Bug Bash involves collective testing where multiple team members identify and report software bugs in a concentrated session, enhancing product quality through diverse feedback. Dogfooding refers to internal teams using the software in real-world scenarios, promoting firsthand experience that uncovers usability issues and drives improvements. Both practices are essential for refining software but differ in approach: Bug Bash emphasizes collaborative bug detection, while Dogfooding focuses on continuous internal use to validate the product.
Table of Comparison
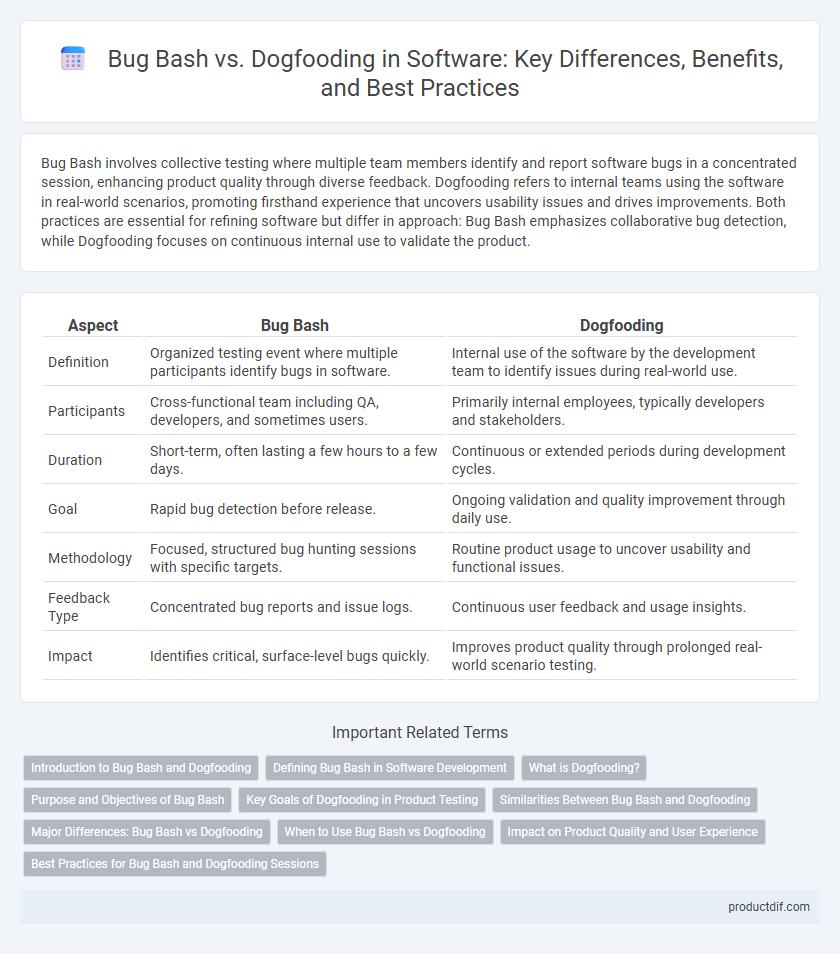
| Aspect | Bug Bash | Dogfooding |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Organized testing event where multiple participants identify bugs in software. | Internal use of the software by the development team to identify issues during real-world use. |
| Participants | Cross-functional team including QA, developers, and sometimes users. | Primarily internal employees, typically developers and stakeholders. |
| Duration | Short-term, often lasting a few hours to a few days. | Continuous or extended periods during development cycles. |
| Goal | Rapid bug detection before release. | Ongoing validation and quality improvement through daily use. |
| Methodology | Focused, structured bug hunting sessions with specific targets. | Routine product usage to uncover usability and functional issues. |
| Feedback Type | Concentrated bug reports and issue logs. | Continuous user feedback and usage insights. |
| Impact | Identifies critical, surface-level bugs quickly. | Improves product quality through prolonged real-world scenario testing. |
Introduction to Bug Bash and Dogfooding
Bug Bash is a collaborative testing event where teams gather to identify and report software bugs intensively within a short timeframe, enhancing defect detection before release. Dogfooding refers to the internal use of a company's own software by employees to test and improve product quality through real-world application. Both practices play crucial roles in early bug identification and continuous improvement in software development cycles.
