Cold pressed juice offers superior nutritional value and fresher taste compared to concentrate juice, as it is extracted without heat, preserving vitamins and enzymes. Concentrate juice undergoes heat treatment and dilution, which often results in a loss of flavor and essential nutrients. Consumers seeking natural, wholesome beverages prefer cold pressed options for a more authentic and healthful experience.
Table of Comparison
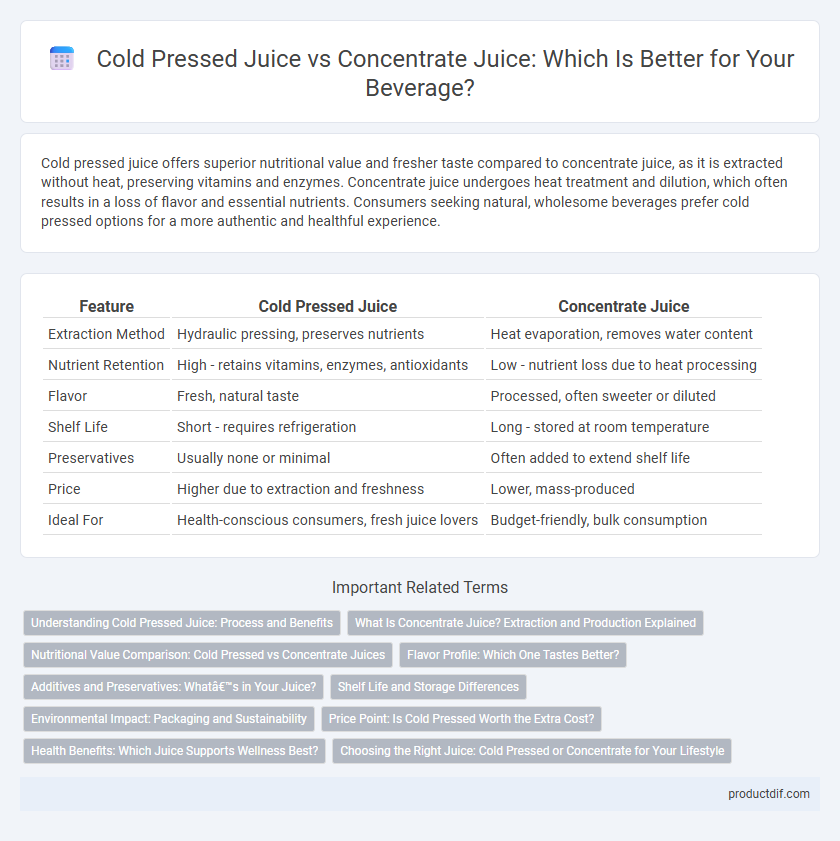
| Feature | Cold Pressed Juice | Concentrate Juice |
|---|---|---|
| Extraction Method | Hydraulic pressing, preserves nutrients | Heat evaporation, removes water content |
| Nutrient Retention | High - retains vitamins, enzymes, antioxidants | Low - nutrient loss due to heat processing |
| Flavor | Fresh, natural taste | Processed, often sweeter or diluted |
| Shelf Life | Short - requires refrigeration | Long - stored at room temperature |
| Preservatives | Usually none or minimal | Often added to extend shelf life |
| Price | Higher due to extraction and freshness | Lower, mass-produced |
| Ideal For | Health-conscious consumers, fresh juice lovers | Budget-friendly, bulk consumption |
Understanding Cold Pressed Juice: Process and Benefits
Cold pressed juice is extracted by mechanically pressing fruits and vegetables without heat, preserving more vitamins, enzymes, and antioxidants compared to traditional juicing methods. This process maintains the natural flavor and nutritional integrity, resulting in a fresher, more nutrient-dense beverage. Benefits include higher retention of nutrients such as vitamin C and phytonutrients, making cold pressed juice a popular choice among health-conscious consumers.
