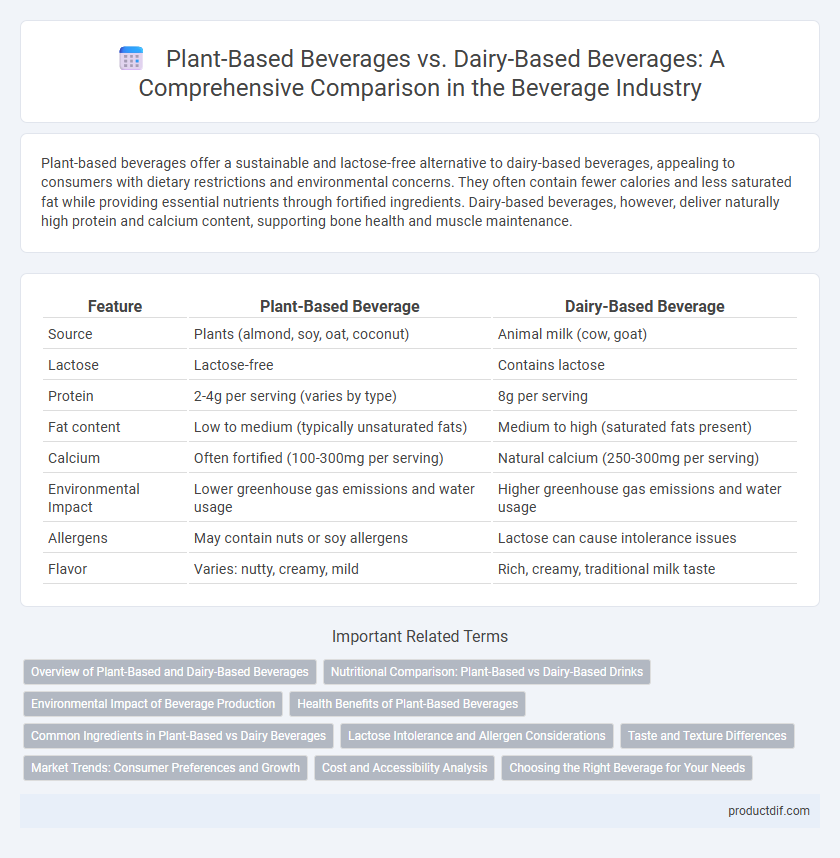
Plant-based beverages offer a sustainable and lactose-free alternative to dairy-based beverages, appealing to consumers with dietary restrictions and environmental concerns. They often contain fewer calories and less saturated fat while providing essential nutrients through fortified ingredients. Dairy-based beverages, however, deliver naturally high protein and calcium content, supporting bone health and muscle maintenance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Plant-Based Beverage | Dairy-Based Beverage |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Plants (almond, soy, oat, coconut) | Animal milk (cow, goat) |
| Lactose | Lactose-free | Contains lactose |
| Protein | 2-4g per serving (varies by type) | 8g per serving |
| Fat content | Low to medium (typically unsaturated fats) | Medium to high (saturated fats present) |
| Calcium | Often fortified (100-300mg per serving) | Natural calcium (250-300mg per serving) |
| Environmental Impact | Lower greenhouse gas emissions and water usage | Higher greenhouse gas emissions and water usage |
| Allergens | May contain nuts or soy allergens | Lactose can cause intolerance issues |
| Flavor | Varies: nutty, creamy, mild | Rich, creamy, traditional milk taste |
Overview of Plant-Based and Dairy-Based Beverages
Plant-based beverages, derived from sources such as almonds, soy, oats, and coconut, offer lactose-free alternatives rich in vitamins, minerals, and lower in saturated fat compared to dairy-based beverages. Dairy-based beverages, primarily made from cow's milk, provide high-quality protein, calcium, and essential nutrients but may pose challenges for lactose-intolerant individuals. The rising consumer demand for plant-based options is driven by health, environmental sustainability, and ethical considerations, reshaping the global beverage market dynamics.
