Sugar reduction offers a balanced approach to lowering sugar content in beverages while maintaining flavor and consumer appeal, making it a preferred choice for those seeking healthier options without sacrificing taste. Sugar-free beverages eliminate sugar entirely, often relying on artificial or natural sweeteners to provide sweetness without calories, catering to individuals with specific dietary restrictions or diabetes. Choosing between sugar reduction and sugar-free depends on consumer preferences, health goals, and product formulation challenges in the beverage industry.
Table of Comparison
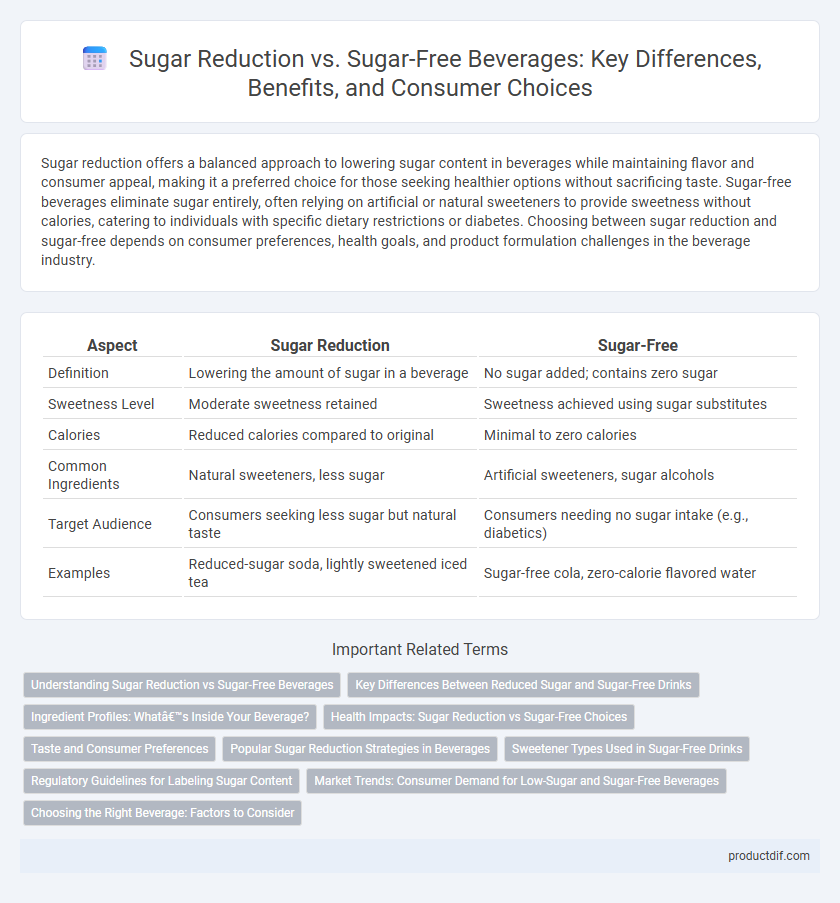
| Aspect | Sugar Reduction | Sugar-Free |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Lowering the amount of sugar in a beverage | No sugar added; contains zero sugar |
| Sweetness Level | Moderate sweetness retained | Sweetness achieved using sugar substitutes |
| Calories | Reduced calories compared to original | Minimal to zero calories |
| Common Ingredients | Natural sweeteners, less sugar | Artificial sweeteners, sugar alcohols |
| Target Audience | Consumers seeking less sugar but natural taste | Consumers needing no sugar intake (e.g., diabetics) |
| Examples | Reduced-sugar soda, lightly sweetened iced tea | Sugar-free cola, zero-calorie flavored water |
Understanding Sugar Reduction vs Sugar-Free Beverages
Sugar reduction in beverages involves lowering the amount of added sugars to maintain flavor while cutting calories, enhancing health benefits without compromising taste. Sugar-free beverages eliminate all sugars, often using artificial or natural non-nutritive sweeteners like stevia or sucralose to provide sweetness without caloric content. Understanding the difference assists consumers in making informed choices based on dietary needs, taste preferences, and metabolic impacts.
