Natural sweeteners like honey, maple syrup, and stevia provide a healthier alternative to artificial sweeteners by offering beneficial nutrients and lower risk of negative health effects. Artificial sweeteners such as aspartame and sucralose are often calorie-free but may contribute to metabolic issues and alter gut microbiota over time. Choosing natural sweeteners in beverages can enhance flavor while supporting overall wellness through more natural ingredients.
Table of Comparison
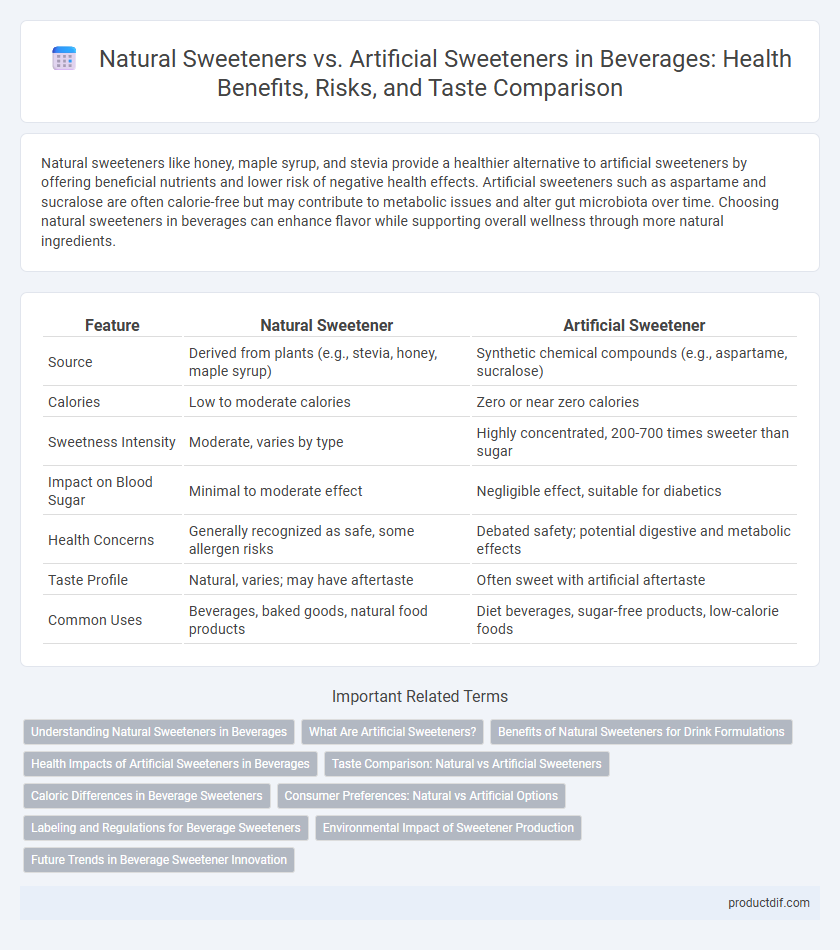
| Feature | Natural Sweetener | Artificial Sweetener |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Derived from plants (e.g., stevia, honey, maple syrup) | Synthetic chemical compounds (e.g., aspartame, sucralose) |
| Calories | Low to moderate calories | Zero or near zero calories |
| Sweetness Intensity | Moderate, varies by type | Highly concentrated, 200-700 times sweeter than sugar |
| Impact on Blood Sugar | Minimal to moderate effect | Negligible effect, suitable for diabetics |
| Health Concerns | Generally recognized as safe, some allergen risks | Debated safety; potential digestive and metabolic effects |
| Taste Profile | Natural, varies; may have aftertaste | Often sweet with artificial aftertaste |
| Common Uses | Beverages, baked goods, natural food products | Diet beverages, sugar-free products, low-calorie foods |
Understanding Natural Sweeteners in Beverages
Natural sweeteners in beverages, such as honey, maple syrup, and stevia, provide a more wholesome alternative to artificial additives by offering essential nutrients and antioxidants. These sweeteners enhance flavor without the chemical aftertaste often associated with synthetic options like aspartame or sucralose. Consumers increasingly prefer natural sweeteners for their perceived health benefits and minimal processing, aligning with the growing demand for clean-label beverages.
