Natural flavors in beverages are derived from real ingredients such as fruits, herbs, and spices, offering an authentic taste profile that consumers often prefer for perceived health benefits. Artificial flavors are synthesized chemically to mimic natural tastes, providing consistency and cost-efficiency but sometimes lacking the complexity and depth found in natural alternatives. Choosing between natural and artificial flavors impacts product labeling, consumer perception, and regulatory compliance in the beverage industry.
Table of Comparison
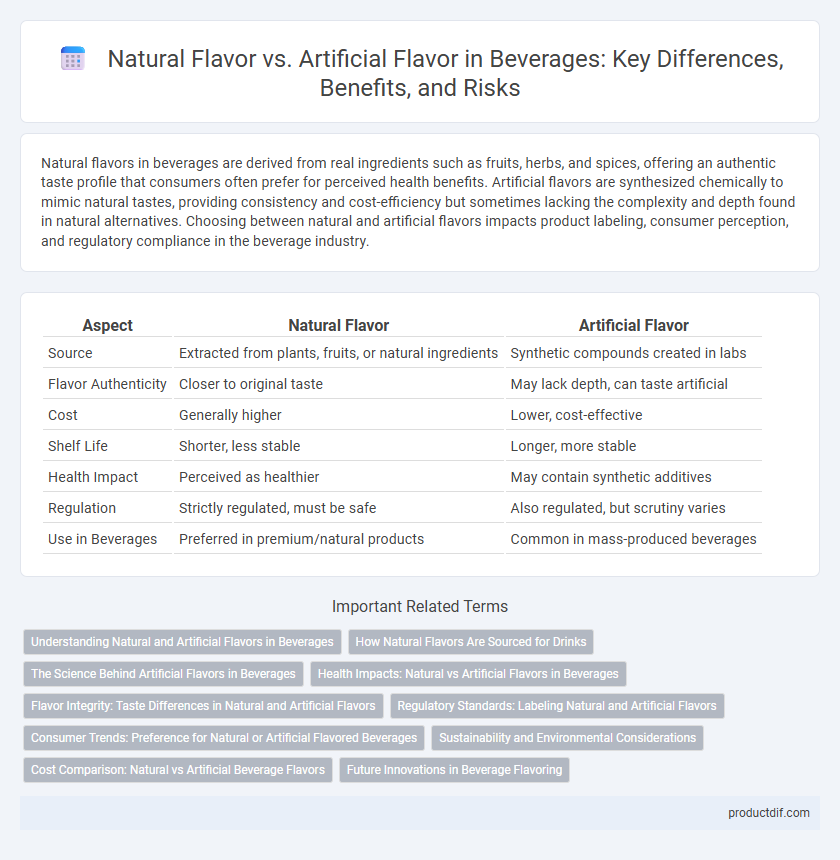
| Aspect | Natural Flavor | Artificial Flavor |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Extracted from plants, fruits, or natural ingredients | Synthetic compounds created in labs |
| Flavor Authenticity | Closer to original taste | May lack depth, can taste artificial |
| Cost | Generally higher | Lower, cost-effective |
| Shelf Life | Shorter, less stable | Longer, more stable |
| Health Impact | Perceived as healthier | May contain synthetic additives |
| Regulation | Strictly regulated, must be safe | Also regulated, but scrutiny varies |
| Use in Beverages | Preferred in premium/natural products | Common in mass-produced beverages |
Understanding Natural and Artificial Flavors in Beverages
Natural flavors in beverages derive from real fruits, herbs, or spices, extracted through physical processes like distillation or cold-pressing to enhance taste authenticity. Artificial flavors are chemically synthesized compounds designed to mimic natural taste profiles, offering consistent flavor intensity and cost efficiency in mass production. Understanding the distinction helps consumers make informed choices based on ingredients, flavor stability, and potential allergen concerns in their beverage selections.
