Tetra Pak packaging offers superior environmental benefits due to its renewable materials and efficient recycling process compared to aluminum cans, which require intensive mining and energy for production. Despite aluminum cans being lightweight and highly recyclable, Tetra Pak's multilayer design preserves beverage freshness and extends shelf life without refrigeration. Consumers seeking sustainability and product integrity often prefer Tetra Pak, while those prioritizing portability and convenience lean towards aluminum cans.
Table of Comparison
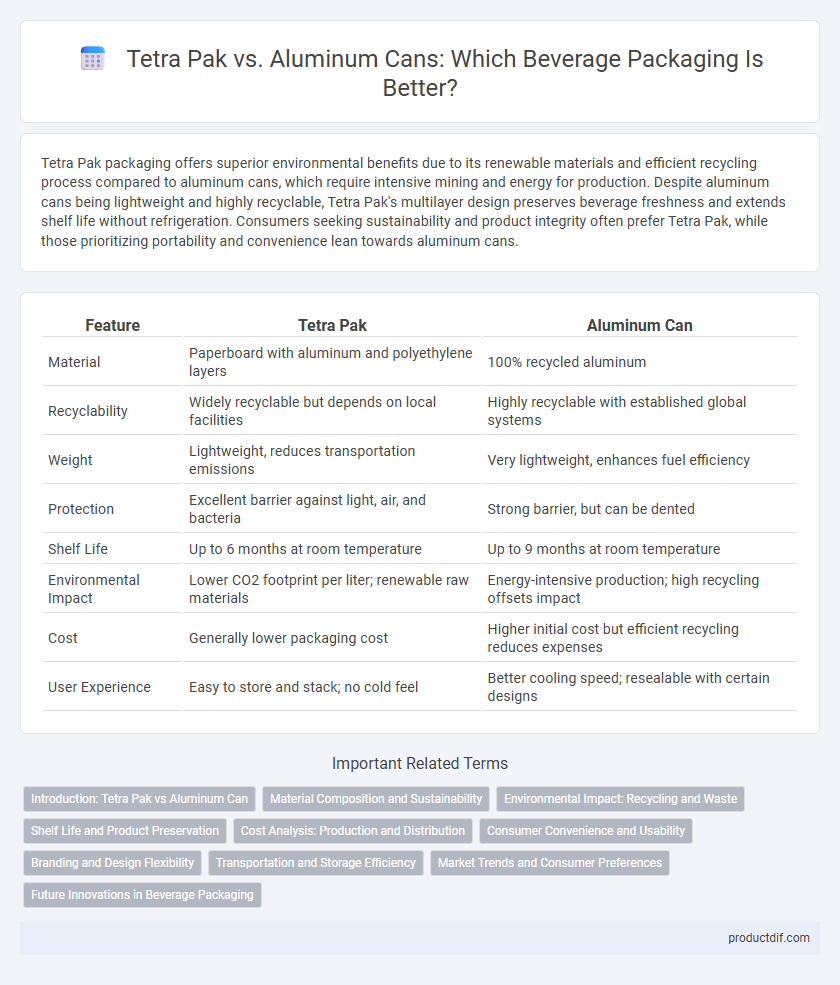
| Feature | Tetra Pak | Aluminum Can |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Paperboard with aluminum and polyethylene layers | 100% recycled aluminum |
| Recyclability | Widely recyclable but depends on local facilities | Highly recyclable with established global systems |
| Weight | Lightweight, reduces transportation emissions | Very lightweight, enhances fuel efficiency |
| Protection | Excellent barrier against light, air, and bacteria | Strong barrier, but can be dented |
| Shelf Life | Up to 6 months at room temperature | Up to 9 months at room temperature |
| Environmental Impact | Lower CO2 footprint per liter; renewable raw materials | Energy-intensive production; high recycling offsets impact |
| Cost | Generally lower packaging cost | Higher initial cost but efficient recycling reduces expenses |
| User Experience | Easy to store and stack; no cold feel | Better cooling speed; resealable with certain designs |
Introduction: Tetra Pak vs Aluminum Can
Tetra Pak and aluminum cans are two popular packaging options in the beverage industry, each offering unique benefits and environmental considerations. Tetra Pak cartons provide lightweight, renewable resource-based packaging with excellent product protection and extended shelf life due to their multi-layer design. Aluminum cans, valued for their recyclability and durability, enable rapid cooling and efficient transportation, making them a preferred choice for many carbonated beverages.
