Hot fill packaging involves filling products at high temperatures to sterilize both the beverage and container, ensuring safety and preserving flavor without preservatives. Aseptic packaging sterilizes the beverage and packaging separately before filling in a sterile environment, allowing extended shelf life without refrigeration. Choosing between hot fill and aseptic packaging depends on product type, shelf-life requirements, and cost considerations.
Table of Comparison
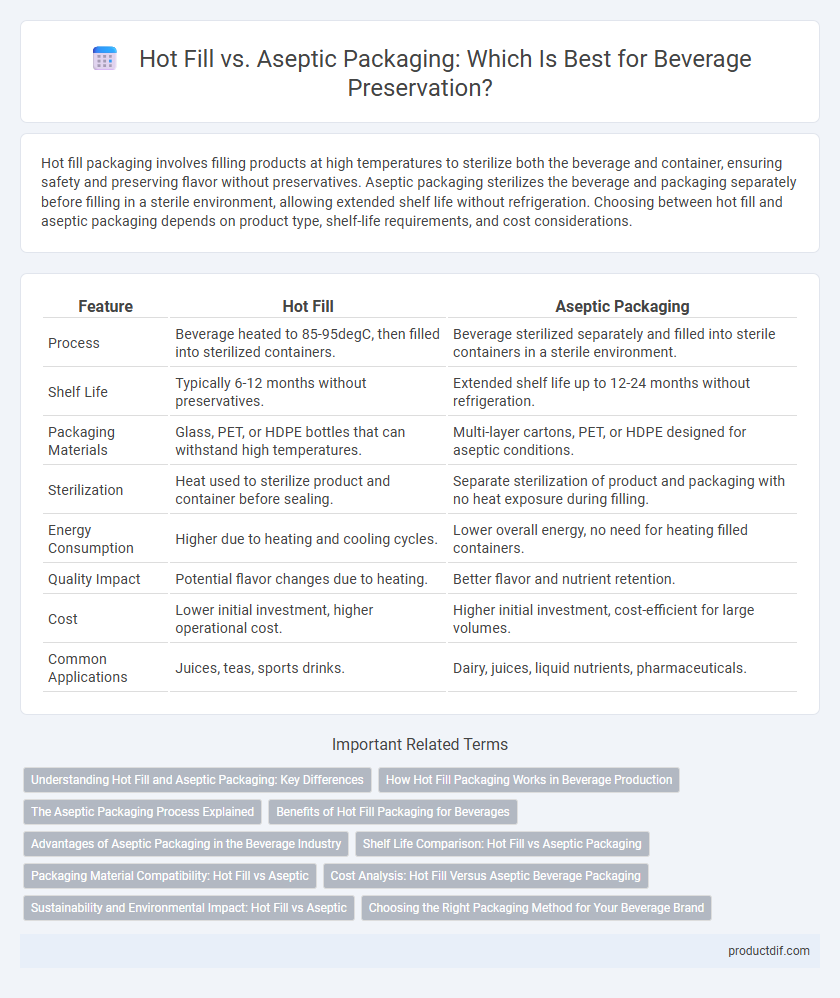
| Feature | Hot Fill | Aseptic Packaging |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Beverage heated to 85-95degC, then filled into sterilized containers. | Beverage sterilized separately and filled into sterile containers in a sterile environment. |
| Shelf Life | Typically 6-12 months without preservatives. | Extended shelf life up to 12-24 months without refrigeration. |
| Packaging Materials | Glass, PET, or HDPE bottles that can withstand high temperatures. | Multi-layer cartons, PET, or HDPE designed for aseptic conditions. |
| Sterilization | Heat used to sterilize product and container before sealing. | Separate sterilization of product and packaging with no heat exposure during filling. |
| Energy Consumption | Higher due to heating and cooling cycles. | Lower overall energy, no need for heating filled containers. |
| Quality Impact | Potential flavor changes due to heating. | Better flavor and nutrient retention. |
| Cost | Lower initial investment, higher operational cost. | Higher initial investment, cost-efficient for large volumes. |
| Common Applications | Juices, teas, sports drinks. | Dairy, juices, liquid nutrients, pharmaceuticals. |
Understanding Hot Fill and Aseptic Packaging: Key Differences
Hot fill packaging involves filling beverages at high temperatures, typically around 85-95degC, to ensure sterilization and extend shelf life without refrigeration. Aseptic packaging, on the other hand, sterilizes both the product and the packaging separately before filling in a sterile environment, allowing for longer shelf stability at ambient temperatures. The key differences lie in the processing temperatures, sterilization methods, and resulting shelf life, with hot fill commonly used for acidic juices and teas, while aseptic packaging suits sensitive beverages like dairy and non-acidic juices.
