Fermented tea, such as kombucha, undergoes a natural fermentation process that enhances probiotic content and offers unique tangy flavors, whereas herbal infusions are made by steeping herbs, flowers, or roots without fermentation, providing a caffeine-free, gentle taste experience. The fermentation process in fermented teas not only imparts health benefits like improved digestion but also develops complex flavor profiles that evolve over time. Herbal infusions prioritize natural antioxidants and soothing properties, often used for relaxation and wellness without the fermentation's microbial activity.
Table of Comparison
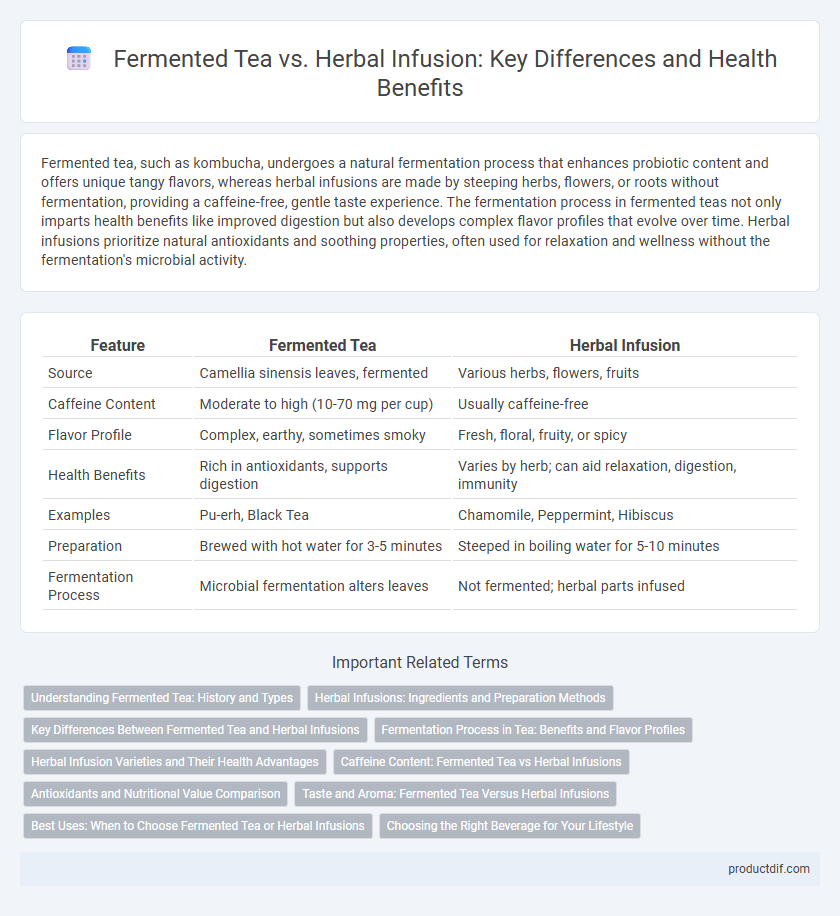
| Feature | Fermented Tea | Herbal Infusion |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Camellia sinensis leaves, fermented | Various herbs, flowers, fruits |
| Caffeine Content | Moderate to high (10-70 mg per cup) | Usually caffeine-free |
| Flavor Profile | Complex, earthy, sometimes smoky | Fresh, floral, fruity, or spicy |
| Health Benefits | Rich in antioxidants, supports digestion | Varies by herb; can aid relaxation, digestion, immunity |
| Examples | Pu-erh, Black Tea | Chamomile, Peppermint, Hibiscus |
| Preparation | Brewed with hot water for 3-5 minutes | Steeped in boiling water for 5-10 minutes |
| Fermentation Process | Microbial fermentation alters leaves | Not fermented; herbal parts infused |
Understanding Fermented Tea: History and Types
Fermented tea, including well-known varieties such as pu-erh and kombucha, boasts a rich history rooted in ancient Chinese culture where it was prized for its unique flavor and health benefits. The fermentation process involves microbial activity that transforms tea leaves, enhancing antioxidants and generating complex flavors distinct from herbal infusions, which are non-tea plant brews like chamomile or peppermint. Understanding the diverse types of fermented tea highlights their cultural significance and the biochemical changes that set them apart from traditional herbal infusions.
