Caffeinated beverages provide an energizing boost by stimulating the central nervous system, enhancing alertness and concentration. Decaffeinated options offer the rich flavor of coffee or tea without the stimulating effects, making them ideal for those sensitive to caffeine or seeking to reduce intake. Both types deliver hydration and can be enjoyed throughout the day, catering to diverse preferences and dietary needs.
Table of Comparison
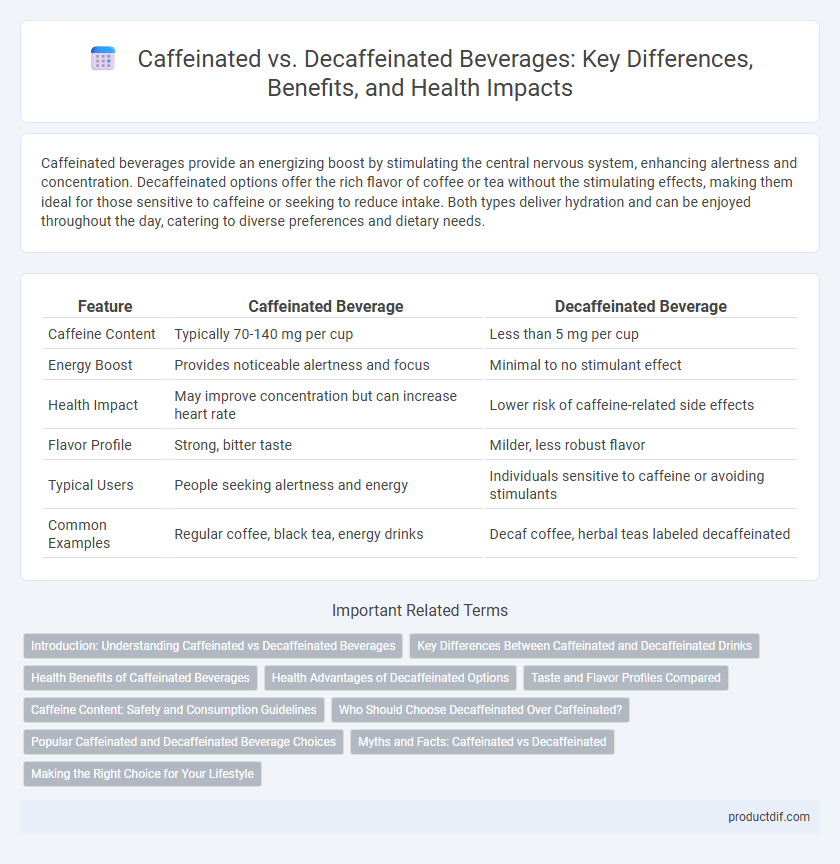
| Feature | Caffeinated Beverage | Decaffeinated Beverage |
|---|---|---|
| Caffeine Content | Typically 70-140 mg per cup | Less than 5 mg per cup |
| Energy Boost | Provides noticeable alertness and focus | Minimal to no stimulant effect |
| Health Impact | May improve concentration but can increase heart rate | Lower risk of caffeine-related side effects |
| Flavor Profile | Strong, bitter taste | Milder, less robust flavor |
| Typical Users | People seeking alertness and energy | Individuals sensitive to caffeine or avoiding stimulants |
| Common Examples | Regular coffee, black tea, energy drinks | Decaf coffee, herbal teas labeled decaffeinated |
Introduction: Understanding Caffeinated vs Decaffeinated Beverages
Caffeinated beverages contain varying amounts of caffeine, a natural stimulant that enhances alertness and energy levels, commonly found in coffee, tea, and energy drinks. Decaffeinated beverages undergo a process to remove most caffeine while retaining flavor, offering an alternative for those sensitive to caffeine or seeking reduced intake. Understanding the differences in caffeine content and effects can help consumers make informed choices based on their health needs and lifestyle preferences.