Nutritional Comparison: Plant-Based vs Dairy-Based Drinks
Plant-based beverages such as almond, soy, and oat milk offer lower saturated fat and cholesterol levels compared to dairy-based milk, making them heart-healthier options. Dairy milk provides higher protein content, essential nutrients like calcium, vitamin B12, and iodine, which are critical for bone health and metabolic functions. Fortified plant-based drinks bridge nutritional gaps by adding calcium and vitamins D and B12, yet their bioavailability and nutrient density often differ from those in dairy products.
Environmental Impact of Beverage Production
Plant-based beverages typically generate lower greenhouse gas emissions and consume less water and land compared to dairy-based beverages, making them a more sustainable option in beverage production. Dairy production accounts for significant methane emissions, a potent greenhouse gas contributing to climate change. Choosing plant-based beverages reduces deforestation and biodiversity loss linked to livestock farming, emphasizing their environmental advantages.
Health Benefits of Plant-Based Beverages
Plant-based beverages such as almond milk, oat milk, and soy milk offer lower cholesterol and saturated fat levels compared to dairy-based beverages, reducing the risk of heart disease and supporting better cardiovascular health. Rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals, plant-based drinks provide anti-inflammatory properties and promote improved digestion and lactose intolerance management. The presence of fiber in many plant-based options enhances gut health and contributes to sustained energy levels throughout the day.
Common Ingredients in Plant-Based vs Dairy Beverages
Plant-based beverages commonly contain ingredients such as water, plant proteins from sources like soy, almond, oat, or rice, natural sweeteners, and stabilizers like carrageenan or gellan gum to enhance texture. Dairy-based beverages primarily consist of milk, lactose, casein, whey proteins, and natural fats, with some variants incorporating added vitamins D and calcium for fortification. Both types often include flavors, emulsifiers, and preservatives to improve taste and shelf life while catering to different dietary preferences and nutritional needs.
Lactose Intolerance and Allergen Considerations
Plant-based beverages offer a lactose-free alternative for individuals with lactose intolerance, reducing digestive discomfort common with dairy-based drinks. These beverages are often hypoallergenic, avoiding common dairy allergens such as casein and whey proteins, which can trigger adverse reactions. Consumers seeking allergen-friendly options frequently prefer plant-based drinks like almond, oat, or soy milk to mitigate risks associated with dairy allergens.
Taste and Texture Differences
Plant-based beverages often offer a lighter, slightly nutty or grainy flavor profile compared to the creamy, rich taste of dairy-based beverages. The texture of plant-based options like almond or oat milk tends to be thinner and less velvety, while dairy milk provides a smooth, thick mouthfeel due to its natural fat content. These differences in taste and texture influence consumer preference and application in recipes such as coffee, smoothies, and baking.
Market Trends: Consumer Preferences and Growth
Plant-based beverages have experienced significant market growth driven by increasing consumer demand for lactose-free, vegan, and environmentally sustainable options. Dairy-based beverages continue to hold a strong market presence but face challenges due to rising awareness of animal welfare and health concerns. The global plant-based beverage market is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 10% between 2023 and 2030, reflecting shifting consumer preferences toward healthier and eco-friendly alternatives.
Cost and Accessibility Analysis
Plant-based beverages generally offer lower production costs due to cheaper raw materials like almonds, oats, or soy compared to dairy's resource-intensive livestock farming. Accessibility varies regionally, with plant-based options increasingly available in urban and health-conscious markets but still limited in rural areas lacking supply chains. Dairy-based beverages maintain strong accessibility through established distribution networks and widespread consumer familiarity, often resulting in competitive pricing despite higher production expenses.
Choosing the Right Beverage for Your Needs
Plant-based beverages such as almond, oat, and soy milk offer lactose-free, low-calorie alternatives rich in vitamins and antioxidants, ideal for individuals with dairy allergies or those seeking sustainable options. Dairy-based beverages provide high-quality protein, calcium, and essential nutrients important for bone health and muscle maintenance, making them suitable for athletes and those with higher protein requirements. Selecting the right beverage depends on dietary restrictions, nutritional goals, and environmental considerations, ensuring alignment with personal health and lifestyle needs.
Plant-Based Beverage vs Dairy-Based Beverage Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com