What Is Concentrate Juice? Extraction and Production Explained
Concentrate juice is produced by removing water from freshly squeezed fruit juice, resulting in a concentrated liquid with enhanced shelf life and reduced volume. The extraction involves heating the juice under vacuum to evaporate water without compromising flavor or nutritional content significantly. This concentrate is later reconstituted by adding water before packaging, making it a cost-effective option for mass production and distribution.
Nutritional Value Comparison: Cold Pressed vs Concentrate Juices
Cold pressed juice retains more vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants due to minimal processing and lack of heat exposure, preserving the natural nutritional profile of fruits and vegetables. Concentrate juice often undergoes heat treatment and reconstitution, which can reduce nutrient levels, especially vitamin C and certain enzymes. Consumers seeking maximum health benefits typically prefer cold pressed juice for its superior freshness and nutrient density.
Flavor Profile: Which One Tastes Better?
Cold pressed juice offers a fresher, more vibrant flavor profile due to minimal processing and the absence of heat, preserving the natural taste and nutrients of fruits and vegetables. Concentrate juice often has a sweeter, more uniform flavor but may lack the complexity and freshness found in cold pressed varieties because of pasteurization and reconstitution processes. Consumers seeking authentic, intense fruit flavors generally prefer cold pressed juice for its richer and more natural taste experience.
Additives and Preservatives: What’s in Your Juice?
Cold pressed juice contains minimal to no additives and preservatives, preserving natural nutrients and flavors through a gentle extraction process. Concentrate juice often includes added sugars, artificial flavors, and preservatives to extend shelf life and enhance taste. Consumers seeking pure, nutrient-rich beverages typically prefer cold pressed juice due to its cleaner ingredient profile.
Shelf Life and Storage Differences
Cold pressed juice retains more nutrients due to minimal processing but has a shorter shelf life, typically lasting 3 to 5 days refrigerated, requiring constant cold storage to maintain freshness. Concentrate juice undergoes pasteurization and water removal, extending its shelf life up to 6 to 12 months when unopened and stored in a cool, dark place. Once opened, concentrate juice should be refrigerated and consumed within 7 to 10 days, contrasting with the immediate consumption need of cold pressed varieties.
Environmental Impact: Packaging and Sustainability
Cold pressed juice typically uses minimal processing and often comes in glass or recyclable bottles, reducing plastic waste and environmental harm compared to concentrate juice, which frequently relies on plastic containers and higher energy consumption during reconstitution. The production of concentrate juice involves significant water and energy use for evaporation and transportation, increasing its carbon footprint relative to cold pressed juice that preserves nutrients without intensive processing. Sustainable packaging innovations, such as plant-based plastics and reusable glass bottles, are more commonly integrated within the cold pressed juice industry, aligning with rising consumer demand for eco-friendly beverage options.
Price Point: Is Cold Pressed Worth the Extra Cost?
Cold pressed juice typically costs 30-50% more than concentrate juice due to its extraction method preserving more nutrients and flavor without heat or additives. Price-conscious consumers may find concentrate juice offers better value, as it often undergoes pasteurization and water removal to extend shelf life and reduce cost. For health-focused buyers, the premium on cold pressed juice may justify the expense through higher antioxidant levels and fresher taste.
Health Benefits: Which Juice Supports Wellness Best?
Cold pressed juice retains more vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants due to minimal processing, making it superior for supporting immune function and reducing inflammation. Concentrate juice often contains added sugars and loses nutrients during processing, which can diminish its health benefits. Choosing cold pressed juice boosts hydration and provides enzymes that aid digestion, enhancing overall wellness more effectively than concentrate juice.
Choosing the Right Juice: Cold Pressed or Concentrate for Your Lifestyle
Cold pressed juice retains higher nutrient levels and enzymes due to minimal processing, making it ideal for health-conscious individuals seeking fresh, natural flavors and maximum vitamin intake. Concentrate juice undergoes heat treatment and reconstitution, offering longer shelf life and affordability, suitable for busy lifestyles or budget-friendly options without fresh produce availability. Selecting between cold pressed and concentrate juice depends on prioritizing nutrient density and freshness versus convenience and cost efficiency.
Cold Pressed Juice vs Concentrate Juice Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com