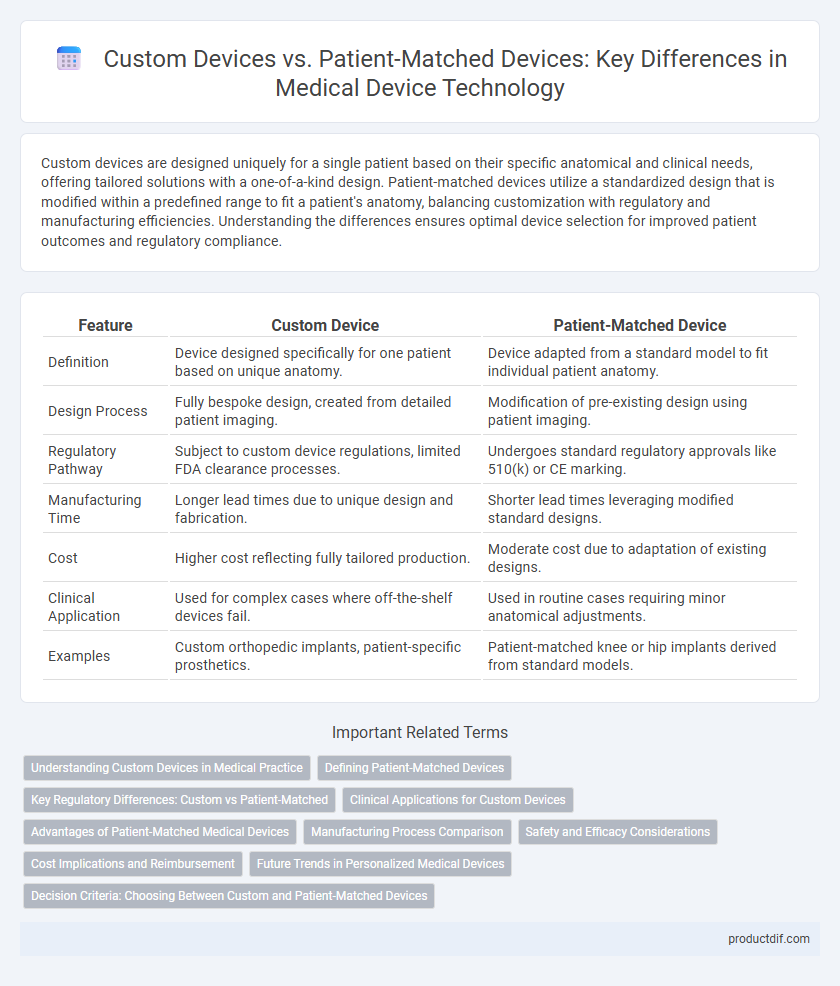
Custom devices are designed uniquely for a single patient based on their specific anatomical and clinical needs, offering tailored solutions with a one-of-a-kind design. Patient-matched devices utilize a standardized design that is modified within a predefined range to fit a patient's anatomy, balancing customization with regulatory and manufacturing efficiencies. Understanding the differences ensures optimal device selection for improved patient outcomes and regulatory compliance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Custom Device | Patient-Matched Device |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Device designed specifically for one patient based on unique anatomy. | Device adapted from a standard model to fit individual patient anatomy. |
| Design Process | Fully bespoke design, created from detailed patient imaging. | Modification of pre-existing design using patient imaging. |
| Regulatory Pathway | Subject to custom device regulations, limited FDA clearance processes. | Undergoes standard regulatory approvals like 510(k) or CE marking. |
| Manufacturing Time | Longer lead times due to unique design and fabrication. | Shorter lead times leveraging modified standard designs. |
| Cost | Higher cost reflecting fully tailored production. | Moderate cost due to adaptation of existing designs. |
| Clinical Application | Used for complex cases where off-the-shelf devices fail. | Used in routine cases requiring minor anatomical adjustments. |
| Examples | Custom orthopedic implants, patient-specific prosthetics. | Patient-matched knee or hip implants derived from standard models. |
Understanding Custom Devices in Medical Practice
Custom devices in medical practice are individually designed and manufactured to meet the unique anatomical and clinical needs of a single patient, often requiring regulatory exemptions due to their tailored nature. Unlike patient-matched devices, which are based on standardized templates adjusted for patient variability, custom devices involve a higher degree of personalization with no broadly applicable models. Understanding the specific regulatory pathways and clinical applications of custom devices is crucial for healthcare providers to ensure compliance and optimize patient outcomes.
