Zero-sugar beverages contain no sugars or calories, making them ideal for those seeking to reduce calorie intake without sacrificing flavor. Low-sugar drinks have a small amount of sugar, offering a balance between sweetness and lower calorie content compared to regular sugary beverages. Choosing between zero-sugar and low-sugar options depends on personal taste preferences and dietary goals.
Table of Comparison
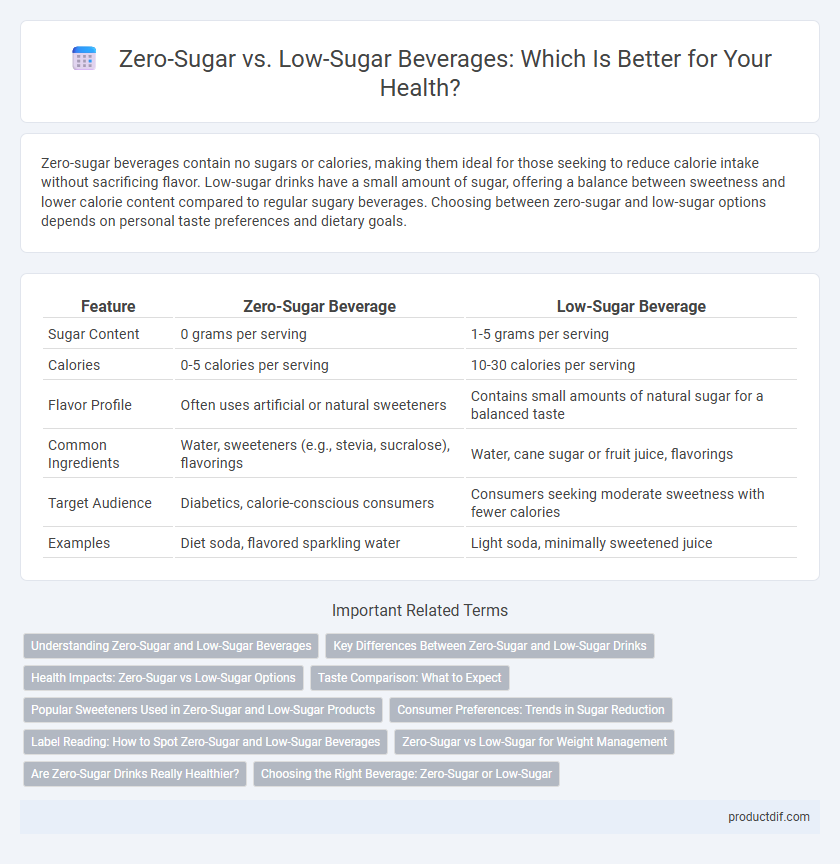
| Feature | Zero-Sugar Beverage | Low-Sugar Beverage |
|---|---|---|
| Sugar Content | 0 grams per serving | 1-5 grams per serving |
| Calories | 0-5 calories per serving | 10-30 calories per serving |
| Flavor Profile | Often uses artificial or natural sweeteners | Contains small amounts of natural sugar for a balanced taste |
| Common Ingredients | Water, sweeteners (e.g., stevia, sucralose), flavorings | Water, cane sugar or fruit juice, flavorings |
| Target Audience | Diabetics, calorie-conscious consumers | Consumers seeking moderate sweetness with fewer calories |
| Examples | Diet soda, flavored sparkling water | Light soda, minimally sweetened juice |
Understanding Zero-Sugar and Low-Sugar Beverages
Zero-sugar beverages contain no sugars or caloric sweeteners, often using artificial or natural non-nutritive sweeteners to maintain sweetness without adding calories. Low-sugar beverages typically have sugar content below a specific threshold, generally under 5 grams per serving, balancing taste and reduced sugar intake. Understanding these distinctions helps consumers make informed choices based on dietary needs, glycemic impact, and overall health goals.
Key Differences Between Zero-Sugar and Low-Sugar Drinks
Zero-sugar drinks contain no added sugars or calories, often using artificial or natural non-nutritive sweeteners like stevia or sucralose, making them ideal for strict sugar restrictions and calorie-conscious consumers. Low-sugar drinks, by contrast, have reduced sugar content compared to regular beverages but still include measurable amounts of natural or added sugars, impacting overall carbohydrate intake. These differences influence taste profiles, health effects, and suitability for diets such as keto or diabetes management.