Defining Bug Bash in Software Development
Bug Bash in software development is a collaborative testing event where multiple team members systematically identify and document defects within an application. This focused session aims to uncover bugs quickly by leveraging diverse perspectives from developers, testers, and stakeholders. The process accelerates quality assurance and enhances product stability before release.
What is Dogfooding?
Dogfooding refers to the practice where software developers and companies use their own products internally to test and identify issues before releasing them to the public. This approach ensures real-world feedback, accelerates bug detection, and improves overall software quality. By adopting dogfooding, teams gain valuable insights into user experience and functionality in everyday use cases.
Purpose and Objectives of Bug Bash
Bug Bash is an organized event where multiple team members, often from diverse roles, collaboratively identify and report software bugs within a fixed timeframe to improve product quality. Its primary objective is to uncover defects that may be missed during regular testing by leveraging varied perspectives and usage patterns. Unlike dogfooding, which involves internal continuous product usage for feedback, Bug Bash targets intensive, time-boxed bug detection to accelerate issue discovery before release.
Key Goals of Dogfooding in Product Testing
Dogfooding in product testing aims to identify real-world usability issues by having internal teams use the software as end-users do, ensuring firsthand feedback on functionality and performance. It enhances product quality through early detection of bugs and fosters a user-centric development environment by integrating user experience insights into iterative improvements. This practice accelerates development cycles by aligning product features with actual user needs, reducing post-release defects and support costs.
Similarities Between Bug Bash and Dogfooding
Bug Bash and Dogfooding both serve crucial roles in software quality assurance by involving internal teams to identify and report defects before public release. Each method leverages user-like interaction within the development environment, fostering early detection of usability issues, functional bugs, and performance bottlenecks. These approaches improve software reliability by combining collaborative testing with real-world usage scenarios, enhancing product readiness for diverse end-users.
Major Differences: Bug Bash vs Dogfooding
Bug Bash involves a coordinated event where multiple testers actively identify and report software bugs within a set timeframe, emphasizing focused defect discovery. Dogfooding refers to internally using the software in real-world scenarios by the development team or company employees to uncover usability issues and ensure product quality. The major difference lies in Bug Bash being a structured, time-bound testing activity, while Dogfooding is an ongoing practice integrated into daily workflows.
When to Use Bug Bash vs Dogfooding
Bug Bash sessions are ideal during the late stages of development to identify and fix critical issues before release, leveraging a diverse group of testers for extensive feedback. Dogfooding is best employed continuously throughout the development cycle to enable internal teams to experience the software firsthand, uncover usability problems, and validate features in a real-world environment. Choosing Bug Bash or Dogfooding depends on project timelines and testing goals, with Bug Bash targeting concentrated defect discovery and Dogfooding fostering ongoing quality improvement.
Impact on Product Quality and User Experience
Bug Bash sessions centralize team efforts to identify critical software defects, significantly improving product quality by ensuring thorough testing before release. Dogfooding immerses employees in real-world product use, enhancing user experience insights and highlighting usability issues early. Combining both approaches accelerates issue resolution, resulting in a more reliable and user-centric software product.
Best Practices for Bug Bash and Dogfooding Sessions
Bug Bash sessions benefit from structured planning, clear bug tracking systems, and diverse participant groups to maximize defect identification across software environments. Dogfooding practices excel when internal users consistently apply the software in real-world scenarios, providing authentic feedback for iterative improvements. Regularly scheduled sessions combined with comprehensive documentation enhance both methods, fostering rapid issue detection and resolution throughout the development cycle.
Bug Bash vs Dogfooding Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com