Sandblasted glass offers a textured, frosted appearance achieved by blasting abrasive particles at high velocity, creating a durable and uniform finish ideal for decorative pet water bowls. Acid-etched glass involves applying acidic chemicals to the surface, producing a softer, more translucent matte effect that is elegant but can be more delicate over time. Both techniques enhance aesthetics and privacy, yet sandblasted glass is typically more resistant to wear and easier to maintain for pet-related use.
Table of Comparison
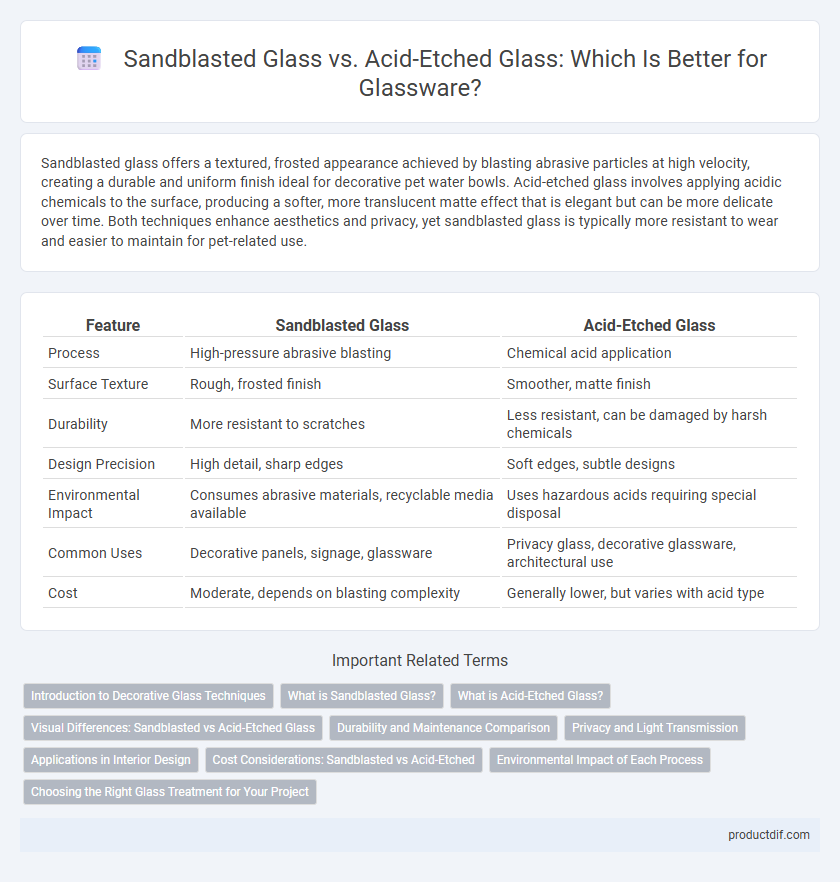
| Feature | Sandblasted Glass | Acid-Etched Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Process | High-pressure abrasive blasting | Chemical acid application |
| Surface Texture | Rough, frosted finish | Smoother, matte finish |
| Durability | More resistant to scratches | Less resistant, can be damaged by harsh chemicals |
| Design Precision | High detail, sharp edges | Soft edges, subtle designs |
| Environmental Impact | Consumes abrasive materials, recyclable media available | Uses hazardous acids requiring special disposal |
| Common Uses | Decorative panels, signage, glassware | Privacy glass, decorative glassware, architectural use |
| Cost | Moderate, depends on blasting complexity | Generally lower, but varies with acid type |
Introduction to Decorative Glass Techniques
Sandblasted glass features a textured, frosted appearance achieved by propelling abrasive particles at high velocity, creating intricate designs on the surface. Acid-etched glass involves a chemical process where hydrofluoric acid is applied to produce a uniformly smooth, matte finish that enhances light diffusion. Both techniques are pivotal in decorative glass applications, offering distinctive aesthetics and varying levels of opacity for architectural and artistic projects.
What is Sandblasted Glass?
