5G technology revolutionizes wireless communication by offering significantly faster data speeds, lower latency, and enhanced network capacity compared to 4G LTE. This advancement enables seamless streaming, real-time gaming, and supports massive IoT connectivity essential for smart cities and autonomous vehicles. The enhanced bandwidth and efficiency of 5G networks pave the way for innovative applications beyond the capabilities of 4G LTE.
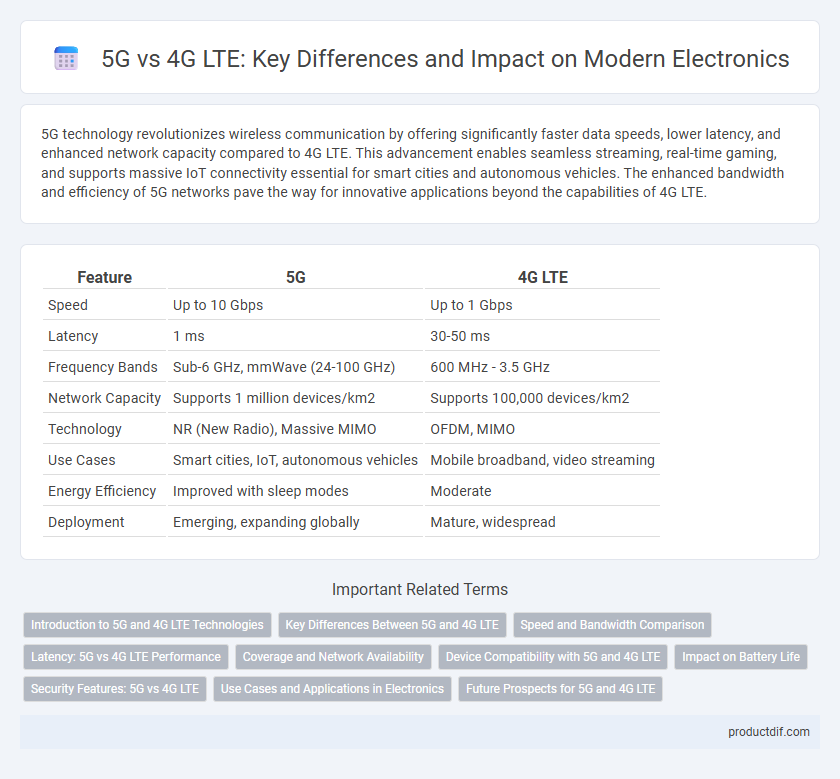
Table of Comparison
| Feature | 5G | 4G LTE |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Up to 10 Gbps | Up to 1 Gbps |
| Latency | 1 ms | 30-50 ms |
| Frequency Bands | Sub-6 GHz, mmWave (24-100 GHz) | 600 MHz - 3.5 GHz |
| Network Capacity | Supports 1 million devices/km2 | Supports 100,000 devices/km2 |
| Technology | NR (New Radio), Massive MIMO | OFDM, MIMO |
| Use Cases | Smart cities, IoT, autonomous vehicles | Mobile broadband, video streaming |
| Energy Efficiency | Improved with sleep modes | Moderate |
| Deployment | Emerging, expanding globally | Mature, widespread |
Introduction to 5G and 4G LTE Technologies
5G technology offers significantly faster data speeds, lower latency, and enhanced connectivity compared to 4G LTE, enabling advanced applications such as IoT, autonomous vehicles, and immersive media experiences. 4G LTE remains widely used for mobile broadband, supporting high-speed internet access with peak download speeds typically up to 1 Gbps, while 5G networks aim for multi-gigabit per second speeds and ultra-reliable low latency communications. The transition from 4G LTE to 5G involves deploying new network infrastructure like millimeter-wave antennas and massive MIMO technology to achieve broader bandwidth and improved spectral efficiency.
Key Differences Between 5G and 4G LTE
5G technology offers significantly higher data speeds, with peak rates up to 20 Gbps compared to 4G LTE's maximum of 1 Gbps, enabling enhanced mobile broadband experiences. Latency in 5G networks is drastically reduced to as low as 1 millisecond, supporting real-time applications such as autonomous vehicles and remote surgery, whereas 4G LTE latency typically ranges from 30 to 50 milliseconds. The network architecture of 5G incorporates advanced features like network slicing and Massive MIMO, improving capacity and connectivity density far beyond the capabilities of 4G LTE.