Herbal Infusions: Ingredients and Preparation Methods
Herbal infusions, commonly known as tisanes, are crafted by steeping various botanical ingredients such as chamomile, peppermint, hibiscus, and rose hips in hot water, extracting their natural flavors and health benefits without involving tea leaves. Preparation methods emphasize temperature control and steeping time, typically between 3 to 10 minutes, to optimize the release of volatile oils and active compounds like antioxidants and flavonoids. This caffeine-free beverage offers diverse therapeutic properties, including digestive aid, relaxation, and anti-inflammatory effects, driven by the specific combination of herbs used.
Key Differences Between Fermented Tea and Herbal Infusions
Fermented tea, such as Pu-erh and Kombucha, undergoes a natural microbial fermentation process that alters its chemical composition, enhancing antioxidants and probiotics. Herbal infusions, or tisanes, are brewed from herbs, flowers, or roots without tea leaves and contain no caffeine or tannins. The primary differences lie in fermentation impacts, caffeine content, and the presence of beneficial microbes unique to fermented teas.
Fermentation Process in Tea: Benefits and Flavor Profiles
Fermented tea undergoes a complex microbial fermentation process that enhances its antioxidant levels and develops unique, robust flavor profiles ranging from earthy to fruity notes. This fermentation transforms catechins into theaflavins and thearubigins, contributing to improved digestion and potential heart health benefits. Unlike herbal infusions, which lack fermentation, fermented teas like Pu-erh and Kombucha provide both probiotic properties and a depth of taste unattainable in non-fermented brews.
Herbal Infusion Varieties and Their Health Advantages
Herbal infusions, such as chamomile, peppermint, and hibiscus, offer a wide range of health benefits including improved digestion, reduced inflammation, and antioxidant properties. Unlike fermented teas like black or oolong, herbal infusions are caffeine-free and contain specific bioactive compounds that support relaxation, immune function, and cardiovascular health. Consuming diverse herbal infusions regularly can enhance hydration while providing targeted wellness advantages through natural phytochemicals.
Caffeine Content: Fermented Tea vs Herbal Infusions
Fermented teas such as black, oolong, and pu-erh contain varying caffeine levels, typically ranging from 30 to 70 mg per cup, providing a mild stimulant effect. Herbal infusions like chamomile, peppermint, or rooibos are naturally caffeine-free, making them ideal for those seeking relaxation or avoiding caffeine altogether. Understanding the caffeine content in fermented tea versus herbal infusions helps consumers select beverages that match their activity level and health preferences.
Antioxidants and Nutritional Value Comparison
Fermented tea, such as black and oolong varieties, contains higher levels of antioxidants like theaflavins and thearubigins, which contribute to cardiovascular health and improved metabolism. Herbal infusions, made from plants like chamomile, hibiscus, or peppermint, offer diverse nutritional compounds including vitamins, minerals, and unique polyphenols, but generally have lower antioxidant capacity compared to fermented teas. Both beverages provide distinct health benefits, with fermented tea excelling in antioxidant potency while herbal infusions contribute additional micronutrients and soothing properties.
Taste and Aroma: Fermented Tea Versus Herbal Infusions
Fermented tea offers a complex, earthy aroma with rich, robust flavors that develop through microbial fermentation, providing depth and subtle sweetness. Herbal infusions present a wide range of vibrant, fresh, and floral notes, often with naturally caffeine-free, light, and refreshing taste profiles. The contrast between the mellow, umami-rich fermented tea and the bright, aromatic herbal infusions highlights distinct sensory experiences preferred by different palates.
Best Uses: When to Choose Fermented Tea or Herbal Infusions
Fermented tea, such as black or pu-erh, is best chosen for its rich antioxidants and digestive benefits, making it ideal for post-meal consumption or afternoon energy boosts. Herbal infusions, including chamomile or peppermint, are preferred for their calming and medicinal properties, suitable for relaxation or soothing digestive discomfort. Selecting between fermented tea and herbal infusion depends on desired effects, whether you seek stimulation and metabolism support or gentle relaxation and therapeutic relief.
Choosing the Right Beverage for Your Lifestyle
Fermented tea, such as kombucha, offers probiotics that support gut health and boost metabolism, making it ideal for those seeking digestive benefits and natural energy. Herbal infusions provide caffeine-free options rich in antioxidants and calming properties, perfect for stress relief and hydration throughout the day. Selecting between fermented tea and herbal infusion depends on your wellness goals and sensitivity to caffeine, aligning your beverage choice with your lifestyle needs.
Fermented Tea vs Herbal Infusion Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com