Health Impacts: Zero-Sugar vs Low-Sugar Options
Zero-sugar beverages eliminate added sugars entirely, reducing calorie intake and lowering the risk of obesity, type 2 diabetes, and heart disease by preventing blood sugar spikes. Low-sugar options contain minimal sugars, offering a moderate calorie count and a slower glucose absorption rate, which can support better energy balance and metabolic health. Choosing zero-sugar drinks often benefits those managing insulin sensitivity, while low-sugar alternatives may be preferable for individuals seeking some natural sweetness without excessive sugar consumption.
Taste Comparison: What to Expect
Zero-sugar beverages often deliver a sharper, more artificial taste due to sugar substitutes like stevia or sucralose, while low-sugar options maintain some natural sweetness, offering a more balanced and familiar flavor profile. Consumers can expect low-sugar drinks to provide a closer resemblance to traditional sugary beverages, appealing to those sensitive to taste alterations. The choice between zero- and low-sugar ultimately depends on personal preference for intensity of sweetness and aftertaste.
Popular Sweeteners Used in Zero-Sugar and Low-Sugar Products
Zero-sugar beverages commonly use artificial sweeteners such as sucralose, aspartame, and stevia to achieve sweetness without added calories, making them popular choices for calorie-conscious consumers. Low-sugar products often incorporate natural sweeteners like honey, agave nectar, and cane sugar in controlled amounts to maintain reduced sugar content while preserving taste. The selection of sweeteners in zero-sugar and low-sugar beverages directly impacts flavor profiles, consumer preference, and nutritional labeling.
Consumer Preferences: Trends in Sugar Reduction
Consumers increasingly prefer zero-sugar beverages as health consciousness rises and sugar-related risks gain awareness. Market data shows a significant shift toward zero-sugar options, with many targeting ketogenic and diabetic audiences, while low-sugar alternatives appeal to those easing into reduced sugar intake. Flavor innovation and natural sweeteners in both categories drive sustained growth in the sugar-reduction segment.
Label Reading: How to Spot Zero-Sugar and Low-Sugar Beverages
Zero-sugar beverages contain less than 0.5 grams of sugar per serving, as labeled "Zero Sugar" or "Sugar-Free," while low-sugar drinks typically have 5 grams or less of sugar per serving, often marked as "Low Sugar" or "Reduced Sugar." Reading nutrition labels and ingredient lists can help identify hidden sugars such as sucrose, glucose, or high-fructose corn syrup in both categories. Understanding these distinctions enables consumers to make informed choices aligned with dietary goals and sugar intake limits.
Zero-Sugar vs Low-Sugar for Weight Management
Zero-sugar beverages contain no calories or carbohydrates, making them ideal for weight management by eliminating sugar intake entirely. Low-sugar drinks have reduced sugar levels but still contribute calories and can impact blood sugar, potentially slowing weight loss progress. Choosing zero-sugar options supports better calorie control and more effective weight management compared to low-sugar alternatives.
Are Zero-Sugar Drinks Really Healthier?
Zero-sugar drinks eliminate added sugars entirely, reducing calorie intake and minimizing the risk of obesity and diabetes compared to low-sugar beverages that still contain small amounts of sugar. However, the use of artificial sweeteners in zero-sugar drinks raises concerns about potential impacts on gut health and insulin sensitivity, which remain under scientific scrutiny. Consumers should consider both sugar content and ingredient quality when evaluating the overall health benefits of zero-sugar versus low-sugar drinks.
Choosing the Right Beverage: Zero-Sugar or Low-Sugar
Choosing between zero-sugar and low-sugar beverages depends on dietary goals and taste preferences; zero-sugar options eliminate sugars entirely, ideal for strict sugar control or ketogenic diets. Low-sugar beverages retain minimal sugar content, offering a balance between flavor and reduced caloric intake, suitable for those easing sugar reduction gradually. Understanding product labels and sugar content per serving ensures informed choices aligned with health and wellness objectives.
Zero-Sugar vs Low-Sugar Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com