Cut-glass pet figurines showcase intricate patterns and sharp detailing achieved through skilled hand-cutting techniques, offering a unique and luxurious aesthetic. Mold-blown glassware, produced by shaping molten glass within molds, provides consistent shapes and smooth finishes ideal for mass production and affordability. Both methods highlight distinct craftsmanship, with cut-glass emphasizing precision and mold-blown focusing on uniformity and accessibility.
Table of Comparison
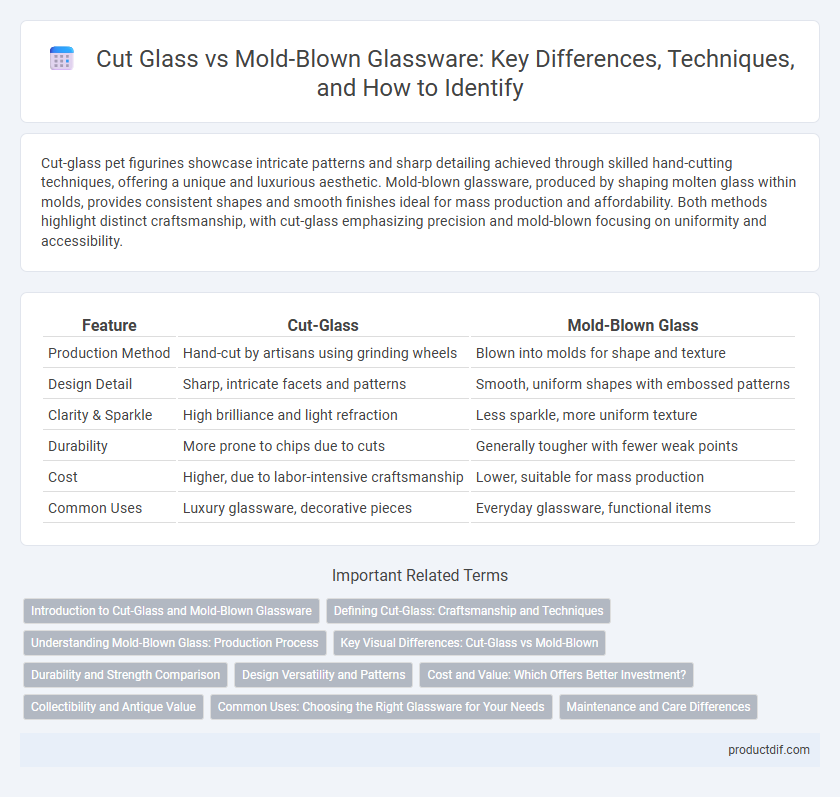
| Feature | Cut-Glass | Mold-Blown Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Production Method | Hand-cut by artisans using grinding wheels | Blown into molds for shape and texture |
| Design Detail | Sharp, intricate facets and patterns | Smooth, uniform shapes with embossed patterns |
| Clarity & Sparkle | High brilliance and light refraction | Less sparkle, more uniform texture |
| Durability | More prone to chips due to cuts | Generally tougher with fewer weak points |
| Cost | Higher, due to labor-intensive craftsmanship | Lower, suitable for mass production |
| Common Uses | Luxury glassware, decorative pieces | Everyday glassware, functional items |
Introduction to Cut-Glass and Mold-Blown Glassware
Cut-glass exhibits intricate patterns created by manually engraving or cutting the surface after the glass is blown, resulting in sharp facets that enhance light reflection. Mold-blown glassware forms by inflating molten glass into a mold, yielding consistent shapes and textured designs without additional cutting. Both techniques highlight different craftsmanship approaches, with cut-glass emphasizing precision and clarity while mold-blown glass showcases uniformity and ornamental surface patterns.
Defining Cut-Glass: Craftsmanship and Techniques
Cut-glass showcases intricate designs created by skilled artisans who carefully carve patterns into solid glass using rotating wheels, enhancing light refraction and brilliance. This craftsmanship contrasts with mold-blown glass, which is shaped by inflating molten glass into molds, resulting in smoother, less detailed surfaces. Techniques like wheel cutting and engraving define cut-glass's distinct texture, depth, and artistic value, making each piece unique and highly collectible.
Understanding Mold-Blown Glass: Production Process
Mold-blown glass is created by inflating molten glass into a mold to shape intricate designs and patterns, allowing for consistent texture and detailed motifs that differ from the sharp facets of cut-glass. This production process involves skilled glassblowers who manipulate the heated glass within metal or wooden molds, producing uniformity and reducing material waste. Mold-blown glassware often features raised patterns and smooth contours, making it a versatile option for decorative and functional items.
Key Visual Differences: Cut-Glass vs Mold-Blown
Cut-glass features sharp, precisely etched patterns created by hand or machine cutting, resulting in a textured surface with facets that refract light brilliantly. Mold-blown glass exhibits smoother surfaces and uniform shapes formed by blowing molten glass into detailed molds, often displaying raised or embossed designs rather than deep cuts. The key visual difference lies in cut-glass's crisp, angular cuts versus mold-blown glass's softer, rounded contours and consistent patterns.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Cut-glass exhibits superior durability and strength due to its thick, hand-cut patterns that reinforce the structural integrity, making it less prone to cracks and chips under stress. Mold-blown glass, created by inflating molten glass into molds, tends to be thinner and more uniform but generally less resistant to impact and wear over time. The intricate facets of cut-glass not only enhance aesthetic appeal but also contribute to its enhanced mechanical resilience compared to the smoother surface of mold-blown glass.
Design Versatility and Patterns
Cut-glass offers intricate, sharp-edged patterns achieved by manually carving designs into solid crystal, providing a high degree of design versatility and uniqueness. Mold-blown glass features patterns formed during the shaping process by pressing molten glass into molds, allowing for mass production of consistent, intricate textures but with less individuality. While cut-glass enables detailed custom patterns and deeper cuts, mold-blown glass excels in replicating complex surface patterns quickly and efficiently.
Cost and Value: Which Offers Better Investment?
Cut-glass typically commands higher prices due to its intricate craftsmanship and superior clarity, making it a more valuable investment for collectors. Mold-blown glass, produced through a faster, mechanized process, tends to be less expensive but offers limited appreciation potential. Investors seeking long-term value often favor cut-glass for its exclusivity and enduring market demand.
Collectibility and Antique Value
Cut-glass items are highly prized among collectors due to their intricate handcrafted designs and superior clarity, which often enhance their antique value significantly compared to mold-blown glass. Mold-blown glass, produced using molds, typically features more uniform shapes but lacks the detailed craftsmanship that elevates cut-glass pieces in rarity and desirability. Collectors often value cut-glass for its unique patterns and historical authenticity, making it a preferred choice in antique glassware markets.
Common Uses: Choosing the Right Glassware for Your Needs
Cut-glass offers intricate, hand-etched designs ideal for formal dining settings and decorative pieces, enhancing elegance and light refraction. Mold-blown glass, known for its durability and versatility, suits everyday use such as tumblers, vases, and casual drinkware. Selecting cut-glass for special occasions versus mold-blown for practical, robust needs ensures the perfect balance between aesthetics and functionality.
Maintenance and Care Differences
Cut-glass requires careful handling and regular polishing to maintain its sharp facets and prevent dullness, as scratches on its surface are more visible due to its intricate patterns. Mold-blown glass, being smoother with fewer surface details, is generally easier to clean and less prone to showing wear, allowing for less intensive maintenance. Proper care for cut-glass involves using non-abrasive cloths and avoiding extreme temperature changes, while mold-blown glass can handle more routine washing methods with mild detergents.
Cut-glass vs Mold-blown Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com