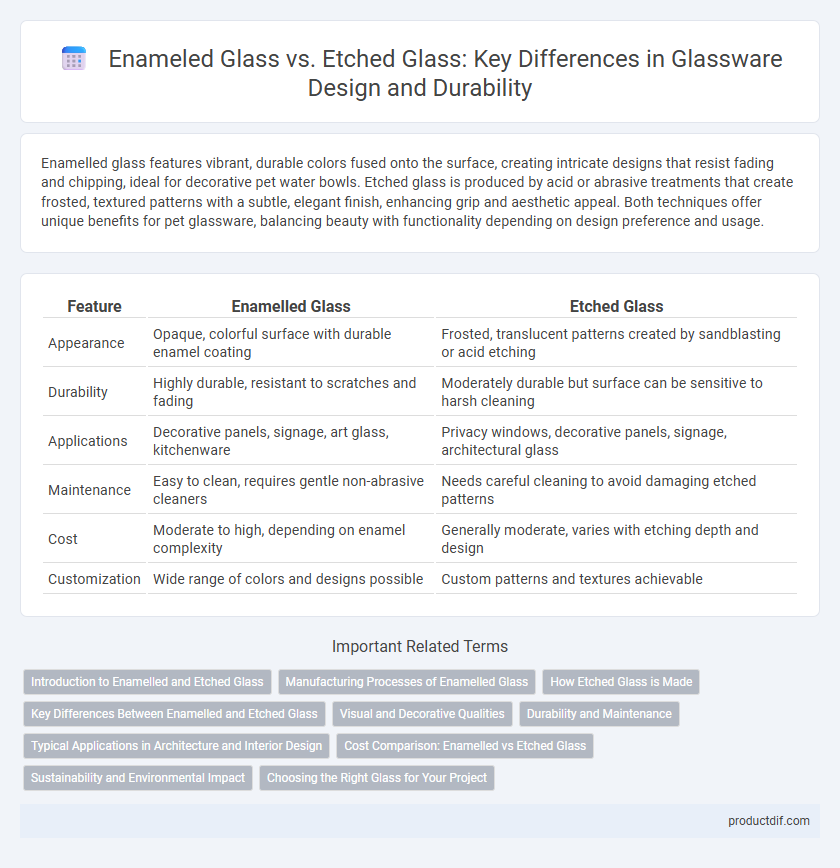
Enamelled glass features vibrant, durable colors fused onto the surface, creating intricate designs that resist fading and chipping, ideal for decorative pet water bowls. Etched glass is produced by acid or abrasive treatments that create frosted, textured patterns with a subtle, elegant finish, enhancing grip and aesthetic appeal. Both techniques offer unique benefits for pet glassware, balancing beauty with functionality depending on design preference and usage.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Enamelled Glass | Etched Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Appearance | Opaque, colorful surface with durable enamel coating | Frosted, translucent patterns created by sandblasting or acid etching |
| Durability | Highly durable, resistant to scratches and fading | Moderately durable but surface can be sensitive to harsh cleaning |
| Applications | Decorative panels, signage, art glass, kitchenware | Privacy windows, decorative panels, signage, architectural glass |
| Maintenance | Easy to clean, requires gentle non-abrasive cleaners | Needs careful cleaning to avoid damaging etched patterns |
| Cost | Moderate to high, depending on enamel complexity | Generally moderate, varies with etching depth and design |
| Customization | Wide range of colors and designs possible | Custom patterns and textures achievable |
Introduction to Enamelled and Etched Glass
Enamelled glass features colorful, opaque designs fused onto its surface through high-temperature firing, creating durable and decorative art pieces. Etched glass involves the technique of removing parts of the glass surface using acid or abrasive tools, resulting in translucent, frosted patterns with subtle texture. Both methods enhance glassware by adding intricate visual elements that combine functionality with artistic expression.
