Juicing extracts liquid from fruits and vegetables, removing pulp and fiber for a smooth, nutrient-dense beverage ideal for quick absorption. Blending retains the whole fruit or vegetable, including fiber, resulting in a thicker, more filling drink that supports digestion and provides sustained energy. Choosing between juicing and blending depends on personal health goals, whether prioritizing rapid nutrient intake or maximizing dietary fiber.
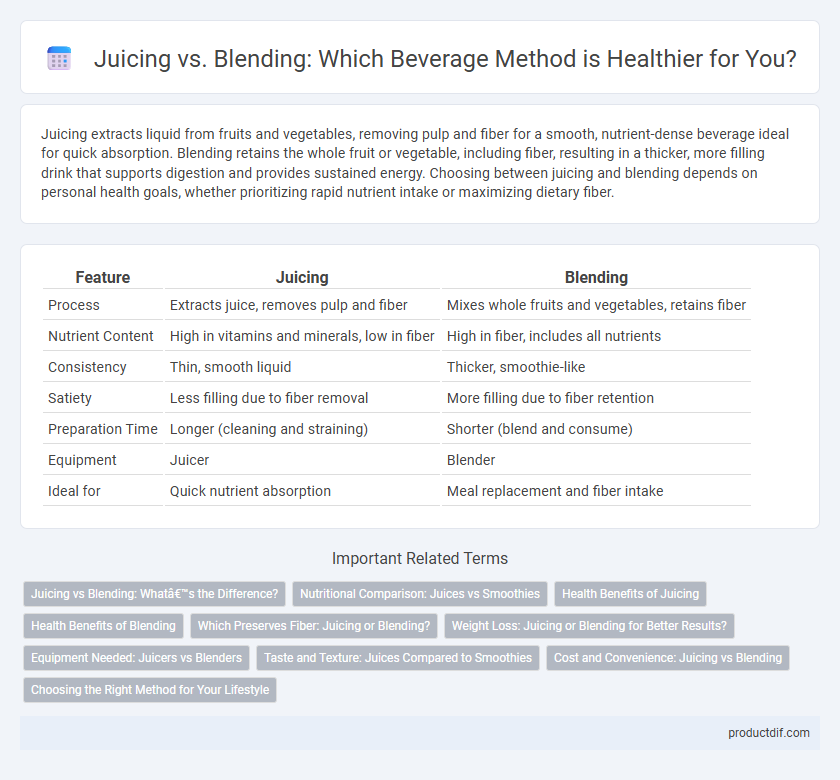
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Juicing | Blending |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Extracts juice, removes pulp and fiber | Mixes whole fruits and vegetables, retains fiber |
| Nutrient Content | High in vitamins and minerals, low in fiber | High in fiber, includes all nutrients |
| Consistency | Thin, smooth liquid | Thicker, smoothie-like |
| Satiety | Less filling due to fiber removal | More filling due to fiber retention |
| Preparation Time | Longer (cleaning and straining) | Shorter (blend and consume) |
| Equipment | Juicer | Blender |
| Ideal for | Quick nutrient absorption | Meal replacement and fiber intake |
Juicing vs Blending: What’s the Difference?
Juicing extracts the liquid from fruits and vegetables, leaving behind the pulp, which results in a nutrient-dense, easily absorbable drink with a smooth texture. Blending uses the whole fruit or vegetable, including fiber, creating a thicker beverage that retains all nutrients and promotes better digestion. Choosing between juicing and blending depends on desired nutrient intake, fiber content, and texture preference.
Nutritional Comparison: Juices vs Smoothies
Juices provide a concentrated source of vitamins and minerals by extracting liquid from fruits and vegetables, but often lack dietary fiber, which is essential for digestion and blood sugar regulation. Smoothies retain the entire fruit or vegetable, including pulp and skin, preserving fiber and creating a more balanced nutrient profile with slower sugar absorption. Nutritional absorption differs, as juices offer quick vitamin boosts, while smoothies support sustained energy and improved gut health through fiber content.
Health Benefits of Juicing
Juicing extracts vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants from fruits and vegetables, providing concentrated nutrients for rapid absorption and enhanced energy levels. It removes fiber, making it easier for the body to digest and utilize essential nutrients quickly. Juicing supports detoxification, improves hydration, and boosts the immune system by delivering a potent dose of phytonutrients and enzymes.
Health Benefits of Blending
Blending preserves the fiber content of fruits and vegetables, promoting better digestion and sustained energy levels compared to juicing, which removes fiber. The antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals remain intact in blended beverages, supporting immune health and reducing inflammation. This method also aids in slower sugar absorption, making blended drinks a healthier option for blood sugar management.
Which Preserves Fiber: Juicing or Blending?
Blending preserves fiber by retaining the entire fruit or vegetable, including the pulp and skin, which are rich in dietary fiber essential for digestive health. Juicing extracts only the liquid content, removing most of the fiber, resulting in a smoother beverage but with reduced fiber content. Therefore, blending offers a higher fiber intake compared to juicing, supporting better satiety and blood sugar regulation.
Weight Loss: Juicing or Blending for Better Results?
Juicing removes fiber from fruits and vegetables, leading to faster absorption of nutrients and potentially quicker weight loss due to lower calorie intake. Blending retains fiber, which promotes satiety, reduces appetite, and supports sustained energy levels throughout the day. For weight loss, blending is often more effective as it helps control hunger and prevents blood sugar spikes associated with juicing.
Equipment Needed: Juicers vs Blenders
Juicers require specialized equipment such as masticating or centrifugal juicers designed to extract liquid by separating pulp and fiber, resulting in smooth, pulp-free juice. Blenders use blades within a high-speed container to pulverize whole fruits and vegetables, preserving fiber and creating thicker smoothies. Both machines vary in price and maintenance, with juicers often needing more cleaning due to pulp removal while blenders are generally easier to clean and more versatile for mixed beverages.
Taste and Texture: Juices Compared to Smoothies
Juices offer a clean, concentrated flavor with a smooth, thin texture that highlights the natural sweetness and acidity of fruits and vegetables. Smoothies retain the fiber and pulp from whole ingredients, resulting in a thicker, creamier texture and a rich, fuller taste experience. The presence of fiber in smoothies not only enhances mouthfeel but also slows sugar absorption, providing a more balanced energy release compared to juices.
Cost and Convenience: Juicing vs Blending
Juicing typically requires a specialized juicer, which can be more expensive upfront and involves separating pulp, increasing preparation and cleanup time. Blending uses a versatile blender that processes whole fruits and vegetables, often being more cost-effective and convenient for daily use. Blending retains fiber, reducing the need for extra ingredients, while juicing delivers a concentrated nutrient boost but may require more frequent purchases of produce.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Lifestyle
Juicing extracts liquid and nutrients from fruits and vegetables, leaving behind fiber, making it ideal for those seeking quick nutrient absorption and lighter drinks. Blending preserves the entire fruit or vegetable, retaining fiber and promoting digestive health, which suits individuals aiming for more filling smoothies and sustained energy. Selecting between juicing and blending depends on your dietary goals, time availability, and need for fiber intake throughout the day.
Juicing vs Blending Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com