Dry construction offers faster installation, reduced moisture issues, and cleaner work environments compared to wet construction, which relies on materials like concrete and plaster that require curing times and are prone to humidity problems. Dry construction utilizes prefabricated panels, metal studs, and drywall, providing flexibility and ease of modification for interior spaces. Wet construction demands skilled labor and extended drying periods, often leading to longer project timelines and potential complications with mold and water damage.
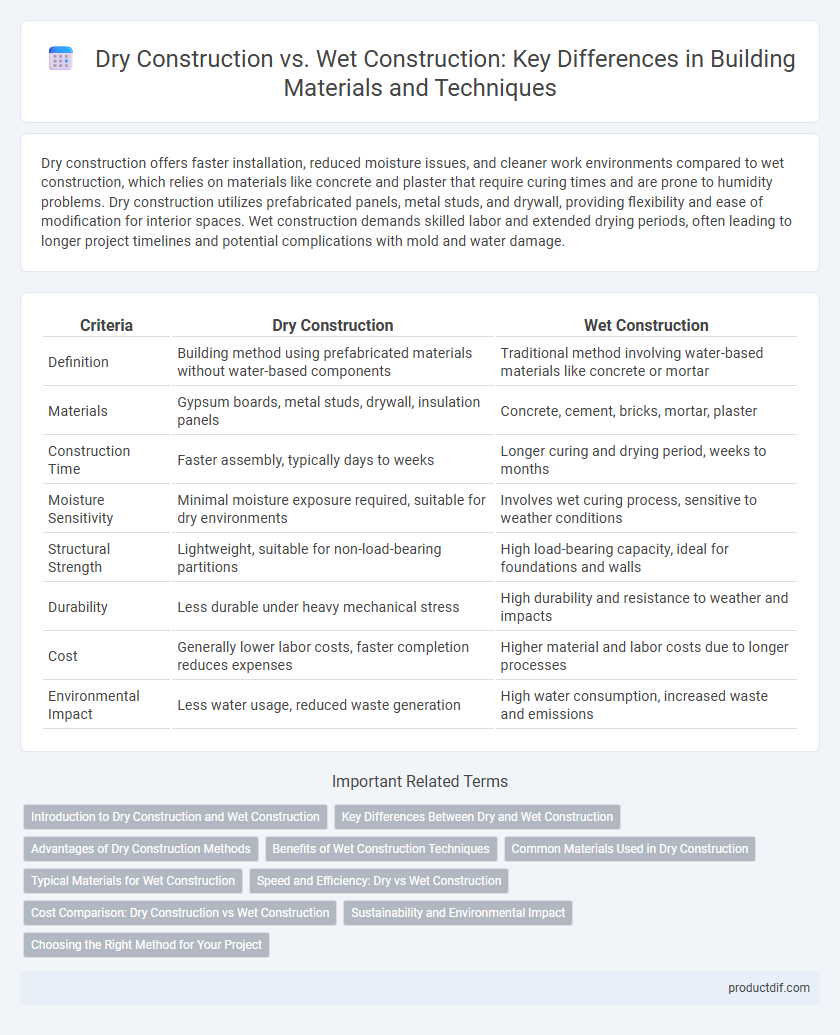
Table of Comparison
| Criteria | Dry Construction | Wet Construction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Building method using prefabricated materials without water-based components | Traditional method involving water-based materials like concrete or mortar |
| Materials | Gypsum boards, metal studs, drywall, insulation panels | Concrete, cement, bricks, mortar, plaster |
| Construction Time | Faster assembly, typically days to weeks | Longer curing and drying period, weeks to months |
| Moisture Sensitivity | Minimal moisture exposure required, suitable for dry environments | Involves wet curing process, sensitive to weather conditions |
| Structural Strength | Lightweight, suitable for non-load-bearing partitions | High load-bearing capacity, ideal for foundations and walls |
| Durability | Less durable under heavy mechanical stress | High durability and resistance to weather and impacts |
| Cost | Generally lower labor costs, faster completion reduces expenses | Higher material and labor costs due to longer processes |
| Environmental Impact | Less water usage, reduced waste generation | High water consumption, increased waste and emissions |
Introduction to Dry Construction and Wet Construction
Dry construction involves assembling prefabricated components such as drywall panels, metal studs, and insulation without using water-based materials, enabling faster installation and reduced curing times. Wet construction relies on materials like concrete, mortar, and plaster, which require drying and setting periods, offering robust structural integrity and durability. Choosing between dry and wet construction depends on project timelines, environmental conditions, and long-term performance requirements of the building.