Key Differences Between Caffeinated and Decaffeinated Drinks
Caffeinated drinks, such as coffee and certain teas, contain varying amounts of caffeine which acts as a stimulant affecting the central nervous system, enhancing alertness and concentration. Decaffeinated beverages undergo a process to remove most caffeine content, typically retaining 97% or more of the original flavor compounds while minimizing stimulant effects. Key differences include the impact on sleep patterns, with caffeinated drinks potentially causing insomnia or restlessness, while decaffeinated options offer similar taste profiles without the associated jitteriness or caffeine dependency.
Health Benefits of Caffeinated Beverages
Caffeinated beverages enhance mental alertness and improve cognitive function due to their stimulating effects on the central nervous system. Moderate caffeine consumption is linked to reduced risks of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's. Furthermore, caffeine boosts metabolism, aiding in weight management and increasing physical performance.
Health Advantages of Decaffeinated Options
Decaffeinated beverages significantly reduce the risk of caffeine-related side effects such as insomnia, increased heart rate, and anxiety, making them a healthier choice for sensitive individuals. Consuming decaffeinated options supports better hydration without the diuretic effects commonly associated with caffeinated drinks. Decaf coffee and tea also retain essential antioxidants, offering health benefits while minimizing stimulant intake.
Taste and Flavor Profiles Compared
Caffeinated beverages typically offer a robust, bitter flavor profile with earthy and slightly acidic notes, enhancing the aromatic complexity of coffee and tea. Decaffeinated options often present a smoother, milder taste due to the removal of caffeine, which can slightly diminish the intensity and depth of flavor compounds. Consumers seeking a less intense sensory experience may prefer decaffeinated drinks, while those valuing bold, rich flavors usually opt for caffeinated varieties.
Caffeine Content: Safety and Consumption Guidelines
Caffeinated beverages typically contain 70-140 mg of caffeine per serving, while decaffeinated options have 2-5 mg, greatly reducing stimulant effects. The FDA recommends a maximum daily caffeine intake of 400 mg for most adults, highlighting safety concerns for sensitive groups such as pregnant women and individuals with heart conditions. Monitoring caffeine content helps consumers adhere to these guidelines, balancing alertness and minimizing risks like insomnia or increased heart rate.
Who Should Choose Decaffeinated Over Caffeinated?
Individuals sensitive to caffeine, such as those with anxiety disorders, heart conditions, or insomnia, should choose decaffeinated beverages to avoid adverse effects like increased heart rate and disrupted sleep patterns. Pregnant women are often advised by healthcare professionals to limit caffeine intake, making decaf beverages a safer alternative to support fetal health. People aiming to reduce overall caffeine consumption without sacrificing the flavor of coffee or tea also benefit from selecting decaffeinated options.
Popular Caffeinated and Decaffeinated Beverage Choices
Coffee and tea are the most popular caffeinated beverages worldwide, known for their robust flavor and stimulating effects due to caffeine content. Decaffeinated coffee and herbal teas serve as the leading decaffeinated options, offering similar taste profiles without the stimulating impact. Consumers often choose based on caffeine sensitivity or health concerns while maintaining their preferred beverage rituals.
Myths and Facts: Caffeinated vs Decaffeinated
Caffeinated beverages contain varying levels of caffeine, a natural stimulant affecting the central nervous system, while decaffeinated options have at least 97% of caffeine removed through processes like Swiss Water or CO2 extraction. Common myths that decaffeinated coffee is completely caffeine-free or that caffeine causes dehydration are debunked by studies showing trace caffeine in decaf and no significant diuretic effect in moderate intake. Research also clarifies that caffeine's impact on anxiety and sleep varies by individual sensitivity rather than beverage type.
Making the Right Choice for Your Lifestyle
Choosing between caffeinated and decaffeinated beverages depends on individual health goals, sensitivity to caffeine, and daily energy needs. Caffeinated drinks provide a natural boost in alertness and metabolism, while decaffeinated options reduce the risk of insomnia and anxiety. Understanding the impact of caffeine on your body helps align beverage choices with lifestyle preferences and wellness priorities.
Caffeinated vs Decaffeinated Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com