Shelf-stable packaging ensures beverages remain safe and fresh at room temperature by using airtight seals and materials that prevent contamination, reducing the need for refrigeration and enhancing convenience. Refrigerated packaging maintains optimal taste and nutritional value by requiring continuous cold storage, which can increase energy costs and limit portability. Choosing between these packaging types depends on factors like product formulation, distribution logistics, and consumer preferences.
Table of Comparison
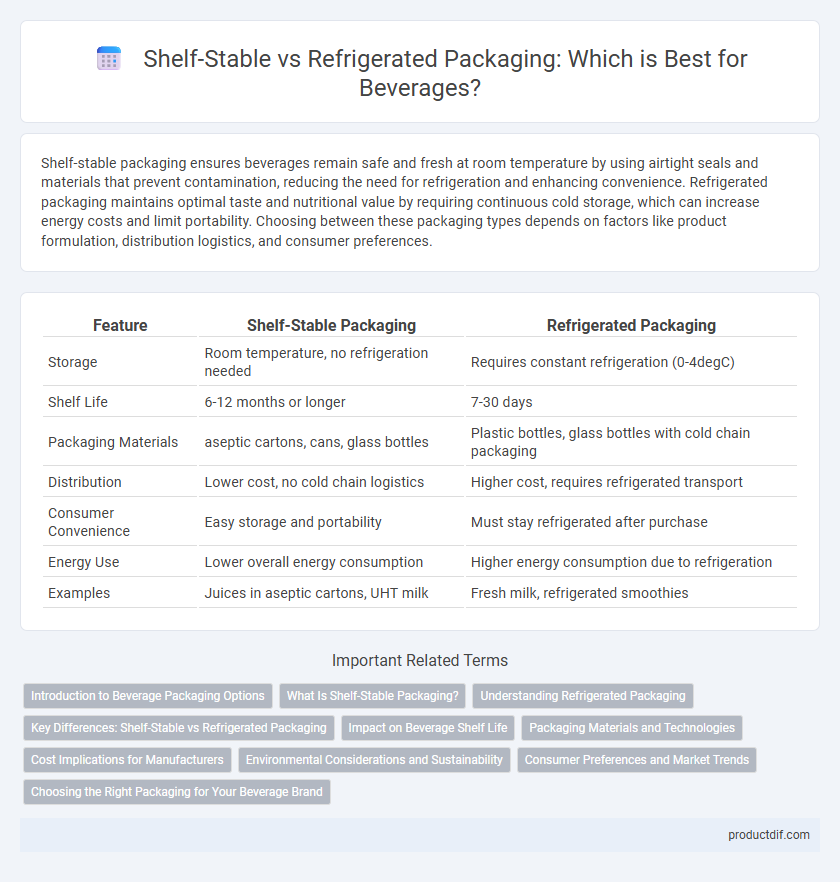
| Feature | Shelf-Stable Packaging | Refrigerated Packaging |
|---|---|---|
| Storage | Room temperature, no refrigeration needed | Requires constant refrigeration (0-4degC) |
| Shelf Life | 6-12 months or longer | 7-30 days |
| Packaging Materials | aseptic cartons, cans, glass bottles | Plastic bottles, glass bottles with cold chain packaging |
| Distribution | Lower cost, no cold chain logistics | Higher cost, requires refrigerated transport |
| Consumer Convenience | Easy storage and portability | Must stay refrigerated after purchase |
| Energy Use | Lower overall energy consumption | Higher energy consumption due to refrigeration |
| Examples | Juices in aseptic cartons, UHT milk | Fresh milk, refrigerated smoothies |
Introduction to Beverage Packaging Options
Shelf-stable packaging preserves beverages through airtight sealing and sterilization, allowing products like juices and milk alternatives to remain safe without refrigeration. Refrigerated packaging relies on cold storage to maintain freshness and prevent spoilage, commonly used for dairy, fresh juices, and craft beers. Choosing between these options impacts supply chain logistics, shelf life, and consumer convenience in the beverage industry.
What Is Shelf-Stable Packaging?
