Low-E glass significantly improves energy efficiency by reflecting infrared heat while allowing visible light to pass through, reducing heating and cooling costs in buildings. Standard glass lacks this reflective coating, resulting in greater heat transfer and less insulation performance. Choosing Low-E glass enhances thermal comfort and lowers energy consumption compared to standard glass options.
Table of Comparison
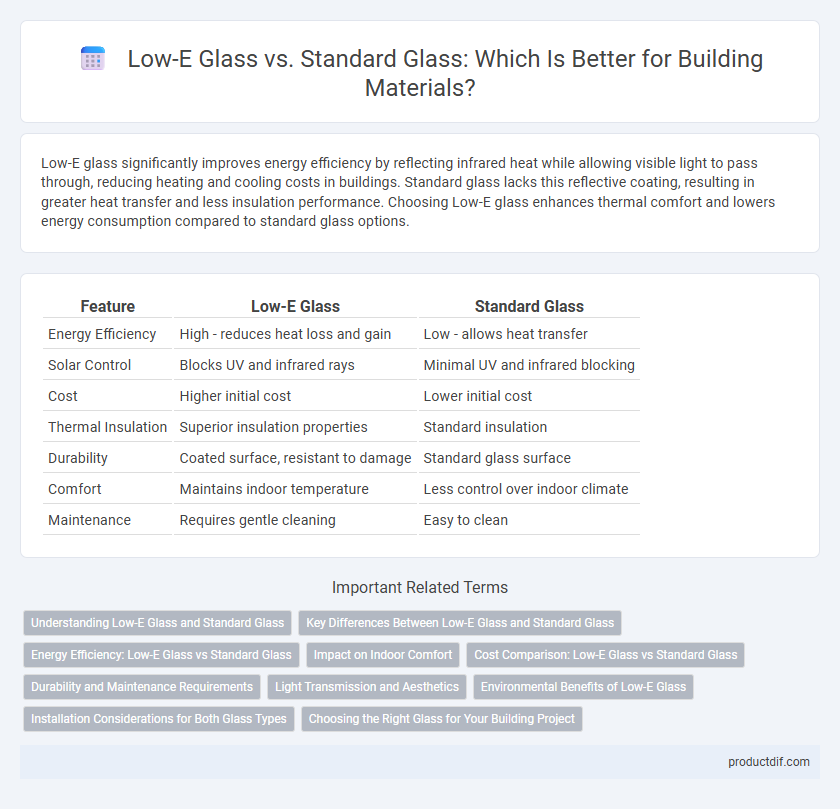
| Feature | Low-E Glass | Standard Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency | High - reduces heat loss and gain | Low - allows heat transfer |
| Solar Control | Blocks UV and infrared rays | Minimal UV and infrared blocking |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower initial cost |
| Thermal Insulation | Superior insulation properties | Standard insulation |
| Durability | Coated surface, resistant to damage | Standard glass surface |
| Comfort | Maintains indoor temperature | Less control over indoor climate |
| Maintenance | Requires gentle cleaning | Easy to clean |
Understanding Low-E Glass and Standard Glass
Low-E glass features a microscopically thin, transparent coating that minimizes infrared and ultraviolet light while allowing visible light to pass through, enhancing energy efficiency in buildings. Standard glass lacks this coating, resulting in higher heat transfer and less insulation, making it less effective at reducing energy costs. Choosing Low-E glass over standard glass improves thermal performance and reduces fading of interior furnishings due to UV exposure.
Key Differences Between Low-E Glass and Standard Glass
Low-E glass features a microscopically thin coating that reflects infrared energy to improve insulation, significantly reducing heat transfer compared to standard glass. Standard glass lacks this specialized coating, resulting in less energy efficiency and higher heat gain or loss through windows. The enhanced thermal performance of Low-E glass leads to lower energy costs and increased indoor comfort.
Energy Efficiency: Low-E Glass vs Standard Glass
Low-E glass significantly improves energy efficiency by reducing heat transfer through windows, thanks to its microscopic metallic coating that reflects infrared energy while allowing visible light to pass. Standard glass lacks this coating, resulting in higher heat loss during winter and increased heat gain in summer, which raises heating and cooling costs. Energy savings with Low-E glass can reach up to 30% compared to standard glass, making it a superior choice for sustainable building materials.
Impact on Indoor Comfort
Low-E glass significantly improves indoor comfort by reducing heat transfer and minimizing UV radiation, resulting in a more consistent indoor temperature and less fading of furniture and fabrics. Standard glass allows more solar heat and harmful UV rays to penetrate, causing increased glare and temperature fluctuations inside the building. By enhancing thermal insulation, Low-E glass reduces the reliance on heating and cooling systems, contributing to energy efficiency and occupant comfort.
Cost Comparison: Low-E Glass vs Standard Glass
Low-E glass typically costs 10-15% more than standard glass due to its advanced coating that improves energy efficiency by reflecting infrared light while allowing visible light to pass through. Despite the higher initial investment, Low-E glass can reduce heating and cooling expenses by up to 25%, leading to significant long-term savings on energy bills. Standard glass has a lower upfront cost but lacks thermal insulation properties, often resulting in higher energy consumption and increased utility costs over time.
Durability and Maintenance Requirements
Low-E glass features a durable coating that resists scratches and reduces the likelihood of degradation compared to standard glass, which is more prone to surface damage and weathering. The maintenance requirements for Low-E glass are minimal due to its protective layer that repels dirt and reduces the need for frequent cleaning, while standard glass often requires regular upkeep to maintain clarity and prevent staining. Enhanced durability and low maintenance make Low-E glass a cost-effective choice for long-term building performance.
Light Transmission and Aesthetics
Low-E glass provides superior light transmission by allowing ample natural light while reducing harmful UV rays, enhancing energy efficiency without compromising brightness. In contrast, standard glass transmits light more uniformly but lacks the specialized coatings that minimize glare and heat gain. Aesthetically, Low-E glass maintains a clear, neutral appearance with minimal tint, whereas standard glass can sometimes appear less refined due to reflections and heat-related distortion.
Environmental Benefits of Low-E Glass
Low-E glass significantly reduces energy consumption by minimizing heat transfer, which lowers the demand for heating and cooling systems and results in decreased greenhouse gas emissions. Its high-performance coatings enhance insulation, contributing to improved indoor temperature regulation and reducing reliance on fossil fuels. Compared to standard glass, Low-E glass supports sustainable building practices by promoting energy efficiency and reducing the overall carbon footprint of structures.
Installation Considerations for Both Glass Types
Low-E glass requires careful handling during installation due to its thin metallic coating, which can be easily scratched or damaged, impacting its energy efficiency. Standard glass is more durable and less sensitive to handling but lacks the specialized coatings that improve thermal performance. Proper sealing and frame compatibility are essential for both types to maintain insulation properties and prevent air or moisture infiltration.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Building Project
Low-E glass features a microscopically thin coating that improves energy efficiency by reflecting infrared energy, helping maintain indoor temperature and reduce heating and cooling costs. Standard glass lacks these coatings, resulting in higher UV and heat transmission, which can increase energy consumption and cause furniture fading. Selecting Low-E glass for your building project enhances thermal performance and durability, making it a superior choice for energy-conscious construction.
Low-E Glass vs Standard Glass Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com