Manufacturing Processes of Enamelled Glass
Enamelled glass is created by applying powdered glass mixed with pigments onto the glass surface, which is then heated in a kiln at temperatures ranging from 600 to 800 degrees Celsius to fuse the enamel to the glass permanently. This process allows for vibrant, multi-colored designs with high durability and resistance to wear, distinguishing it from etched glass, where acid or abrasive materials are used to create frosted or textured surfaces. The precision of enamel application enables intricate patterns and detailed artwork, making enamelled glass a popular choice for decorative and functional glassware.
How Etched Glass is Made
Etched glass is created through processes such as acid etching or sandblasting, which remove microscopic layers from the glass surface to produce a frosted, translucent design. This technique allows for intricate patterns and textures that are permanent and resistant to fading or peeling. Unlike enamelled glass that involves applying colored paint fused by heat, etched glass relies on physical or chemical abrasion to achieve its distinctive matte finish.
Key Differences Between Enamelled and Etched Glass
Enamelled glass features a painted or fused layer of colored enamel that creates vivid, decorative designs with a smooth, durable finish, while etched glass involves mechanically or chemically abrading the surface to produce frosted, translucent patterns. The enamelled technique allows for vibrant, multi-colored imagery ideal for artistic and ornamental applications, whereas etched glass typically exhibits a monochromatic, matte effect suited for privacy or subtle embellishment. Durability differs as enamelled glass coatings resist fading and wear, whereas etched glass patterns are integral to the surface but may be more susceptible to surface damage or staining over time.
Visual and Decorative Qualities
Enamelled glass features vibrant, opaque colors fused onto the surface, creating bold and intricate designs that offer a striking visual impact and a tactile, textured finish. Etched glass provides subtle translucency with frosted patterns achieved by acid or sandblasting, highlighting delicate and refined decorative elements that interact softly with light. Both techniques enhance glassware aesthetics but cater to different stylistic preferences, with enamelled glass emphasizing vivid ornamentation and etched glass showcasing understated elegance.
Durability and Maintenance
Enamelled glass features a durable, colored coating fused onto the surface, offering resistance to scratches and fading, making it ideal for long-term use with minimal upkeep. Etched glass has a delicate, frosted design created by sandblasting or acid etching, which can be more prone to wear and requires gentle cleaning methods to preserve the intricate patterns. Regular maintenance of enamelled glass typically involves simple washing, while etched glass demands careful handling to avoid damage to its textured surface.
Typical Applications in Architecture and Interior Design
Enamelled glass is commonly used in architectural facades and interior partitions due to its vibrant color options and durability, offering both aesthetic appeal and functional benefits such as UV resistance and ease of cleaning. Etched glass is typically applied in office interiors, bathroom windows, and decorative panels where privacy and subtle opacity are essential, providing a tactile, frosted finish that diffuses light while maintaining a sleek appearance. Both materials enhance spatial design but serve distinct roles based on transparency, texture, and maintenance needs.
Cost Comparison: Enamelled vs Etched Glass
Enamelled glass typically incurs higher production costs due to the intricate process of applying and firing colored enamel coatings, resulting in a more durable and vibrant finish. In contrast, etched glass is often more cost-effective, as it involves simpler techniques like acid or sandblasting to create frosted designs, reducing labor and material expenses. When budgeting for decorative glassware, enamelled glass offers premium aesthetic appeal at a higher price point, while etched glass provides a budget-friendly option with elegant textural effects.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Enamelled glass involves applying colored glass powders fused at high temperatures, which can include heavy metals that pose recycling challenges and environmental hazards if not properly managed. Etched glass, created by acid or sandblasting processes, typically requires less energy and avoids harmful chemical residues, making it a more sustainable option in production and disposal. Choosing etched glass reduces ecological impact due to its recyclability and minimal toxic waste compared to enamelled glass manufacturing.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Project
Enamelled glass offers vibrant, durable colors fused onto the surface, ideal for decorative projects requiring long-lasting visual impact. Etched glass provides a subtle, frosted finish achieved through acid or sandblasting methods, perfect for adding privacy and intricate designs without compromising light transmission. Selecting the right glass depends on project goals, balancing aesthetic preferences, durability needs, and functional requirements like opacity or ease of cleaning.
Enamelled Glass vs Etched Glass Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com