Low-calorie beverages offer a refreshing alternative for those seeking to reduce sugar intake without sacrificing flavor, often utilizing artificial or natural sweeteners to maintain taste. Full-calorie drinks provide a richer, more satisfying experience with their traditional sugar content, appealing to consumers desiring maximum flavor and energy from their beverage. Choosing between low-calorie and full-calorie options depends on individual health goals and taste preferences, balancing enjoyment with nutritional considerations.
Table of Comparison
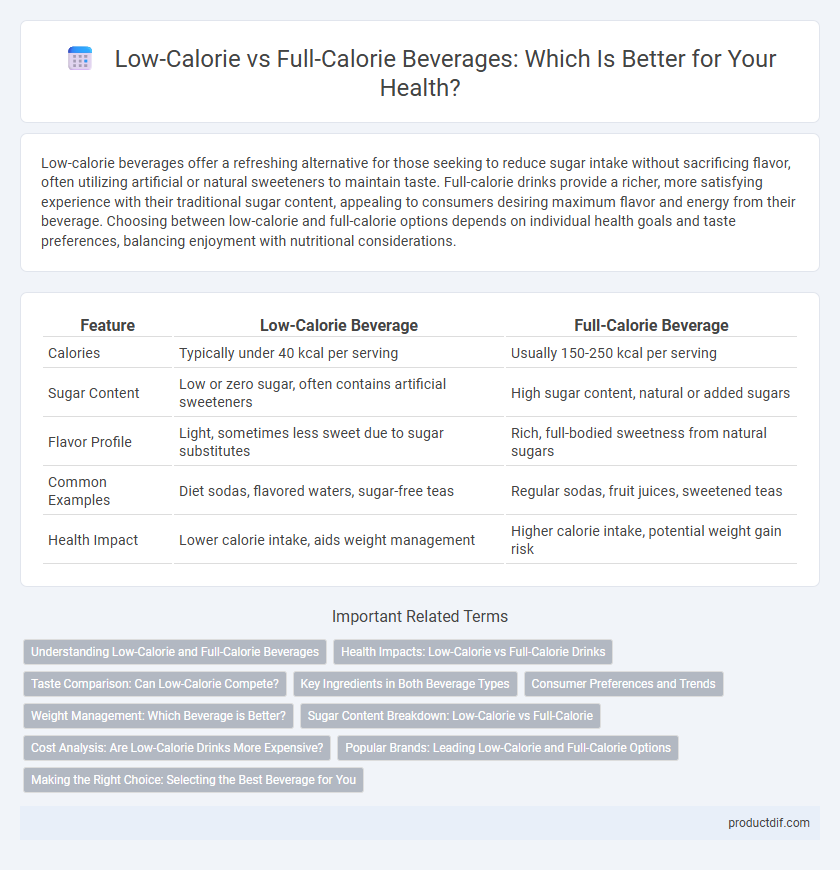
| Feature | Low-Calorie Beverage | Full-Calorie Beverage |
|---|---|---|
| Calories | Typically under 40 kcal per serving | Usually 150-250 kcal per serving |
| Sugar Content | Low or zero sugar, often contains artificial sweeteners | High sugar content, natural or added sugars |
| Flavor Profile | Light, sometimes less sweet due to sugar substitutes | Rich, full-bodied sweetness from natural sugars |
| Common Examples | Diet sodas, flavored waters, sugar-free teas | Regular sodas, fruit juices, sweetened teas |
| Health Impact | Lower calorie intake, aids weight management | Higher calorie intake, potential weight gain risk |
Understanding Low-Calorie and Full-Calorie Beverages
Low-calorie beverages typically contain fewer than 40 calories per serving, often achieved by using artificial sweeteners or natural low-calorie ingredients to reduce sugar content without sacrificing flavor. Full-calorie beverages, on the other hand, include the standard amount of sugars and carbohydrates, providing energy but with higher calorie intake. Understanding the differences in calorie content helps consumers make informed choices that align with their dietary goals and lifestyle needs.