Key Differences Between Reduced Sugar and Sugar-Free Drinks
Reduced sugar drinks contain a lower amount of sugar compared to regular beverages but still include some natural or added sugars, allowing for gradual sugar intake reduction. Sugar-free drinks use artificial sweeteners or sugar substitutes to eliminate sugar entirely, catering to those needing zero sugar for health reasons like diabetes management. The key difference lies in sugar content, taste profile, and target consumer needs, with reduced sugar providing a moderated sweetness and sugar-free offering a completely sugarless option.
Ingredient Profiles: What’s Inside Your Beverage?
Sugar reduction beverages contain lower amounts of sugar compared to traditional drinks, often using natural sweeteners like stevia or monk fruit to maintain flavor with fewer calories. Sugar-free beverages eliminate sugar entirely, relying on artificial or non-nutritive sweeteners such as sucralose, aspartame, or erythritol for sweetness. Ingredient profiles differ significantly, impacting taste, caloric content, and potential health effects, making label scrutiny essential for consumers seeking specific dietary needs.
Health Impacts: Sugar Reduction vs Sugar-Free Choices
Choosing sugar-reduced beverages helps lower calorie intake and reduces the risk of insulin resistance, while sugar-free options eliminate sugar entirely but may contain artificial sweeteners with debated health effects. Studies link moderate sugar reduction to improved metabolic health and lower obesity rates, whereas sugar-free drinks may influence gut microbiota and appetite regulation differently. Consumers prioritizing health impacts should consider personal tolerance to sweeteners and consult current research on long-term effects when selecting between sugar reduction and sugar-free beverages.
Taste and Consumer Preferences
Sugar reduction in beverages maintains a balance between sweetness and flavor complexity, appealing to consumers seeking healthier options without sacrificing taste. Sugar-free beverages often use artificial or natural sweeteners that can produce aftertastes, influencing consumer preferences based on individual sensitivity. Market studies show a growing demand for reduced-sugar products due to increasing health awareness, while taste acceptance remains a critical factor in product success.
Popular Sugar Reduction Strategies in Beverages
Popular sugar reduction strategies in beverages include reformulating recipes to lower added sugars, using natural sweeteners like stevia or monk fruit, and incorporating sugar alcohols such as erythritol for reduced caloric content. Another approach involves blending fruit juices with water or sparkling water to dilute sugar concentration while maintaining flavor. These methods cater to health-conscious consumers seeking lower sugar intake without sacrificing taste.
Sweetener Types Used in Sugar-Free Drinks
Sugar-free beverages commonly use artificial sweeteners such as sucralose, aspartame, and acesulfame potassium to provide sweetness without calories. Natural sweeteners like stevia and monk fruit extract offer sugar-free alternatives with plant-based origins and minimal impact on blood glucose levels. These sweeteners cater to health-conscious consumers seeking low-calorie options that maintain flavor without sugar content.
Regulatory Guidelines for Labeling Sugar Content
Regulatory guidelines for labeling sugar content in beverages distinguish between sugar reduction and sugar-free claims to ensure consumer clarity. Sugar reduction typically requires a specified percentage decrease from the original sugar content, often around 25%, while sugar-free labels mandate less than 0.5 grams of sugar per serving according to FDA or EFSA standards. Compliance with these regulations helps manufacturers avoid misleading claims and meet market expectations for healthier beverage options.
Market Trends: Consumer Demand for Low-Sugar and Sugar-Free Beverages
The beverage market shows a significant rise in consumer demand for both low-sugar and sugar-free options, driven by increasing health awareness and regulatory pressures. Brands adopting sugar reduction strategies optimize taste retention while catering to calorie-conscious buyers, whereas sugar-free products appeal to diabetics and those avoiding artificial sweeteners. Market data reveals a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 5% in low-sugar and sugar-free beverage segments through 2028, reflecting shifting consumer preferences toward healthier alternatives.
Choosing the Right Beverage: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right beverage involves evaluating sugar reduction and sugar-free options based on taste preference, dietary needs, and health goals. Sugar-reduced beverages contain lower sugar levels, offering a balance between flavor and calorie control, while sugar-free drinks use artificial or natural sweeteners to eliminate sugar completely. Consumers should consider factors like insulin response, risk of dental issues, and ingredient transparency when selecting beverages to optimize health benefits.
Sugar Reduction vs Sugar-Free Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com