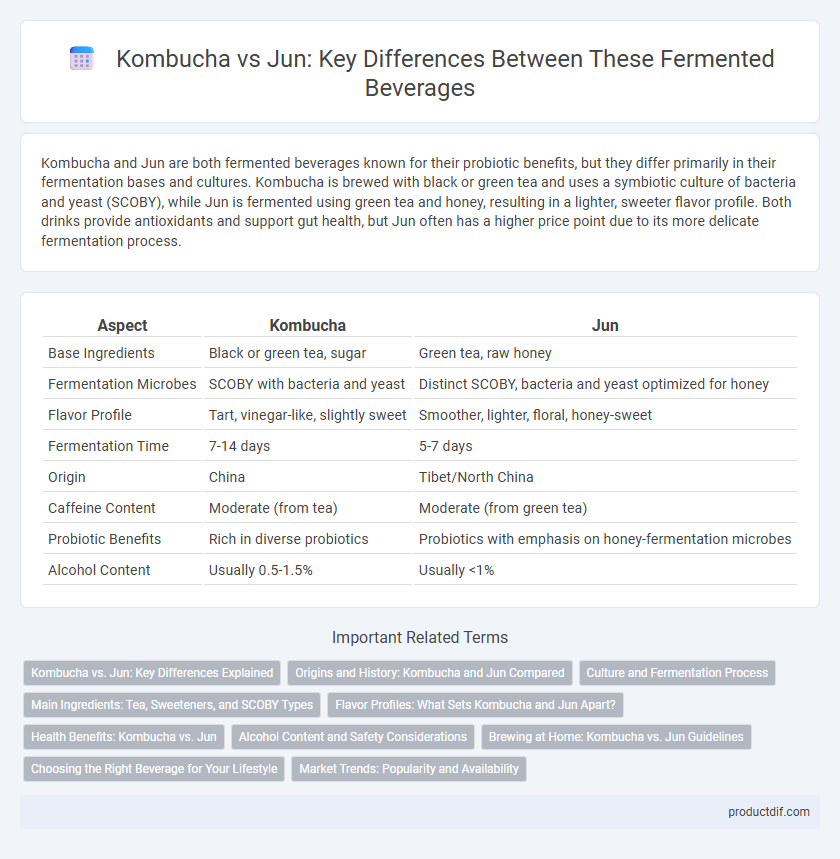
Kombucha and Jun are both fermented beverages known for their probiotic benefits, but they differ primarily in their fermentation bases and cultures. Kombucha is brewed with black or green tea and uses a symbiotic culture of bacteria and yeast (SCOBY), while Jun is fermented using green tea and honey, resulting in a lighter, sweeter flavor profile. Both drinks provide antioxidants and support gut health, but Jun often has a higher price point due to its more delicate fermentation process.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Kombucha | Jun |
|---|---|---|
| Base Ingredients | Black or green tea, sugar | Green tea, raw honey |
| Fermentation Microbes | SCOBY with bacteria and yeast | Distinct SCOBY, bacteria and yeast optimized for honey |
| Flavor Profile | Tart, vinegar-like, slightly sweet | Smoother, lighter, floral, honey-sweet |
| Fermentation Time | 7-14 days | 5-7 days |
| Origin | China | Tibet/North China |
| Caffeine Content | Moderate (from tea) | Moderate (from green tea) |
| Probiotic Benefits | Rich in diverse probiotics | Probiotics with emphasis on honey-fermentation microbes |
| Alcohol Content | Usually 0.5-1.5% | Usually <1% |
Kombucha vs. Jun: Key Differences Explained
Kombucha and Jun are both fermented teas, but Kombucha is typically brewed with black or green tea and sugar, while Jun uses green tea and raw honey, resulting in a lighter, more delicate flavor. The fermentation process for Jun is faster and occurs at cooler temperatures, which preserves the probiotics and enzymes that support gut health. Kombucha tends to have a more robust, tangy taste and higher acidity, making it a popular choice for detoxification and digestive benefits.
Origins and History: Kombucha and Jun Compared
Kombucha originated in Northeast China around 220 B.C. and spread to Russia and Eastern Europe, known for its fermented tea using black or green tea and a symbiotic culture of bacteria and yeast (SCOBY). Jun, often called the "champagne of kombucha," is believed to have Tibetan or Korean origins and is brewed with green tea and honey, resulting in a lighter, sweeter flavor profile. Both drinks share a fermentation process but differ in cultural background, ingredient base, and historical development, influencing their taste, probiotics, and health benefits.