Shelf-stable packaging refers to containers designed to preserve beverages at room temperature without the need for refrigeration, using technologies such as airtight seals, sterilization, and aseptic processing to maintain product safety and quality. This type of packaging extends shelf life by preventing microbial growth and oxidation, making it ideal for juice boxes, canned drinks, and certain dairy alternatives. Shelf-stable beverages offer convenience and reduced energy consumption compared to refrigerated packaging, supporting long-term storage and distribution.
Understanding Refrigerated Packaging
Refrigerated packaging is designed to maintain beverage freshness by protecting products from spoilage through temperature control, utilizing materials with superior insulation properties and barrier technology to extend shelf life. This packaging type often incorporates features like vacuum sealing and modified atmosphere packaging (MAP) to inhibit microbial growth and preserve taste and nutritional value. Understanding these technologies is crucial for beverage manufacturers aiming to ensure product quality during distribution and retail display in chilled environments.
Key Differences: Shelf-Stable vs Refrigerated Packaging
Shelf-stable packaging preserves beverages by using airtight containers and thermal processing methods like UHT or retort sterilization, ensuring long shelf life without refrigeration. Refrigerated packaging requires constant cold storage to maintain freshness and prevent spoilage, commonly used for perishable drinks such as dairy or fresh juices. The key difference lies in temperature dependency for preservation, impacting distribution, storage costs, and consumer convenience.
Impact on Beverage Shelf Life
Shelf-stable packaging significantly extends beverage shelf life by utilizing airtight, heat-treated containers that prevent microbial growth and oxidation, enabling storage at room temperature for several months to years. Refrigerated packaging, relying on cold temperatures to inhibit spoilage, offers a shorter shelf life typically ranging from days to weeks but preserves fresh taste and nutritional quality. Selecting between these packaging types depends on balancing shelf life requirements with desired flavor retention and storage conditions.
Packaging Materials and Technologies
Shelf-stable packaging for beverages typically utilizes aseptic cartons, multi-layered plastics, and metal cans that provide oxygen and light barriers to extend product longevity without refrigeration. Refrigerated packaging often employs high-barrier plastics and glass bottles designed to maintain freshness and prevent contamination under cold storage conditions. Advances in active packaging technologies, such as oxygen scavengers and antimicrobial coatings, enhance both shelf-stable and refrigerated beverage packaging performance by preserving flavor and safety.
Cost Implications for Manufacturers
Shelf-stable packaging significantly reduces manufacturing costs by minimizing the need for refrigeration during storage and transportation, leading to lower energy consumption and extended product shelf life. Refrigerated packaging requires costly cold chain logistics, including refrigerated trucks and storage facilities, which increase operational expenses for manufacturers. These cost differences heavily influence packaging decisions, especially for companies targeting wide distribution or export markets.
Environmental Considerations and Sustainability
Shelf-stable packaging reduces energy consumption by eliminating the need for constant refrigeration during storage and transportation, resulting in a smaller carbon footprint compared to refrigerated packaging. Materials used in shelf-stable packaging, such as aseptic cartons and lightweight plastics, often promote recyclability and reduce overall waste, enhancing sustainability efforts. In contrast, refrigerated packaging relies heavily on cold chain logistics, which increases greenhouse gas emissions and energy use, posing greater environmental challenges.
Consumer Preferences and Market Trends
Consumer preferences increasingly favor shelf-stable packaging due to its convenience, longer shelf life, and reduced need for refrigeration, aligning with busy lifestyles and on-the-go consumption trends. Market trends indicate a surge in demand for sustainable, lightweight materials in shelf-stable options, supporting environmental concerns and cost-efficiency in distribution. Despite this, refrigerated packaging maintains a niche appeal for premium, fresh beverages where taste preservation and product quality are paramount.
Choosing the Right Packaging for Your Beverage Brand
Choosing the right packaging for your beverage brand depends on factors like product type, shelf life, and distribution channels. Shelf-stable packaging, such as aseptic cartons or retort pouches, offers extended shelf life without refrigeration, reducing transportation costs and expanding market reach. Refrigerated packaging ensures freshness and flavor preservation for perishable beverages like dairy and fresh juices but involves higher storage and logistical expenses.
Shelf-Stable Packaging vs Refrigerated Packaging Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com