Flash chilling preserves the vibrant flavors and aromatic notes of beverages by rapidly cooling hot-brewed liquids, preventing bitterness and oxidation. Hot brewing enhances extraction of rich compounds, offering a full-bodied taste, but prolonged heat exposure can diminish freshness. Choosing between flash chilling and hot brewing depends on desired flavor intensity and serving temperature preferences.
Table of Comparison
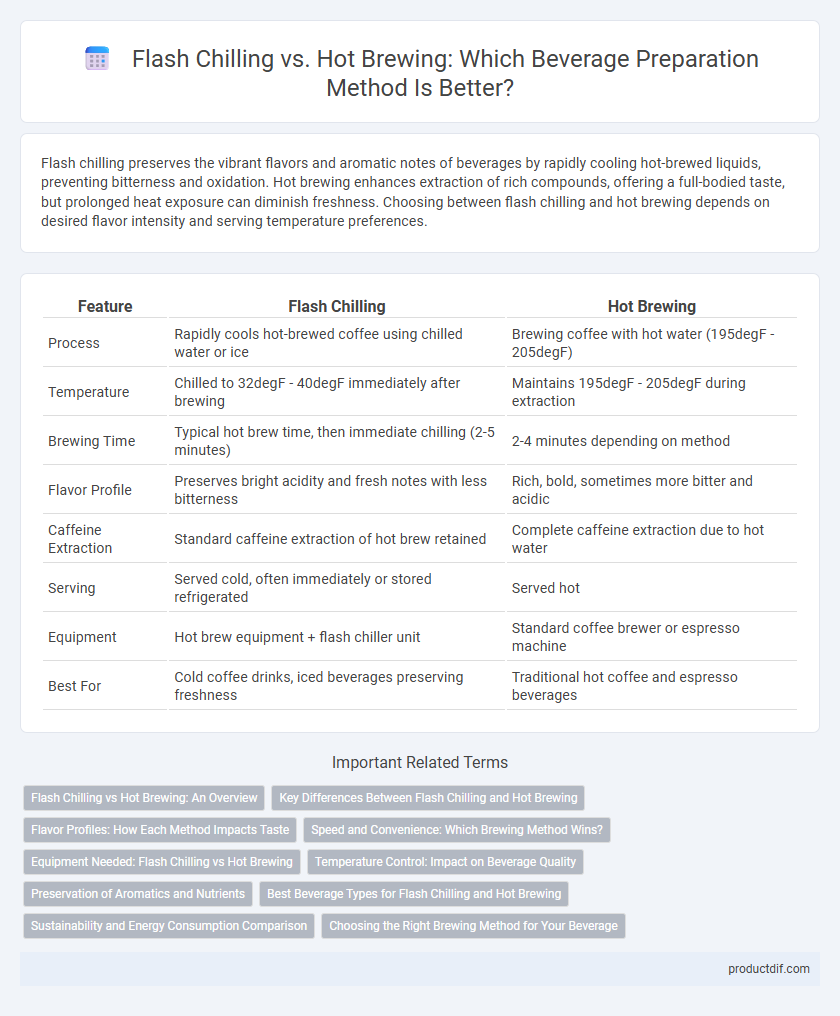
| Feature | Flash Chilling | Hot Brewing |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Rapidly cools hot-brewed coffee using chilled water or ice | Brewing coffee with hot water (195degF - 205degF) |
| Temperature | Chilled to 32degF - 40degF immediately after brewing | Maintains 195degF - 205degF during extraction |
| Brewing Time | Typical hot brew time, then immediate chilling (2-5 minutes) | 2-4 minutes depending on method |
| Flavor Profile | Preserves bright acidity and fresh notes with less bitterness | Rich, bold, sometimes more bitter and acidic |
| Caffeine Extraction | Standard caffeine extraction of hot brew retained | Complete caffeine extraction due to hot water |
| Serving | Served cold, often immediately or stored refrigerated | Served hot |
| Equipment | Hot brew equipment + flash chiller unit | Standard coffee brewer or espresso machine |
| Best For | Cold coffee drinks, iced beverages preserving freshness | Traditional hot coffee and espresso beverages |
Flash Chilling vs Hot Brewing: An Overview
Flash chilling rapidly cools brewed coffee to preserve volatile aromatics and maintain a fresh flavor profile, while hot brewing involves extracting coffee at higher temperatures to maximize solubility and richness. Flash chilling minimizes oxidation and bitterness by quickly lowering temperature, enhancing clarity and brightness in cold beverages. Hot brewing emphasizes boldness and body, making it ideal for traditional hot coffee experiences, whereas flash chilling optimizes cold coffee's smoothness and acidity balance.
