Eco-friendly dyes derived from natural sources reduce environmental pollution and minimize health risks compared to synthetic dyes, which often contain harmful chemicals. Using biodegradable ingredients, eco-friendly dyes promote sustainable apparel production by conserving water and reducing toxic effluents. In contrast, synthetic dyes provide vibrant colors but contribute to water contamination and pose challenges in wastewater treatment.
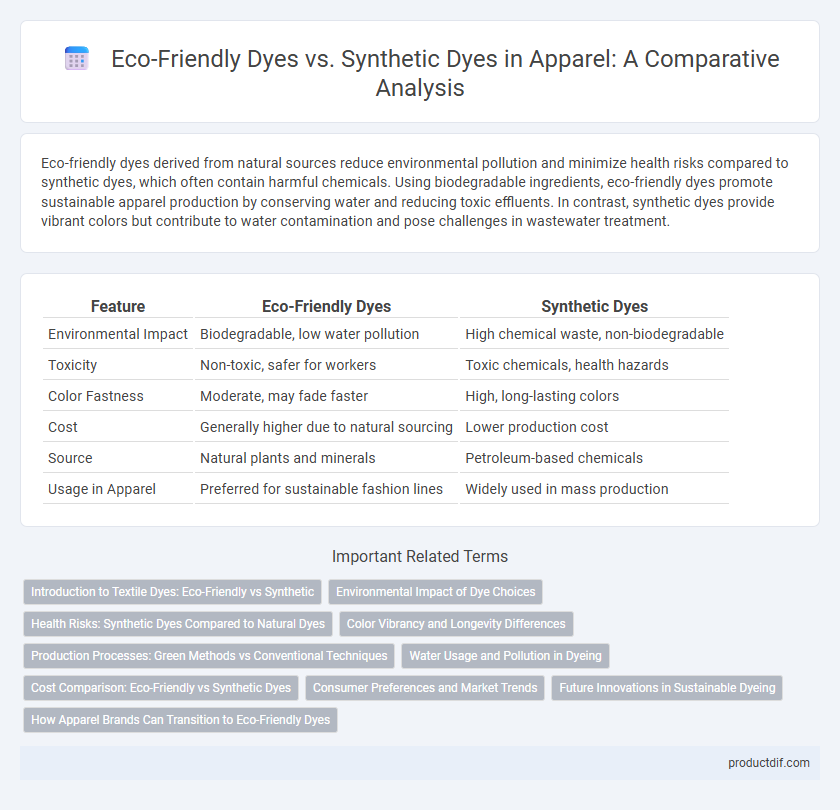
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Eco-Friendly Dyes | Synthetic Dyes |
|---|---|---|
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, low water pollution | High chemical waste, non-biodegradable |
| Toxicity | Non-toxic, safer for workers | Toxic chemicals, health hazards |
| Color Fastness | Moderate, may fade faster | High, long-lasting colors |
| Cost | Generally higher due to natural sourcing | Lower production cost |
| Source | Natural plants and minerals | Petroleum-based chemicals |
| Usage in Apparel | Preferred for sustainable fashion lines | Widely used in mass production |
Introduction to Textile Dyes: Eco-Friendly vs Synthetic
Textile dyes play a crucial role in apparel manufacturing, with eco-friendly dyes emerging as sustainable alternatives to conventional synthetic dyes. Eco-friendly dyes, derived from natural sources or biodegradable chemicals, reduce environmental impact by minimizing toxic runoff and chemical waste. Synthetic dyes, though widely used for their vibrant colors and durability, pose significant ecological challenges due to their reliance on petrochemicals and lengthy degradation processes.
Environmental Impact of Dye Choices
Eco-friendly dyes, derived from natural sources such as plants and minerals, significantly reduce water pollution and biodegrade without releasing toxic chemicals, making them a sustainable option for apparel production. Synthetic dyes, often made from petrochemicals, contribute to hazardous wastewater that contaminates rivers and harms aquatic ecosystems due to their non-biodegradable and toxic components. Choosing eco-friendly dyes lowers carbon emissions and minimizes the ecological footprint of textile manufacturing, promoting healthier ecosystems and supporting circular fashion initiatives.