Speed and Bandwidth Comparison
5G technology delivers peak download speeds of up to 10 Gbps, which is approximately 100 times faster than the maximum 4G LTE speeds of 100 Mbps. The bandwidth capacity in 5G networks significantly surpasses 4G, supporting enhanced data transfer and lower latency for high-demand applications. This improved speed and bandwidth enable seamless streaming, faster downloads, and more reliable connections for IoT devices and smart cities.
Latency: 5G vs 4G LTE Performance
5G technology significantly reduces latency compared to 4G LTE, achieving response times as low as 1 millisecond versus 30-50 milliseconds in 4G networks. This ultra-low latency enables real-time applications such as augmented reality, autonomous vehicles, and remote surgeries. Enhanced network slicing in 5G also optimizes latency for specific use cases, improving overall performance and user experience.
Coverage and Network Availability
5G networks offer significantly enhanced coverage and network availability compared to 4G LTE, utilizing advanced small cell technology and millimeter wave frequencies to deliver faster data speeds and lower latency. While 4G LTE provides widespread coverage with reliable connectivity in urban and rural areas, 5G's dense network infrastructure aims to fill gaps in urban centers and high-demand zones, improving overall user experience. Network availability for 5G continues to expand rapidly worldwide, leveraging existing 4G infrastructure to ensure seamless transitions and broader access as deployment progresses.
Device Compatibility with 5G and 4G LTE
5G devices support a broader range of frequency bands, including sub-6 GHz and millimeter wave (mmWave) spectrums, enabling faster data transfer and lower latency compared to 4G LTE. Most 5G smartphones are backward compatible with 4G LTE networks, ensuring seamless connectivity in areas without 5G coverage. Network operators continue to maintain extensive 4G LTE infrastructure to guarantee uninterrupted service during the transition to widespread 5G adoption.
Impact on Battery Life
5G networks offer significantly faster data transfer speeds compared to 4G LTE, but this high performance often results in increased power consumption, which can reduce battery life on mobile devices. Despite 5G's advanced energy-saving technologies like dynamic spectrum sharing and efficient beamforming, real-world usage typically demands more frequent charging than 4G LTE. Optimizing device hardware and software for 5G connectivity is crucial to balancing enhanced performance with manageable battery lifespan.
Security Features: 5G vs 4G LTE
5G security features significantly outperform 4G LTE with enhanced encryption algorithms and improved authentication protocols such as 5G-AKA, which mitigates vulnerabilities found in 4G's EPS-AKA. Network slicing in 5G ensures isolated, secure virtual networks tailored for specific applications, reducing attack surfaces compared to the more uniform 4G LTE architecture. Moreover, 5G incorporates advanced subscriber privacy protections and stronger integrity checks, addressing threats posed by location tracking and signal interception common in 4G LTE environments.
Use Cases and Applications in Electronics
5G technology enables ultra-low latency and massive device connectivity, revolutionizing electronics applications such as autonomous vehicles, smart cities, and IoT networks, which require real-time data processing and seamless communication. While 4G LTE supports high-speed mobile internet and video streaming, 5G's enhanced bandwidth and reliability facilitate advanced use cases including remote surgery, augmented reality, and industrial automation. Electronics manufacturers leverage 5G to integrate AI and edge computing in devices, driving innovation in wearable technology and smart home systems.
Future Prospects for 5G and 4G LTE
5G technology offers significantly higher data speeds, ultra-low latency, and massive connectivity potential compared to 4G LTE, enabling advancements in IoT, autonomous vehicles, and smart cities. While 4G LTE remains crucial for global coverage and legacy support, 5G's evolving infrastructure promises to transform industries through enhanced network slicing, edge computing, and AI integration. The future of telecommunications heavily leans on 5G adoption, with continuous improvements expected to surpass 4G LTE capabilities and drive next-generation digital innovations.
5G vs 4G LTE Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com