Key Differences Between Dry and Wet Construction
Dry construction methods utilize prefabricated components like drywall and metal studs, enabling faster installation and reduced curing times compared to traditional wet construction techniques that rely on concrete, mortar, or plaster. Wet construction involves the application of liquid materials that harden on-site, providing enhanced durability and sound insulation but requiring longer drying periods. Key differences include material handling, installation speed, environmental impact, and adaptability to modifications.
Advantages of Dry Construction Methods
Dry construction methods offer significant advantages including faster installation times and reduced labor costs due to the use of prefabricated panels and lightweight materials. These techniques minimize moisture-related issues, enhancing structural durability and indoor air quality by preventing mold growth. Dry construction also allows for greater flexibility in design changes and easier dismantling or remodeling compared to traditional wet construction methods.
Benefits of Wet Construction Techniques
Wet construction techniques offer enhanced structural durability due to the integration of materials like concrete, mortar, and plaster, which cure to form strong, long-lasting bonds. This method provides superior sound insulation and fire resistance, essential for building safety and comfort. Moreover, wet construction allows for greater flexibility in shaping complex architectural designs and integrating reinforcement elements.
Common Materials Used in Dry Construction
Dry construction primarily utilizes materials such as gypsum board, metal or wooden studs, and insulation panels, which facilitate faster assembly without the need for water-based mixtures. These materials are lightweight, prefabricated, and promote efficient soundproofing and thermal insulation in interior walls and ceilings. Common components include drywall sheets, metal framing profiles, and mineral wool or foam boards, making dry construction ideal for renovations and modular building projects.
Typical Materials for Wet Construction
Typical materials for wet construction include concrete, mortar, cement, plaster, and bricks, which require water for mixing and curing processes. These materials offer strong structural integrity and durability, making them ideal for foundations, walls, and load-bearing elements. The curing time and moisture content significantly influence the strength and long-term performance of wet construction assemblies.
Speed and Efficiency: Dry vs Wet Construction
Dry construction methods significantly enhance speed and efficiency by eliminating drying times associated with traditional wet construction, enabling faster project completion. Prefabricated panels and lightweight materials in dry construction reduce labor costs and minimize site disruption, optimizing resource use. Wet construction requires curing periods for materials like concrete and mortar, prolonging timelines and increasing the risk of weather-related delays.
Cost Comparison: Dry Construction vs Wet Construction
Dry construction typically incurs lower labor and material costs due to faster installation times and reduced need for drying periods, making it economically advantageous for projects with tight schedules. Wet construction, while often more durable, involves higher expenses related to materials like concrete and plaster, as well as extended curing times that increase labor costs. Overall, dry construction offers cost efficiency through decreased labor hours and minimal material wastage compared to the more resource-intensive wet construction methods.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Dry construction techniques, such as modular panels and steel framing, minimize waste and reduce energy consumption during installation, enhancing overall sustainability. Wet construction methods often involve concrete and mortar, which have higher carbon footprints due to cement production and longer curing times. Choosing dry construction supports eco-friendly building practices by lowering material waste, reducing water usage, and enabling easier recycling or reuse of components.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Project
Dry construction methods use prefabricated components like drywall, metal studs, and panels for faster installation and reduced drying time, making them ideal for interior renovations and projects with tight deadlines. Wet construction relies on materials such as concrete, mortar, and plaster, providing superior durability, sound insulation, and thermal mass suitable for structural elements and exterior walls. Selecting the right method depends on factors like project timeline, budget, structural requirements, and desired finish quality.
Dry construction vs Wet construction Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com