Isotonic drinks contain a similar concentration of salts and sugar as found in the human body, which helps quickly replace fluids and electrolytes lost during intense exercise, making them ideal for prolonged physical activity. Hypotonic drinks have a lower concentration of salts and sugars than the body's fluids, enabling rapid hydration with fewer calories, suitable for light workouts or quick rehydration. Choosing between isotonic and hypotonic drinks depends on the intensity and duration of exercise as well as hydration needs.
Table of Comparison
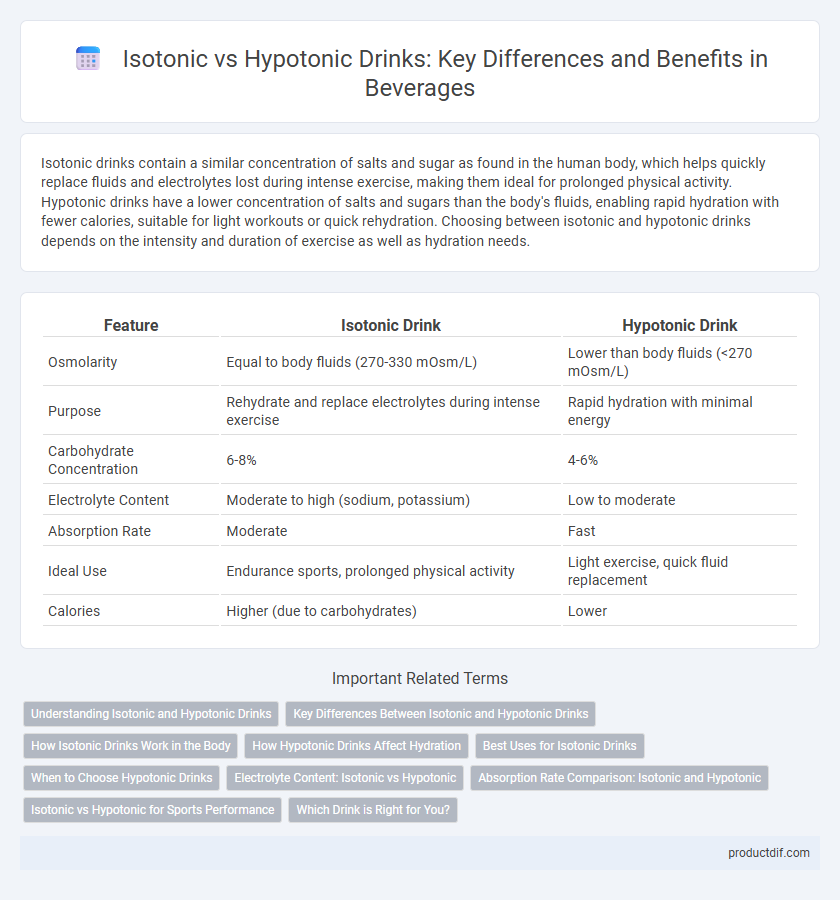
| Feature | Isotonic Drink | Hypotonic Drink |
|---|---|---|
| Osmolarity | Equal to body fluids (270-330 mOsm/L) | Lower than body fluids (<270 mOsm/L) |
| Purpose | Rehydrate and replace electrolytes during intense exercise | Rapid hydration with minimal energy |
| Carbohydrate Concentration | 6-8% | 4-6% |
| Electrolyte Content | Moderate to high (sodium, potassium) | Low to moderate |
| Absorption Rate | Moderate | Fast |
| Ideal Use | Endurance sports, prolonged physical activity | Light exercise, quick fluid replacement |
| Calories | Higher (due to carbohydrates) | Lower |
Understanding Isotonic and Hypotonic Drinks
Isotonic drinks contain a similar concentration of salts and sugars as found in the human body, enabling rapid hydration and energy replenishment during intense physical activity. Hypotonic drinks have a lower concentration of electrolytes and carbohydrates compared to body fluids, facilitating quicker absorption and hydration with minimal energy supply. Both beverage types are designed to optimize hydration but cater to different intensity levels and hydration needs.
