Freemium software offers basic features for free while charging for premium capabilities, allowing users to test functionality before committing financially. Paid software requires an upfront purchase or subscription, providing full access to all features and often including dedicated support and regular updates. Choosing between freemium and paid models depends on user needs, budget, and desired level of service and functionality.
Table of Comparison
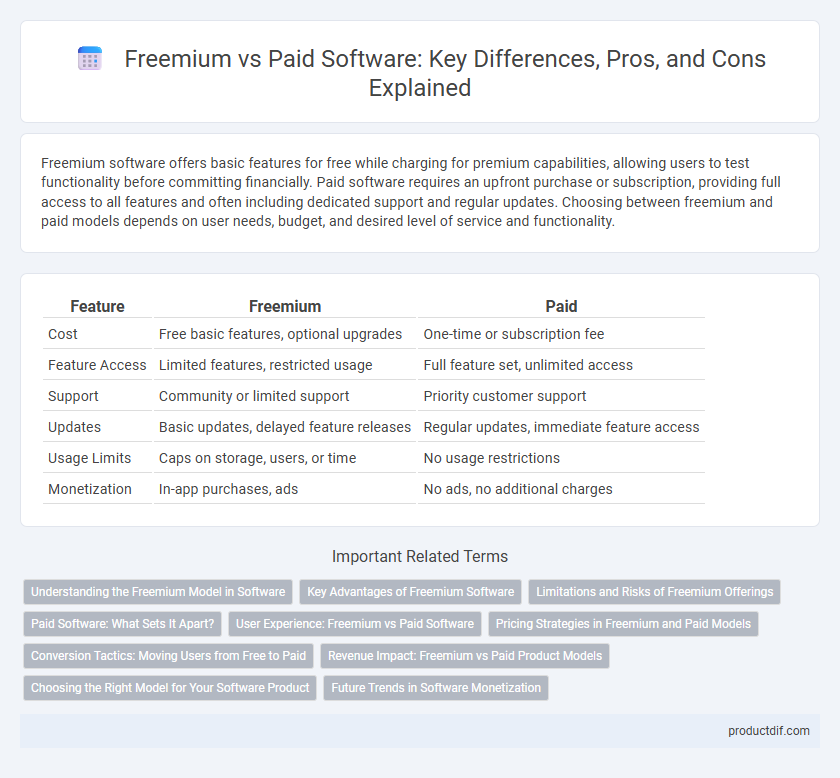
| Feature | Freemium | Paid |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Free basic features, optional upgrades | One-time or subscription fee |
| Feature Access | Limited features, restricted usage | Full feature set, unlimited access |
| Support | Community or limited support | Priority customer support |
| Updates | Basic updates, delayed feature releases | Regular updates, immediate feature access |
| Usage Limits | Caps on storage, users, or time | No usage restrictions |
| Monetization | In-app purchases, ads | No ads, no additional charges |
Understanding the Freemium Model in Software
The freemium model in software offers a basic version of an application for free while charging users for premium features, enhancing user acquisition and engagement. This approach enables companies to build a large user base quickly, gather valuable usage data, and convert free users into paying customers through feature upgrades or subscription plans. Successful freemium software balances valuable free functionality with compelling paid features to maximize revenue without deterring user adoption.
Key Advantages of Freemium Software
Freemium software offers key advantages such as broad user acquisition by providing free access to essential features, which drives higher adoption rates and market penetration. This model enables continuous user engagement and feedback, allowing developers to improve products rapidly while reducing marketing expenses. Additionally, freemium software creates upsell opportunities through premium feature upgrades, generating sustainable revenue streams without alienating the base user community.
Limitations and Risks of Freemium Offerings
Freemium software often restricts key features, storage capacity, and usage limits, forcing users to upgrade for full functionality. Relying on freemium models can expose businesses to risks such as inconsistent revenue streams and potential security vulnerabilities from minimal support. Limited customization and aggressive upselling may also impact user experience and loyalty compared to paid software solutions.
Paid Software: What Sets It Apart?
Paid software offers enhanced features, dedicated customer support, and regular updates that free or freemium versions often lack, delivering a more robust and reliable user experience. It typically includes advanced security measures and seamless integration capabilities essential for professional or enterprise use. Investing in paid software ensures access to premium functionalities, boosting productivity and long-term value beyond basic free offerings.
User Experience: Freemium vs Paid Software
Freemium software offers users a risk-free entry with basic features, allowing them to explore the interface and functionality before committing financially, which enhances initial user experience and accessibility. Paid software typically provides a more polished, ad-free environment with full access to premium features, resulting in a smoother and more robust user experience for professional or intensive use. User satisfaction in freemium models often depends on the balance between free limitations and upgrade incentives, while paid models prioritize comprehensive support and uninterrupted usage.
Pricing Strategies in Freemium and Paid Models
Freemium pricing strategies leverage a free basic version to attract a wide user base while monetizing through premium features, subscriptions, or in-app purchases, optimizing customer acquisition costs. Paid models rely on upfront payments or tiered subscriptions, emphasizing perceived value and feature differentiation to justify cost and maximize revenue per user. Both strategies require careful analysis of user behavior and lifetime value to balance conversion rates and profitability effectively.
Conversion Tactics: Moving Users from Free to Paid
Effective conversion tactics for transitioning users from freemium to paid software include offering limited-time premium feature trials that showcase enhanced functionality unavailable in the free version. Leveraging user behavior analytics enables personalized upsell prompts targeting users most likely to benefit from advanced capabilities. Strategic usage caps and value-driven messaging emphasize the ROI of paid plans, increasing subscription rates and customer lifetime value.
Revenue Impact: Freemium vs Paid Product Models
Freemium models drive extensive user acquisition by offering free access with limited features, converting a small percentage into paying customers, which generates steady but often slower revenue growth. Paid product models deliver immediate revenue from all users, typically resulting in higher upfront income but with a potentially smaller user base and slower market penetration. Analyzing customer lifetime value (CLTV) and conversion rates is critical to optimizing revenue impact between freemium and paid software business models.
Choosing the Right Model for Your Software Product
Selecting the appropriate revenue model for your software product hinges on target audience and market positioning. Freemium models attract a wider user base by offering essential features for free, driving engagement and potential upsells to premium tiers. Paid models generate immediate revenue and attract committed users willing to invest upfront, often suited for specialized or enterprise software with clear value propositions.
Future Trends in Software Monetization
Freemium models increasingly leverage AI-driven personalization to enhance user engagement and convert free users into paying customers by offering tailored premium features. The rise of subscription-based paid software emphasizes continuous value delivery through frequent updates and cloud integration, fostering customer retention and predictable revenue streams. Emerging trends include hybrid monetization strategies combining freemium access with microtransactions and blockchain-enabled licensing for transparent, secure software usage tracking.
Freemium vs Paid Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com