Key Differences Between Flash Chilling and Hot Brewing
Flash chilling rapidly cools brewed coffee to preserve flavor compounds and reduce acidity, typically using specialized machines that lower temperature within seconds. Hot brewing involves steeping coffee grounds in hot water between 195degF to 205degF, extracting oils and aromas through prolonged heat exposure. The key differences lie in temperature control, extraction time, and flavor profiles, with flash chilling emphasizing freshness and brightness, while hot brewing delivers richer, bolder taste.
Flavor Profiles: How Each Method Impacts Taste
Flash chilling preserves the bright, crisp flavors and aromatic compounds of coffee by rapidly cooling brewed coffee, minimizing oxidation and bitterness. Hot brewing extracts a fuller body and deeper flavors, enhancing the richness and intensity of the beverage through prolonged contact with hot water. Each method influences acidity, sweetness, and bitterness, shaping distinct sensory experiences tailored to different preferences.
Speed and Convenience: Which Brewing Method Wins?
Flash chilling offers unmatched speed by rapidly cooling hot-brewed coffee within minutes, ensuring a fresh iced beverage without waiting hours for dilution or melting ice. Hot brewing provides convenience through simplicity and traditional flavor extraction but lacks the rapid turnaround time critical for busy cafes and consumers. For swift service and immediate iced coffee gratification, flash chilling outperforms hot brewing in both speed and user convenience.
Equipment Needed: Flash Chilling vs Hot Brewing
Flash chilling requires specialized equipment such as a commercial-grade flash chiller or rapid cooling system designed to quickly reduce the temperature of brewed coffee without compromising flavor. Hot brewing relies on standard coffee makers or espresso machines equipped with heating elements capable of maintaining optimal extraction temperatures typically between 195degF and 205degF. While flash chilling equipment emphasizes rapid temperature reduction and preservation, hot brewing equipment prioritizes consistent heat control for precise extraction.
Temperature Control: Impact on Beverage Quality
Precise temperature control in flash chilling preserves the delicate aromas and flavors by rapidly lowering the beverage temperature, preventing the growth of unwanted bacteria and oxidation. In contrast, hot brewing relies on maintaining consistent high temperatures to optimize extraction, enhancing bitterness and intensity but risking over-extraction if temperature fluctuates. Proper temperature management in both methods directly influences the final beverage quality, affecting taste profiles and shelf-life stability.
Preservation of Aromatics and Nutrients
Flash chilling rapidly cools brewed beverages, effectively preserving aromatic compounds and essential nutrients by minimizing oxidation and degradation. Hot brewing, while traditional and effective for extraction, exposes delicate aromatics and heat-sensitive nutrients to prolonged high temperatures, often resulting in diminished flavor profile and nutrient loss. The controlled temperature drop in flash chilling ensures maximum retention of volatile oils and antioxidants, enhancing the beverage's sensory and health attributes.
Best Beverage Types for Flash Chilling and Hot Brewing
Flash chilling excels with delicate beverages like tea, specialty coffee, and fruit infusions, preserving aroma and flavor by rapidly cooling brewed liquids. Hot brewing is ideal for robust drinks such as espresso, black coffee, and herbal teas, as high temperatures effectively extract bold flavors and essential oils. Choosing between flash chilling and hot brewing depends on the desired flavor profile and beverage type, with flash chilling enhancing freshness and hot brewing emphasizing richness.
Sustainability and Energy Consumption Comparison
Flash chilling significantly reduces energy consumption by rapidly cooling hot-brewed beverages using chilled water or a heat exchanger, minimizing refrigeration time compared to traditional hot brewing followed by cooling. Hot brewing consumes extensive energy for prolonged heating and gradual cooling processes, leading to higher carbon emissions and a larger environmental footprint. Incorporating flash chilling in beverage production enhances sustainability by lowering overall energy demand and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Choosing the Right Brewing Method for Your Beverage
Flash chilling preserves the bright, vibrant flavors of coffee by rapidly cooling hot brewed coffee, making it ideal for iced beverages and cold brews with a smooth finish. Hot brewing extracts robust flavors and aromatic compounds essential for traditional hot coffee, providing a richer, fuller-bodied taste. Selecting the right method depends on your beverage preference, desired flavor profile, and serving temperature, balancing extraction time and temperature control for optimal taste.
Flash Chilling vs Hot Brewing Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com