Key Differences Between Isotonic and Hypotonic Drinks
Isotonic drinks contain similar concentrations of salts and sugars as found in the human body, making them ideal for rapid hydration and energy replenishment during intense exercise. Hypotonic drinks have a lower concentration of salts and sugars compared to body fluids, allowing faster absorption and hydration but less energy replacement. The choice between isotonic and hypotonic drinks depends on the athlete's hydration needs and the intensity and duration of physical activity.
How Isotonic Drinks Work in the Body
Isotonic drinks contain electrolyte concentrations similar to the body's natural fluids, facilitating rapid absorption and rehydration during intense physical activity. They replenish sodium, potassium, and carbohydrates lost through sweat, helping maintain optimal hydration and energy levels. By balancing fluid and electrolyte levels, isotonic beverages support endurance and recovery in athletes and active individuals.
How Hypotonic Drinks Affect Hydration
Hypotonic drinks contain lower concentrations of electrolytes and carbohydrates compared to body fluids, enabling faster absorption and quicker rehydration during mild dehydration or light exercise. These drinks rapidly replenish water lost through sweat without overly saturating the stomach, making them ideal for athletes engaged in short-duration activities. Their efficient hydration mechanism helps maintain optimal fluid balance and supports sustained performance with minimal gastrointestinal discomfort.
Best Uses for Isotonic Drinks
Isotonic drinks are ideal for athletes engaging in moderate to intense exercise lasting between 30 minutes to 2 hours, as they effectively replenish fluids, electrolytes, and energy lost through sweat. These beverages typically contain 6-8% carbohydrate concentration, matching the body's osmotic pressure, which enhances rapid absorption and energy delivery. Best suited for endurance sports like running, cycling, and team sports, isotonic drinks help maintain hydration and improve athletic performance during prolonged physical activity.
When to Choose Hypotonic Drinks
Hypotonic drinks are ideal for rapid rehydration during light to moderate exercise sessions lasting less than an hour, as they contain lower concentrations of electrolytes and carbohydrates than body fluids. Athletes engaged in activities like jogging or yoga benefit from hypotonic drinks because they quickly replenish water lost through sweat without causing stomach discomfort. Choosing hypotonic drinks over isotonic options helps maintain optimal hydration levels when electrolyte replacement demands are minimal.
Electrolyte Content: Isotonic vs Hypotonic
Isotonic drinks contain electrolyte levels similar to those found in human blood, typically around 6-8% carbohydrate concentration, which supports rapid hydration and energy replenishment during intense exercise. Hypotonic drinks have lower electrolyte and carbohydrate content, often below 4%, enabling quicker absorption to effectively rehydrate without providing significant energy. Understanding these electrolyte differences helps athletes select the appropriate beverage for hydration and performance needs.
Absorption Rate Comparison: Isotonic and Hypotonic
Isotonic drinks typically contain 6-8% carbohydrate concentration, enabling rapid fluid and electrolyte absorption that closely matches the body's natural blood composition, making them ideal for intense, sustained exercise. Hypotonic drinks have a lower carbohydrate concentration, usually less than 4%, allowing faster gastric emptying and quicker hydration, which benefits athletes during short, high-intensity activities or when rapid rehydration is necessary. The absorption rate of hypotonic drinks is generally faster than isotonic drinks due to their lower solute concentration, but isotonic drinks provide better electrolyte replacement for prolonged endurance performance.
Isotonic vs Hypotonic for Sports Performance
Isotonic drinks contain similar concentrations of salts and sugars as found in the human body, making them ideal for rapid hydration and energy replenishment during intense sports activities. Hypotonic drinks have lower concentrations of salts and sugars, allowing faster fluid absorption but providing less energy compared to isotonic options. Athletes engaging in prolonged or high-intensity exercise benefit from isotonic drinks to maintain electrolyte balance and sustain performance, while hypotonic drinks suit those needing quick hydration with minimal carbohydrate intake.
Which Drink is Right for You?
Isotonic drinks contain similar concentrations of salts and sugars as the human body, making them ideal for replenishing fluids and electrolytes lost during intense or prolonged exercise. Hypotonic drinks have lower concentrations of salt and sugar, allowing for faster hydration without providing significant energy, suitable for light workouts or everyday hydration. Choosing between isotonic and hypotonic drinks depends on exercise intensity and hydration needs, with isotonic best for endurance and hypotonic for quick fluid replacement.
Isotonic Drink vs Hypotonic Drink Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com