Ready-to-drink beverages offer convenience and immediate consumption without preparation, making them ideal for on-the-go lifestyles. Concentrate products require dilution, providing cost-efficiency and longer shelf life while allowing customization of flavor strength. Choosing between ready-to-drink and concentrate depends on consumer preferences for convenience versus flexibility.
Table of Comparison
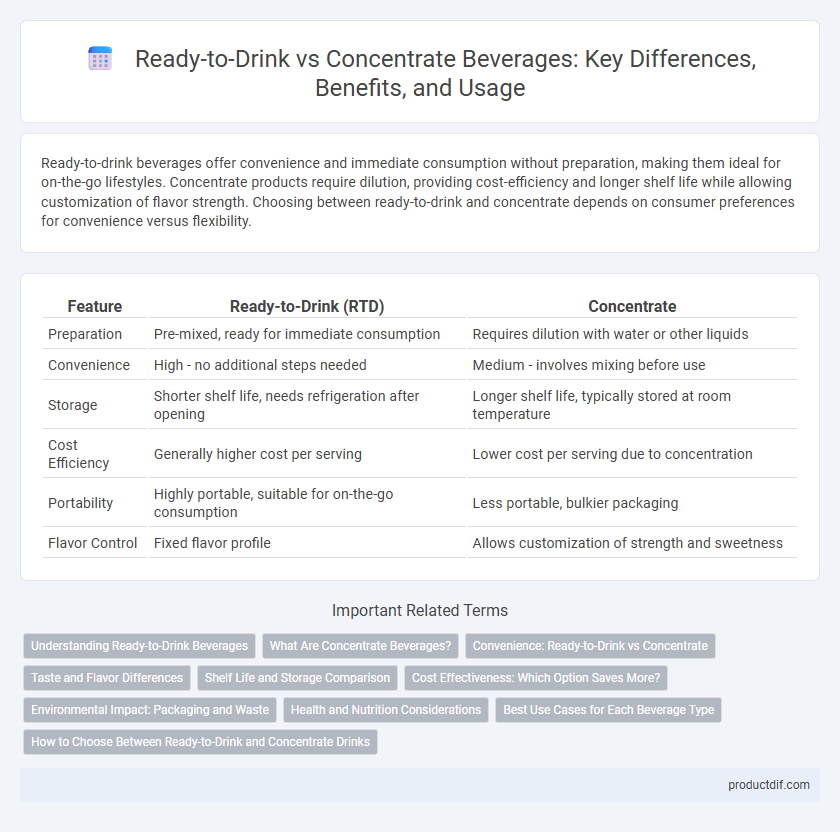
| Feature | Ready-to-Drink (RTD) | Concentrate |
|---|---|---|
| Preparation | Pre-mixed, ready for immediate consumption | Requires dilution with water or other liquids |
| Convenience | High - no additional steps needed | Medium - involves mixing before use |
| Storage | Shorter shelf life, needs refrigeration after opening | Longer shelf life, typically stored at room temperature |
| Cost Efficiency | Generally higher cost per serving | Lower cost per serving due to concentration |
| Portability | Highly portable, suitable for on-the-go consumption | Less portable, bulkier packaging |
| Flavor Control | Fixed flavor profile | Allows customization of strength and sweetness |
Understanding Ready-to-Drink Beverages
Ready-to-drink (RTD) beverages offer convenience by eliminating the need for preparation, providing consumers with a pre-mixed, easily accessible option. These products maintain flavor consistency and meet quality standards through advanced preservation techniques such as pasteurization and aseptic packaging. Market trends show a growing preference for RTD beverages due to busy lifestyles and increasing demand for portable, on-the-go hydration.
What Are Concentrate Beverages?
Concentrate beverages are liquid or powdered mixtures that contain a high concentration of flavor, sugar, or other key ingredients, requiring dilution with water before consumption. These products offer extended shelf life and cost-effectiveness by allowing consumers to control the beverage's strength and sweetness. Popular examples include fruit juice concentrates, iced tea concentrates, and flavored drink mixes used in both household and commercial beverage preparation.
Convenience: Ready-to-Drink vs Concentrate
Ready-to-drink beverages offer maximum convenience with no preparation required, making them ideal for on-the-go consumption. Concentrates require dilution, which involves additional time and equipment but provide cost savings and longer shelf life. Consumers prioritize ready-to-drink options for immediate use, while concentrate appeals to those seeking flexibility and bulk storage.
Taste and Flavor Differences
Ready-to-drink beverages offer consistent flavor profiles with balanced sweetness and freshness due to their pre-mixed formulation, ensuring immediate consumption satisfaction. Concentrates require dilution, which can lead to variability in taste intensity and sometimes a less vibrant flavor compared to ready-to-drink options. The flavor complexity in ready-to-drink beverages is often more pronounced, while concentrates provide customization flexibility but may compromise aroma and mouthfeel.
Shelf Life and Storage Comparison
Ready-to-drink (RTD) beverages typically offer a shorter shelf life of 3 to 12 months due to their pre-mixed composition and need for refrigeration or cold storage. Concentrate products, on the other hand, can last 1 to 2 years or more when stored in sealed, cool, and dry conditions, benefiting from reduced water content and preservative formulation. Storage for RTD drinks often requires refrigerated environments to maintain freshness, whereas concentrates remain shelf-stable at room temperature until dilution.
Cost Effectiveness: Which Option Saves More?
Ready-to-drink beverages generally come at a higher per-serving cost compared to concentrates due to added processing, packaging, and convenience factors. Concentrates offer significant cost savings by allowing consumers to dilute them with water, reducing transportation and packaging expenses while maximizing servings per container. Evaluating cost effectiveness depends on consumption frequency and storage preferences, with concentrates providing better value for bulk use and ready-to-drink favored for immediate convenience despite higher prices.
Environmental Impact: Packaging and Waste
Ready-to-drink beverages typically generate more packaging waste due to single-use bottles, increasing environmental burden through plastic and aluminum use. Concentrate products often use smaller, more compact packaging, which reduces greenhouse gas emissions and landfill waste by minimizing transportation volume and container disposal. Efficient recycling systems and biodegradable materials in both formats can significantly mitigate their ecological impact.
Health and Nutrition Considerations
Ready-to-Drink beverages offer convenience and consistent portion control, often containing balanced nutrients and lower added sugars compared to concentrates. Concentrates may require dilution, which can lead to inconsistent nutrient intake and higher risks of overconsumption of sugars or preservatives. Consumers prioritizing health should evaluate ingredient labels and nutritional information to choose options with minimal additives, natural ingredients, and appropriate serving sizes.
Best Use Cases for Each Beverage Type
Ready-to-drink (RTD) beverages offer convenience and portability, making them ideal for on-the-go consumption, quick refreshment, and single-serve situations such as outdoor activities or office breaks. Concentrate beverages are best suited for cost-effective bulk preparation, allowing users to customize strength and flavor while reducing packaging waste, which is advantageous for home use, restaurants, and catering services. Both beverage types cater to distinct consumer preferences and usage scenarios, optimizing hydration and flavor delivery according to lifestyle needs.
How to Choose Between Ready-to-Drink and Concentrate Drinks
Choosing between ready-to-drink and concentrate beverages depends on convenience, shelf life, and customization preferences. Ready-to-drink drinks offer immediate consumption with consistent flavor profiles, ideal for on-the-go lifestyles and minimal preparation time. Concentrate beverages provide greater control over sweetness and strength, allowing cost savings and longer storage periods before dilution.
Ready-to-Drink vs Concentrate Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com