What Are Artificial Sweeteners?
Artificial sweeteners are synthetic sugar substitutes designed to provide sweetness without the calories of natural sugars. Common types include aspartame, sucralose, and saccharin, widely used in diet beverages and low-calorie food products. These sweeteners are intensely sweet, often hundreds of times sweeter than sucrose, allowing minimal quantities to achieve the desired taste.
Benefits of Natural Sweeteners for Drink Formulations
Natural sweeteners like stevia and agave syrup enhance drink formulations by providing a low-calorie option that maintains a clean, natural taste favored by health-conscious consumers. These sweeteners exhibit a lower glycemic index, contributing to better blood sugar control and making beverages suitable for diabetics and those managing weight. Their plant-based origin aligns with the growing demand for organic and minimally processed ingredients in the beverage industry.
Health Impacts of Artificial Sweeteners in Beverages
Artificial sweeteners in beverages, such as aspartame, sucralose, and saccharin, have been linked to potential health risks including metabolic disruptions, altered gut microbiota, and increased cravings for sweet foods. Studies suggest that long-term consumption may affect insulin sensitivity and contribute to weight gain despite their low-calorie content. Monitoring intake and opting for natural sweeteners like stevia or monk fruit can reduce these adverse health impacts.
Taste Comparison: Natural vs Artificial Sweeteners
Natural sweeteners like honey and stevia provide a complex flavor profile with subtle floral or herbal notes, making beverages taste richer and more authentic. Artificial sweeteners such as aspartame and sucralose often deliver intense sweetness but can leave a lingering aftertaste or chemical flavor. Consumer preference tends to favor natural sweeteners for a smoother, more balanced taste experience in drinks.
Caloric Differences in Beverage Sweeteners
Natural sweeteners such as honey, maple syrup, and agave nectar typically contain calories ranging from 15 to 60 per teaspoon, directly impacting the beverage's energy content. Artificial sweeteners like sucralose, aspartame, and stevia provide sweetness with negligible or zero calories, significantly reducing the caloric load of drinks. This caloric difference influences consumer choices, especially among those focused on weight management and diabetic-friendly beverage options.
Consumer Preferences: Natural vs Artificial Options
Consumer preferences in the beverage industry increasingly favor natural sweeteners such as stevia, honey, and agave due to their perception of health benefits and clean-label appeal. Market research reveals a growing demand for beverages with natural ingredients, driving product innovation and reformulation to replace artificial sweeteners like aspartame and sucralose. Despite this trend, some segments still prefer artificial sweeteners for their low-calorie properties and sweetness intensity without altering taste profiles.
Labeling and Regulations for Beverage Sweeteners
Beverage labeling regulations mandate clear disclosure of natural sweeteners such as stevia, honey, and agave to inform consumers seeking clean-label options. Artificial sweeteners like aspartame, sucralose, and saccharin are subject to strict regulatory limits on usage levels and must include warnings if required by authorities such as the FDA or EFSA. Regulatory frameworks prioritize transparency, ensuring beverages indicate sweetener type and concentration to maintain compliance and support consumer safety.
Environmental Impact of Sweetener Production
Natural sweetener production often involves agricultural practices that demand significant land use and water resources, contributing to deforestation and biodiversity loss. Artificial sweeteners are typically synthesized through chemical processes with lower direct land use but rely on energy-intensive manufacturing and non-renewable chemical inputs, leading to greenhouse gas emissions and potential environmental toxicity. Evaluating the overall environmental impact requires lifecycle assessments comparing water footprint, carbon emissions, and ecological disturbances associated with both sweetener types.
Future Trends in Beverage Sweetener Innovation
Future trends in beverage sweetener innovation emphasize the growing consumer demand for natural sweeteners such as stevia, monk fruit, and agave, driven by health-conscious choices and clean-label preferences. Advances in biotechnological methods are enabling the development of novel natural sweeteners with improved taste profiles and reduced caloric content, positioning them as sustainable alternatives to traditional sugar and artificial sweeteners like aspartame and sucralose. The integration of plant-based sweeteners with functional ingredients also reflects the industry's shift toward combining health benefits and flavor enhancement in beverage formulations.
Natural Sweetener vs Artificial Sweetener Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com