How Hot Fill Packaging Works in Beverage Production
Hot fill packaging in beverage production involves heating the liquid to temperatures around 85-95degC to eliminate microbes, then filling the sterilized container while still hot to create a vacuum seal as it cools. This vacuum effect helps preserve the product by preventing contamination and extending shelf life without the need for refrigeration. The hot fill process suits high-acid beverages like juices, teas, and sports drinks, ensuring safety and maintaining flavor integrity.
The Aseptic Packaging Process Explained
The aseptic packaging process involves sterilizing both the beverage and the packaging separately before filling in a sterile environment to prevent microbial contamination and extend shelf life without refrigeration. This method utilizes ultra-high temperature (UHT) treatment for the liquid and steam or chemical sterilization for the packaging materials. Aseptic packaging ensures product safety and preservation of flavor and nutrients, making it ideal for juice, dairy, and other perishable beverages.
Benefits of Hot Fill Packaging for Beverages
Hot fill packaging enables effective sterilization by heating beverages to high temperatures before filling, extending shelf life without preservatives. This method preserves flavor integrity and nutritional quality, particularly for fruit juices and teas, while ensuring product safety through microbial elimination. Hot fill is cost-efficient for medium-acid beverages and supports environmentally friendly PET bottles due to its lower heat resistance requirements compared to aseptic packaging.
Advantages of Aseptic Packaging in the Beverage Industry
Aseptic packaging offers significant advantages in the beverage industry by enabling longer shelf life without the need for preservatives or refrigeration, preserving product freshness and flavor. This technology reduces contamination risks through sterile processing and packaging, enhancing safety and quality control. It also supports sustainable practices by lowering energy consumption during storage and transportation compared to hot fill methods.
Shelf Life Comparison: Hot Fill vs Aseptic Packaging
Hot fill packaging involves heating the beverage to around 85-95degC to sterilize both the product and the container, resulting in a shelf life of typically 6 to 12 months without refrigeration. Aseptic packaging uses ultra-high temperature (UHT) treatment combined with sterile packaging environments, extending shelf life up to 12 to 18 months at room temperature while preserving flavor and nutritional quality better than hot fill. Shelf life in aseptic packaging outperforms hot fill by reducing thermal impact and contamination risk, making it ideal for sensitive beverages requiring longer preservation.
Packaging Material Compatibility: Hot Fill vs Aseptic
Hot fill packaging requires materials that can withstand high temperatures, such as PET or glass, ensuring the integrity of the container during pasteurization without compromising barrier properties. Aseptic packaging utilizes multilayer cartons or plastic bottles with specialized barrier films designed to maintain sterility and protect against oxygen and light without heat exposure. Compatibility between packaging material and filling process directly impacts product shelf life, safety, and quality in beverage production.
Cost Analysis: Hot Fill Versus Aseptic Beverage Packaging
Hot fill beverage packaging typically incurs lower initial capital investment compared to aseptic systems, making it cost-effective for small to medium production volumes. However, aseptic packaging offers longer shelf life and reduced need for preservatives, potentially lowering distribution and inventory costs over time. Evaluating total cost of ownership must include factors such as equipment, sterilization processes, packaging materials, and product stability when choosing between hot fill and aseptic technologies.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact: Hot Fill vs Aseptic
Hot fill packaging typically uses glass or PET bottles that require energy-intensive heating but enables use of recyclable materials, reducing plastic waste. Aseptic packaging utilizes lightweight cartons made of multilayer materials that are harder to recycle, raising concerns over long-term environmental impact. Assessing carbon footprint, hot fill processes may emit more CO2 initially, while aseptic packaging's complex disposal challenges contribute to persistent ecological effects.
Choosing the Right Packaging Method for Your Beverage Brand
Choosing the right packaging method for your beverage brand depends on factors such as product shelf life, production scale, and cost efficiency. Hot fill packaging is ideal for fruit juices and teas that require pasteurization, ensuring microbial safety while preserving flavor, but it demands heat-resistant containers and higher energy use. Aseptic packaging provides extended shelf life without refrigeration by sterilizing both the product and packaging separately, making it suitable for dairy and plant-based beverages seeking long-term distribution and retail without preservatives.
Hot Fill vs Aseptic Packaging Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com