glass is typically found in everyday applications including windows, bottles, and simple containers where optical quality is less critical. The enhanced optical properties of optic glass make it essential for scientific and optical devices, whereas plain glass remains the standard for general-purpose use.
Pricing and Value Considerations
Optic glass typically commands a higher price than plain glass due to its superior clarity, precision cutting, and durable composition, making it ideal for high-end glassware applications. Plain glass is more affordable but lacks the refined optical qualities, often resulting in lower aesthetic value and reduced longevity. When prioritizing investment, optic glass offers better long-term value through enhanced durability and visual appeal despite its higher initial cost.
Maintenance and Cleaning Tips
Optic glass resists scratches and retains clarity longer due to its high-quality, lead-free composition, requiring gentle cleaning with a mild detergent and a soft cloth to avoid damage. Plain glass is more prone to scratches and cloudiness, necessitating careful handling and regular washing with non-abrasive cleaners to maintain transparency. Both types benefit from drying with a lint-free towel to prevent water spots and preserve their visual appeal.
Choosing the Right Glassware for Your Needs
Optic glass features a unique ridged or pressed pattern that enhances grip and light refraction, making it ideal for formal table settings or decorative purposes. Plain glass offers a smooth, clear surface that suits everyday use and versatile drinkware needs due to its simple, timeless look. Selecting between optic and plain glass depends on factors such as aesthetic preference, durability, and the intended occasion or functionality of the glassware.
Optic Glass vs Plain Glass Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com