Health Impacts: Low-Calorie vs Full-Calorie Drinks
Low-calorie drinks typically contain fewer sugars and artificial sweeteners, reducing overall calorie intake and potentially lowering the risk of obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases. Full-calorie beverages often have high sugar content, contributing to increased blood sugar levels, weight gain, and metabolic syndrome when consumed excessively. Choosing low-calorie options can support weight management and improve metabolic health, especially in individuals prone to insulin resistance and other chronic conditions.
Taste Comparison: Can Low-Calorie Compete?
Low-calorie beverages often struggle to match the rich, full-bodied flavor profile of full-calorie drinks, which benefit from natural sugars and higher ingredient density. Advanced sweeteners and flavor enhancers in low-calorie options aim to mimic the taste but can sometimes result in aftertastes that diverge from traditional flavors. Consumer taste tests reveal a growing acceptance of certain low-calorie brands, though many still prefer full-calorie beverages for their authentic and satisfying taste experience.
Key Ingredients in Both Beverage Types
Low-calorie beverages typically contain artificial sweeteners like aspartame, sucralose, or stevia, which provide sweetness without the added sugars and calories found in full-calorie drinks. Full-calorie beverages are often rich in high-fructose corn syrup, sucrose, or natural sugars, contributing to their higher caloric content and distinct flavor profile. Both types may include flavorings, preservatives, and carbonation, but the key difference lies in the sweetening agents and their impact on calorie count.
Consumer Preferences and Trends
Consumer preferences increasingly favor low-calorie beverages as health-conscious trends drive demand for options with reduced sugar and fewer calories. Market data shows a significant rise in sales of low-calorie sodas, flavored waters, and fitness drinks, reflecting a shift toward balanced nutrition and weight management. Full-calorie beverages maintain a loyal base, particularly among consumers seeking traditional taste and energy-boosting effects, but overall industry growth aligns with low-calorie product innovation.
Weight Management: Which Beverage is Better?
Low-calorie beverages typically contain fewer than 40 calories per serving, making them a preferred choice for weight management due to reduced energy intake while maintaining hydration. Full-calorie beverages, often high in sugars and calories, can contribute to weight gain and increased risk of obesity when consumed in excess. Choosing low-calorie options, such as diet sodas or infused waters, supports calorie control and can aid in achieving or maintaining a healthy weight more effectively.
Sugar Content Breakdown: Low-Calorie vs Full-Calorie
Low-calorie beverages typically contain 1 to 40 grams of sugar per serving, significantly less than full-calorie drinks, which often exceed 100 grams of sugar per serving. The reduced sugar content in low-calorie options lowers overall calorie intake and minimizes spikes in blood glucose levels. Choosing low-calorie beverages supports better weight management and reduces the risk of sugar-related health issues like diabetes.
Cost Analysis: Are Low-Calorie Drinks More Expensive?
Low-calorie beverages typically involve higher production costs due to specialized ingredients like artificial sweeteners and advanced manufacturing processes, which often results in a higher retail price compared to full-calorie drinks. However, economies of scale and increasing consumer demand for healthier options can narrow the price gap over time. Cost analysis reveals that while low-calorie drinks may initially seem more expensive, long-term pricing trends show increasing competitiveness with full-calorie counterparts.
Popular Brands: Leading Low-Calorie and Full-Calorie Options
Leading low-calorie beverages such as Coca-Cola Zero Sugar and Pepsi Max offer flavorful alternatives with minimal calories, appealing to health-conscious consumers. Full-calorie options like classic Coca-Cola and Pepsi Original continue to dominate the market with their traditional taste profiles and strong brand loyalty. Popularity trends indicate a growing shift towards low-calorie brands as demand for healthier lifestyle choices increases globally.
Making the Right Choice: Selecting the Best Beverage for You
Choosing between low-calorie and full-calorie beverages depends on your health goals, dietary needs, and taste preferences. Low-calorie options often contain fewer sugars and artificial sweeteners, making them ideal for weight management and reducing calorie intake. Full-calorie beverages provide natural energy and essential nutrients but may contribute to increased calorie consumption if not consumed in moderation.
Low-Calorie vs Full-Calorie Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com