Material Composition and Sustainability
Tetra Pak cartons are primarily made of paperboard, combined with thin layers of polyethylene and aluminum, providing lightweight packaging with high recyclability rates in regions with advanced recycling systems. Aluminum cans consist mainly of aluminum, a highly recyclable metal that can be repeatedly recycled without losing quality, offering robust sustainability through a circular economy. While aluminum cans require more energy to produce initially, their infinite recyclability and strong recycling infrastructure often result in lower overall environmental impact compared to composite Tetra Pak cartons.
Environmental Impact: Recycling and Waste
Tetra Pak containers are composed primarily of paperboard, with layers of plastic and aluminum foil, making their recycling process complex yet increasingly supported by specialized facilities; their lightweight nature and efficient transportation reduce carbon emissions during distribution. Aluminum cans are widely recycled globally, supporting a closed-loop system that saves up to 95% of the energy required for primary production, but mining and refining aluminum present significant environmental challenges. Both packaging types contribute to waste management efforts, but optimizing recycling infrastructure and consumer participation remains crucial to minimizing their ecological footprints.
Shelf Life and Product Preservation
Tetra Pak cartons provide superior shelf life and product preservation for beverages due to their multi-layered construction that protects contents from light, air, and contaminants, extending freshness without refrigeration. Aluminum cans offer excellent barrier properties against oxygen and light, maintaining carbonation and flavor integrity, but they may be prone to corrosion if damaged. Both packaging types enhance product longevity, yet Tetra Pak often leads in preserving sensitive nutrients and flavor profiles for extended periods.
Cost Analysis: Production and Distribution
Tetra Pak cartons exhibit lower production costs due to lighter weight and efficient material usage, reducing raw material expenses compared to aluminum cans. Distribution expenses for Tetra Pak are minimized by their compact, stackable design, which optimizes shipping space and lowers transportation emissions. Aluminum cans incur higher costs from energy-intensive smelting and recycling processes, as well as heavier weight impacting fuel consumption during distribution.
Consumer Convenience and Usability
Tetra Pak cartons offer lightweight design and easy-to-open features, enhancing on-the-go convenience and reducing spillage risks for consumers. Aluminum cans provide superior recyclability and cold retention, appealing to users who prioritize rapid chilling and environmental impact. Both packaging types cater to different usability preferences, balancing portability and sustainability in the beverage market.
Branding and Design Flexibility
Tetra Pak offers unparalleled design flexibility with its customizable surface area, allowing vibrant, high-resolution graphics that enhance brand visibility on shelves. Aluminum cans provide a sleek, modern look but have limited printable surface compared to Tetra Pak, restricting branding options. Brands choosing Tetra Pak benefit from the ability to create unique, eye-catching packaging that effectively communicates product identity and appeals to consumers.
Transportation and Storage Efficiency
Tetra Pak cartons are lightweight and stackable, maximizing space efficiency during transportation and reducing shipping costs compared to aluminum cans. The rectangular shape of Tetra Pak allows for optimized palletizing with minimal wasted space, enhancing storage capacity in warehouses and retail environments. Aluminum cans, though durable, require more protective packaging and occupy more volume per unit, impacting overall transport and storage efficiency.
Market Trends and Consumer Preferences
Tetra Pak cartons have gained market share due to their lightweight design, sustainability advantages, and convenience for on-the-go consumers. Aluminum cans remain popular for their recyclability, durability, and strong association with carbonated beverages, driving continued demand in the soft drink and beer segments. Consumer preferences increasingly favor eco-friendly packaging solutions, with increasing interest in Tetra Pak's renewable materials and reduced carbon footprint influencing purchasing decisions.
Future Innovations in Beverage Packaging
Future innovations in beverage packaging will prioritize sustainability and smart technology integration. Tetra Pak is developing biodegradable materials and enhancing aseptic packaging to extend shelf life without preservatives. Aluminum can manufacturers are exploring lightweight alloys and digital QR code labeling to improve recyclability and consumer engagement.
Tetra Pak vs Aluminum Can Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com