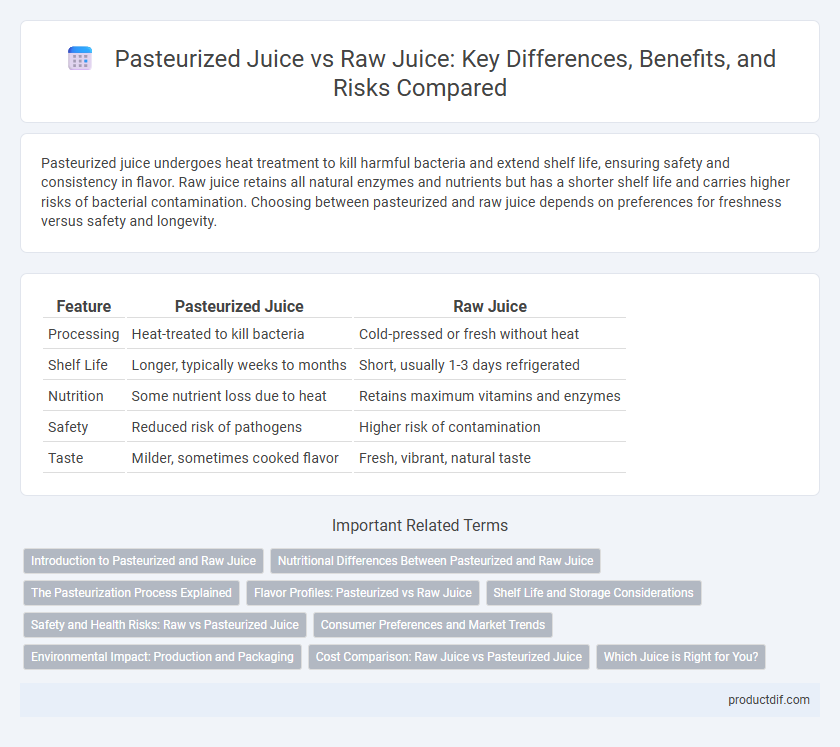
Pasteurized juice undergoes heat treatment to kill harmful bacteria and extend shelf life, ensuring safety and consistency in flavor. Raw juice retains all natural enzymes and nutrients but has a shorter shelf life and carries higher risks of bacterial contamination. Choosing between pasteurized and raw juice depends on preferences for freshness versus safety and longevity.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Pasteurized Juice | Raw Juice |
|---|---|---|
| Processing | Heat-treated to kill bacteria | Cold-pressed or fresh without heat |
| Shelf Life | Longer, typically weeks to months | Short, usually 1-3 days refrigerated |
| Nutrition | Some nutrient loss due to heat | Retains maximum vitamins and enzymes |
| Safety | Reduced risk of pathogens | Higher risk of contamination |
| Taste | Milder, sometimes cooked flavor | Fresh, vibrant, natural taste |
Introduction to Pasteurized and Raw Juice
Pasteurized juice undergoes heat treatment to eliminate harmful bacteria, extending shelf life and ensuring safety for consumption. Raw juice is extracted directly from fruits or vegetables without any heat processing, preserving its natural enzymes and nutrients but carrying a higher risk of microbial contamination. Choosing between pasteurized and raw juice depends on preferences for freshness, nutritional value, and food safety.
Nutritional Differences Between Pasteurized and Raw Juice
Raw juice retains more heat-sensitive vitamins like vitamin C and certain B vitamins due to the absence of heat treatment, preserving natural enzymes and antioxidants. Pasteurized juice undergoes heat processing to eliminate harmful pathogens, which can reduce levels of some nutrients but extends shelf life and ensures safety. While pasteurization slightly diminishes nutrient density, it offers a safer option for consumption, especially for vulnerable populations.
The Pasteurization Process Explained
The pasteurization process involves heating juice to a specific temperature, usually between 135degF and 160degF, for a short time to kill harmful bacteria and extend shelf life without significantly affecting flavor. This method ensures safety by eliminating pathogens such as Salmonella and E. coli, commonly found in raw juice. While raw juice retains more natural enzymes and nutrients, pasteurized juice offers a reliable option for consumers seeking safe, longer-lasting beverage choices.
Flavor Profiles: Pasteurized vs Raw Juice
Raw juice offers a vibrant, fresh flavor profile with natural sweetness and nutrient-rich undertones, preserving enzymes and volatile aromatics that define its crisp taste. Pasteurized juice, subjected to heat treatment, tends to have a milder, more uniform flavor, with reduced brightness and complexity due to the breakdown of delicate flavor compounds. The flavor of pasteurized juice is often described as smoother but less dynamic compared to the bold, intense essence found in raw juice.
Shelf Life and Storage Considerations
Pasteurized juice undergoes heat treatment to eliminate harmful microorganisms, significantly extending its shelf life to several weeks or months when refrigerated. Raw juice retains more nutrients and enzymes but is highly perishable, typically lasting only 1 to 3 days under refrigeration. Proper storage for pasteurized juice involves consistent refrigeration at or below 40degF, while raw juice requires immediate consumption or freezing to prevent spoilage and microbial growth.
Safety and Health Risks: Raw vs Pasteurized Juice
Pasteurized juice undergoes heat treatment to eliminate harmful pathogens, significantly reducing the risk of foodborne illnesses compared to raw juice. Raw juice retains more natural enzymes and nutrients but poses a higher risk of contamination from bacteria, viruses, and parasites. Consumers seeking safer options with extended shelf life should prefer pasteurized juice, while those prioritizing nutrient retention must weigh the potential health risks associated with raw juice consumption.
Consumer Preferences and Market Trends
Consumer preferences are increasingly shifting towards pasteurized juice due to its longer shelf life and perceived safety, driving significant market growth in packaged juice segments globally. Despite this, raw juice maintains a strong niche appeal among health-conscious consumers seeking preservative-free, nutrient-rich options, fueling demand in organic and artisanal beverage markets. Market trends indicate a rising investment in cold-pressed and minimally processed juices that balance freshness with extended preservation, reflecting evolving consumer priorities for both convenience and natural quality.
Environmental Impact: Production and Packaging
Pasteurized juice production requires higher energy consumption due to heat treatment, increasing its carbon footprint compared to raw juice, which undergoes minimal processing. Packaging for pasteurized juice often involves Tetra Pak cartons or plastic bottles with multiple layers for extended shelf life, contributing to complex recycling challenges. Raw juice typically uses simpler packaging, such as glass bottles or recyclable plastic, which lowers environmental impact but may compromise shelf stability and distribution efficiency.
Cost Comparison: Raw Juice vs Pasteurized Juice
Raw juice typically costs more due to shorter shelf life, higher perishability, and the need for quicker distribution channels. Pasteurized juice benefits from extended shelf life and reduced spoilage, lowering transportation and storage expenses, making it more cost-effective for mass production. Production costs for pasteurization equipment are offset by economies of scale, resulting in lower overall retail prices compared to raw juice.
Which Juice is Right for You?
Pasteurized juice offers enhanced safety by eliminating harmful pathogens through heat treatment, making it suitable for those with weakened immune systems or children. Raw juice retains more natural enzymes and nutrients but carries a higher risk of contamination, appealing to health enthusiasts prioritizing freshness and maximum nutrient intake. Choosing between pasteurized and raw juice depends on individual health needs and safety preferences.
Pasteurized Juice vs Raw Juice Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com