How Natural Flavors Are Sourced for Drinks
Natural flavors in beverages are primarily sourced from essential oils, extracts, and distillates derived from fruits, herbs, spices, and other plant materials. Techniques such as cold pressing, solvent extraction, and steam distillation are employed to capture the authentic aromatic compounds responsible for the natural taste profile. These sourcing methods ensure that the flavor compounds are both potent and closely aligned with the original botanical sources, enhancing the overall sensory experience of the drink.
The Science Behind Artificial Flavors in Beverages
Artificial flavors in beverages are created through synthetic chemicals designed to mimic natural taste compounds found in fruits, spices, and herbs. These flavor molecules interact with the olfactory receptors to produce consistent, intensified taste experiences unmatched by many natural ingredients. Advanced techniques in flavor chemistry involve isolating key aromatic compounds and replicating them with cost-effective, stable substances tailored for beverage formulations.
Health Impacts: Natural vs Artificial Flavors in Beverages
Natural flavors in beverages are derived from real fruit, plant, or animal sources and often contain fewer synthetic chemicals, potentially reducing exposure to allergens and irritants linked to artificial additives. Artificial flavors are chemically synthesized and may include substances that can trigger sensitivity or adverse reactions in some individuals, raising concerns about long-term health effects and cumulative exposure. Studies suggest choosing beverages with natural flavors can support a cleaner diet and lower the risk of negative health outcomes related to artificial chemical intake.
Flavor Integrity: Taste Differences in Natural and Artificial Flavors
Natural flavors preserve flavor integrity by capturing essential oils and aromatic compounds directly from fruits, herbs, and spices, resulting in a more authentic and complex taste profile. Artificial flavors, synthesized to mimic these natural compounds, often lack the nuanced depth and can sometimes present a sharper or one-dimensional taste. The sensory experience of natural flavors typically offers a richer, more balanced palate that appeals to consumers seeking genuine beverage authenticity.
Regulatory Standards: Labeling Natural and Artificial Flavors
Regulatory standards for labeling natural and artificial flavors in beverages require strict adherence to definitions set by agencies like the FDA and EFSA. Natural flavors must originate from natural sources such as fruits, herbs, or spices, while artificial flavors are chemically synthesized to mimic natural taste profiles. Clear labeling ensures consumer transparency, with natural flavors typically indicated as derived from natural substances and artificial flavors explicitly identified to prevent misleading information.
Consumer Trends: Preference for Natural or Artificial Flavored Beverages
Consumer trends increasingly show a preference for natural flavors in beverages due to growing health consciousness and demand for clean-label products. Market data reveals a higher willingness to pay for drinks labeled with natural ingredients, reflecting skepticism toward artificial additives. This shift drives beverage manufacturers to reformulate recipes, prioritizing natural flavor extracts to meet rising consumer expectations.
Sustainability and Environmental Considerations
Natural flavors in beverages often rely on renewable agricultural sources, supporting sustainable farming practices and reducing carbon footprints associated with synthetic chemical production. Artificial flavors require petrochemical inputs and energy-intensive manufacturing processes, leading to higher greenhouse gas emissions and greater environmental impact. Choosing natural flavors contributes to biodiversity preservation and decreases chemical pollution in ecosystems, enhancing overall sustainability in beverage production.
Cost Comparison: Natural vs Artificial Beverage Flavors
Natural flavors in beverages generally cost significantly more than artificial flavors due to the complex extraction processes and seasonal availability of raw materials. Artificial flavors offer a cost-effective alternative, providing consistent taste profiles at a fraction of the price, which is crucial for large-scale beverage production and pricing strategies. The price difference can impact product formulation decisions, with manufacturers balancing authentic taste appeal against budget constraints.
Future Innovations in Beverage Flavoring
Future innovations in beverage flavoring emphasize the use of natural flavor sources derived from plant extracts, essential oils, and fermentation processes, enhancing authenticity and health benefits. Advances in biotechnology enable the creation of novel natural flavor compounds through microbial synthesis, reducing reliance on synthetic chemicals. These developments are poised to meet consumer demand for clean-label beverages while maintaining consistent taste and stability.
Natural Flavor vs Artificial Flavor Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com