Defining Patient-Matched Devices
Patient-matched devices are medical implants or instruments specifically designed using patient imaging data to closely fit an individual's unique anatomy, enabling tailored treatment with improved surgical outcomes. These devices differ from custom devices by adhering to standardized manufacturing processes and regulatory pathways while offering personalized design variations within predetermined parameters. Defined by regulatory bodies like the FDA, patient-matched devices balance customization and reproducibility, ensuring safety and efficacy in patient-specific applications.
Key Regulatory Differences: Custom vs Patient-Matched
Custom medical devices are designed and manufactured for individual patients under specific regulatory exemptions, often exempt from premarket approval but requiring documentation of uniqueness and limited production. Patient-matched devices are produced based on pre-approved designs and software workflows, requiring conformity to regulatory standards such as FDA's 510(k) clearance or CE marking, ensuring consistent quality and safety. Unlike custom devices, patient-matched devices undergo more rigorous regulatory scrutiny, including validation of design processes and post-market surveillance obligations.
Clinical Applications for Custom Devices
Custom medical devices are specifically designed and manufactured to fit the unique anatomical requirements of an individual patient, often used in complex surgical procedures where standard devices fail to provide adequate solutions. These devices demonstrate significant clinical efficacy in orthopedic implants, craniofacial reconstruction, and dental prosthetics, improving patient outcomes through personalized fit and function. Their tailored design reduces intraoperative adjustments and postoperative complications, enhancing overall recovery and satisfaction.
Advantages of Patient-Matched Medical Devices
Patient-matched medical devices offer enhanced precision by conforming to the unique anatomical features of each individual, thereby improving surgical outcomes and reducing complications. These devices facilitate better integration with patient tissue, leading to faster recovery times compared to custom devices that may not account for subtle variances in patient anatomy. The streamlined regulatory pathway for patient-matched devices also accelerates availability, ensuring timely access to personalized therapeutic solutions.
Manufacturing Process Comparison
Custom devices are individually crafted through manual or semi-automated processes tailored to a single patient's unique anatomy, often requiring extensive design iterations and specialized manufacturing techniques such as additive manufacturing or 3D printing. Patient-matched devices leverage standardized digital workflows that utilize patient imaging data to efficiently produce multiple devices with customizable parameters within predefined design frameworks, enabling scalable and reproducible manufacturing. The manufacturing process of custom devices typically involves longer lead times and higher costs due to bespoke fabrication, whereas patient-matched devices benefit from streamlined processes and improved consistency through automation and integrated data management systems.
Safety and Efficacy Considerations
Custom devices are individually designed for a specific patient without standardized manufacturing processes, which can pose challenges for consistent safety and efficacy validation. Patient-matched devices are developed using standardized protocols and digital imaging to tailor fit while ensuring regulatory compliance, improving predictability of clinical outcomes. Regulatory agencies emphasize rigorous testing and documentation to ensure both device types meet safety standards and demonstrate reliable therapeutic effectiveness.
Cost Implications and Reimbursement
Custom medical devices often involve higher manufacturing costs due to bespoke design and individualized production processes, leading to limited reimbursement options from insurers. Patient-matched devices, manufactured using standardized protocols with minor modifications to fit individual anatomy, typically have lower production costs and more predictable reimbursement pathways. Understanding the cost implications and reimbursement criteria is crucial for healthcare providers when selecting between these device categories.
Future Trends in Personalized Medical Devices
Future trends in personalized medical devices emphasize the integration of advanced manufacturing technologies such as 3D printing and AI-driven design algorithms to enhance both custom devices and patient-matched devices. Custom devices are tailored specifically to an individual's unique anatomy and physiological needs, offering maximum personalization without standardized constraints. Patient-matched devices utilize predefined design templates adjusted to fit patient-specific data, enabling scalable production while maintaining personalized treatment efficacy and improved clinical outcomes.
Decision Criteria: Choosing Between Custom and Patient-Matched Devices
Decision criteria for selecting between custom and patient-matched medical devices hinge on the complexity of the anatomical structure and clinical needs. Custom devices provide unique fabrication tailored entirely to an individual's specific anatomy, ideal for rare or complex cases requiring precise conformity. Patient-matched devices, created from existing design templates with adjustments based on patient imaging, offer faster production and cost-efficiency for more common anatomical variations.
Custom Device vs Patient-Matched Device Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com