Culture and Fermentation Process
Kombucha and Jun both utilize symbiotic cultures of bacteria and yeast (SCOBY) for fermentation, but Jun is fermented using green tea and raw honey, while Kombucha typically uses black or green tea and cane sugar. The fermentation process of Jun tends to be faster, often completed within 5-7 days, producing a lighter, more effervescent beverage with a delicate, floral flavor profile. The unique microbial culture in Jun promotes a distinct metabolic activity that results in lower acidity and a smoother taste compared to the tangier, more robust fermentation of Kombucha.
Main Ingredients: Tea, Sweeteners, and SCOBY Types
Kombucha is traditionally brewed using black or green tea sweetened with cane sugar, while Jun uses green tea paired with raw honey as its sweetening agent. The SCOBY (Symbiotic Culture of Bacteria and Yeast) in kombucha is composed of yeast and acetic acid bacteria adapted to fermenting cane sugar, whereas Jun's SCOBY is adapted to fermenting honey, resulting in distinct microbial compositions. These differences in tea base, sweetener, and SCOBY types influence the flavor profiles and fermentation dynamics of each beverage.
Flavor Profiles: What Sets Kombucha and Jun Apart?
Kombucha typically features a bold, tangy flavor with a pronounced vinegar-like tartness derived from fermenting sweetened black or green tea, whereas Jun has a subtler, floral, and mildly sweet taste due to its fermentation with raw honey and green tea. The presence of different SCOBY cultures in both beverages contributes to unique flavor compounds, with Jun often described as smoother and less acidic. These distinct fermentation processes result in complementary profiles, making Kombucha sharper and more robust, while Jun offers a delicate, effervescent alternative.
Health Benefits: Kombucha vs. Jun
Kombucha and Jun are both fermented teas known for their probiotic benefits, supporting gut health and boosting the immune system. While Kombucha is brewed with black or green tea and cane sugar, Jun uses green tea and raw honey, resulting in a lighter, floral flavor and potentially higher antioxidant content. Both beverages contain enzymes, B vitamins, and organic acids, but Jun's raw honey fermentation may offer enhanced antibacterial properties and reduced sugar levels compared to Kombucha.
Alcohol Content and Safety Considerations
Kombucha typically contains 0.5% to 1.5% alcohol due to fermentation, while Jun often has slightly lower alcohol levels, around 0.2% to 0.5%. Both beverages undergo natural fermentation with different tea bases--black or green tea for kombucha and green tea with honey for jun--affecting their alcohol content and flavor profile. Safety considerations include monitoring fermentation time and storage conditions to prevent excessive alcohol production and contamination by harmful bacteria or mold.
Brewing at Home: Kombucha vs. Jun Guidelines
Brewing kombucha at home requires fermenting sweetened black or green tea with SCOBY (symbiotic culture of bacteria and yeast) for about 7-14 days, while Jun uses raw honey and green tea, fermenting faster typically within 5-7 days due to its unique culture. Both beverages need strict temperature control around 70-80degF to maintain microbial activity and develop balanced acidity and carbonation. Proper sanitation and monitoring of pH levels between 2.5 and 3.5 ensure safe fermentation, with Jun often considered more delicate and sensitive to brewing conditions compared to kombucha.
Choosing the Right Beverage for Your Lifestyle
Kombucha, fermented with black or green tea and sugar, offers a tangy flavor and probiotics ideal for those seeking digestive health benefits. Jun, brewed with green tea and raw honey, provides a gentler, slightly sweeter taste favored by individuals avoiding refined sugars and seeking a milder fermented drink. Selecting between Kombucha and Jun depends on personal dietary goals, sugar tolerance, and flavor preference to best complement your lifestyle.
Market Trends: Popularity and Availability
Kombucha dominates the global fermented tea market with a CAGR of over 20%, driven by widespread availability in supermarkets and cafes across North America and Europe. Jun, often dubbed the "champagne of kombucha," is gaining niche popularity in health-conscious markets, especially in Asia and urban U.S. areas, but remains less accessible due to limited artisanal production. Market trends indicate a growing demand for low-sugar, probiotic beverages, positioning both kombucha and jun as key players in the functional drink segment.
Kombucha vs Jun Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com