Health Risks: Synthetic Dyes Compared to Natural Dyes
Synthetic dyes in apparel often contain harmful chemicals such as azo compounds, which pose significant health risks including skin allergies, respiratory issues, and potential carcinogenic effects. Natural dyes extracted from plants and minerals offer a safer alternative, minimizing toxic exposure for both consumers and workers involved in textile production. Choosing eco-friendly dyes reduces the risk of chemical-related health problems while supporting sustainable fashion practices.
Color Vibrancy and Longevity Differences
Eco-friendly dyes, derived from natural sources like plants and minerals, offer vibrant colors that tend to fade more quickly when exposed to sunlight and frequent washing, compared to synthetic dyes. Synthetic dyes, formulated with chemical compounds, provide intense color vibrancy and superior longevity, maintaining their brightness and resistance to fading over extended wear and multiple laundering cycles. The environmental benefits of eco-friendly dyes include biodegradability and reduced toxicity, but synthetic dyes are often favored in apparel manufacturing for their durability and consistent color retention.
Production Processes: Green Methods vs Conventional Techniques
Eco-friendly dyes are produced using renewable raw materials and non-toxic chemicals, minimizing water pollution and energy consumption through biodegradable inputs and low-impact methods. Synthetic dyes rely on petrochemical derivatives and intensive chemical treatments, often generating hazardous waste and requiring high-temperature processes. Green dyeing techniques emphasize closed-loop water systems and enzymatic reactions, contrasting with conventional techniques that discharge untreated effluents into ecosystems.
Water Usage and Pollution in Dyeing
Eco-friendly dyes significantly reduce water usage in apparel dyeing by utilizing natural ingredients and low-water techniques, whereas synthetic dyes demand extensive water for processing and rinsing. Water pollution from eco-friendly dyes is minimal due to biodegradable components that break down naturally, contrasting with synthetic dyes that often release toxic chemicals harmful to aquatic ecosystems. Choosing eco-friendly dyes supports sustainable water management and decreases environmental contamination in textile production.
Cost Comparison: Eco-Friendly vs Synthetic Dyes
Eco-friendly dyes generally incur higher upfront costs due to organic sourcing and eco-certification processes, but they reduce environmental compliance expenses and wastewater treatment fees over time. Synthetic dyes are often cheaper initially because of mass production and well-established supply chains, yet they can lead to increased long-term costs related to environmental fines and health hazards. Brands investing in eco-friendly dyes benefit from growing consumer demand for sustainable apparel, potentially offsetting the higher material costs with enhanced market positioning and brand loyalty.
Consumer Preferences and Market Trends
Consumer preferences reveal a growing demand for eco-friendly dyes in the apparel industry, driven by increased awareness of environmental impact and sustainability. Market trends indicate a surge in the adoption of natural and plant-based dyes, highlighting a shift towards cruelty-free and biodegradable solutions in textile manufacturing. Brands leveraging eco-friendly dyes often gain competitive advantage through enhanced brand loyalty and alignment with global environmental regulations.
Future Innovations in Sustainable Dyeing
Future innovations in sustainable dyeing in the apparel industry focus on bio-based dyes derived from agricultural waste and microorganisms, significantly reducing water usage and toxic effluents compared to synthetic dyes. Advanced nanotechnology enables precise dye application, enhancing colorfastness while minimizing environmental contamination. Emerging enzymatic processes further improve dye absorption and biodegradability, positioning eco-friendly dyes as a scalable alternative to conventional synthetic options.
How Apparel Brands Can Transition to Eco-Friendly Dyes
Apparel brands can transition to eco-friendly dyes by investing in sustainable dyeing technologies such as plant-based, low-water, and biodegradable formulations that reduce environmental impact compared to conventional synthetic dyes derived from petrochemicals. Partnering with suppliers specializing in natural dyes like indigo, turmeric, and madder root helps promote traceability and transparency in the supply chain while meeting consumer demand for green products. Implementing rigorous testing to ensure colorfastness and fabric compatibility preserves garment quality, enabling brands to maintain competitive pricing and profitability during the sustainable shift.
Eco-Friendly Dyes vs Synthetic Dyes Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com