Sandblasted glass is created by forcibly propelling fine abrasive particles onto the glass surface, producing a smooth, frosted finish that obscures visibility while allowing light to pass through. This technique enhances privacy and adds a decorative texture commonly used in windows, partitions, and glassware. Sandblasting achieves a uniform matte appearance and can be precisely controlled for detailed designs or patterns on glass surfaces.
What is Acid-Etched Glass?
Acid-etched glass is a type of glass treated with hydrofluoric acid to create a smooth, frosted surface that diffuses light evenly while maintaining translucency. This process results in a uniform, matte finish that resists fingerprints and smudges better than sandblasted glass. Acid-etched glass is commonly used in decorative partitions, privacy panels, and modern glassware to achieve a sleek, elegant appearance.
Visual Differences: Sandblasted vs Acid-Etched Glass
Sandblasted glass features a uniformly matte, frosted surface created by high-pressure abrasive blasting, resulting in a textured finish that diffuses light softly but maintains opacity. Acid-etched glass undergoes a chemical process that produces a smoother, velvety surface with a more subtle, translucent appearance and less texture compared to sandblasting. The visual difference is most apparent in clarity and light diffusion: sandblasted glass provides a rougher, more opaque look, while acid-etched glass offers a refined, softer translucency with minimal surface texture.
Durability and Maintenance Comparison
Sandblasted glass features a rougher, more textured surface that resists scratches and masks fingerprints effectively, enhancing its durability compared to acid-etched glass. Acid-etched glass exhibits a smoother, more delicate finish that can be prone to surface wear and requires gentle cleaning with non-abrasive agents to maintain its appearance. Both types demand regular maintenance, but sandblasted glass tolerates harsher cleaning methods, making it a more practical choice for high-traffic or frequently handled glassware.
Privacy and Light Transmission
Sandblasted glass offers superior privacy by creating a uniformly frosted surface that diffuses light evenly, reducing visibility while maintaining natural illumination. Acid-etched glass provides a more subtle translucency, allowing higher light transmission but offering less privacy compared to sandblasted counterparts. Both techniques enhance aesthetic appeal but differ significantly in balancing privacy needs with light diffusion characteristics.
Applications in Interior Design
Sandblasted glass offers a versatile matte finish ideal for creating privacy partitions and decorative panels in modern interiors, enhancing texture while maintaining light diffusion. Acid-etched glass provides a smoother, more refined frosted appearance frequently used in high-end settings for glass doors and cabinet inserts, adding an elegant, uniform translucency. Both techniques are essential in interior design for customizing ambiance and visual interest while balancing function and style.
Cost Considerations: Sandblasted vs Acid-Etched
Sandblasted glass typically incurs higher costs due to the use of specialized equipment and longer labor time compared to acid-etched glass, which involves chemical treatments that are generally faster and less labor-intensive. The price difference also reflects the durability and texture variance, with sandblasted finishes offering deeper, more textured surfaces that may justify the premium in decorative applications. Budget-conscious projects often favor acid-etched glass for its economical production and consistent quality in large-scale manufacturing.
Environmental Impact of Each Process
Sandblasted glass involves the mechanical abrasion of glass surfaces using high-pressure sand particles, which generates silica dust that can pose respiratory hazards and requires proper disposal to minimize environmental contamination. Acid-etched glass employs hydrofluoric acid to chemically roughen glass surfaces, producing hazardous chemical waste that demands careful handling and neutralization to prevent soil and water pollution. Both processes have significant environmental impacts, with sandblasting primarily contributing particulate waste and acid etching involving toxic chemicals, making waste management and environmental controls critical for sustainable glass manufacturing.
Choosing the Right Glass Treatment for Your Project
Sandblasted glass offers a textured, frosted appearance achieved by propelling abrasive material at high velocity, ideal for privacy and decorative effects with a more tactile surface. Acid-etched glass provides a smoother, satin-like finish through chemical treatment, suited for a refined, elegant look that softens light without compromising translucency. Selecting between sandblasted and acid-etched glass depends on desired aesthetics, surface texture, light diffusion, and the specific requirements of privacy and durability for your architectural or interior design project.
Sandblasted glass vs Acid-etched glass Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com