No-sugar beverages contain absolutely no added sugars, making them ideal for those seeking to eliminate sugar from their diet entirely. Sugar-free beverages may include sugar substitutes like artificial sweeteners or natural alternatives to mimic sweetness without the calories. Choosing between no-sugar and sugar-free options depends on personal health goals and taste preferences.
Table of Comparison
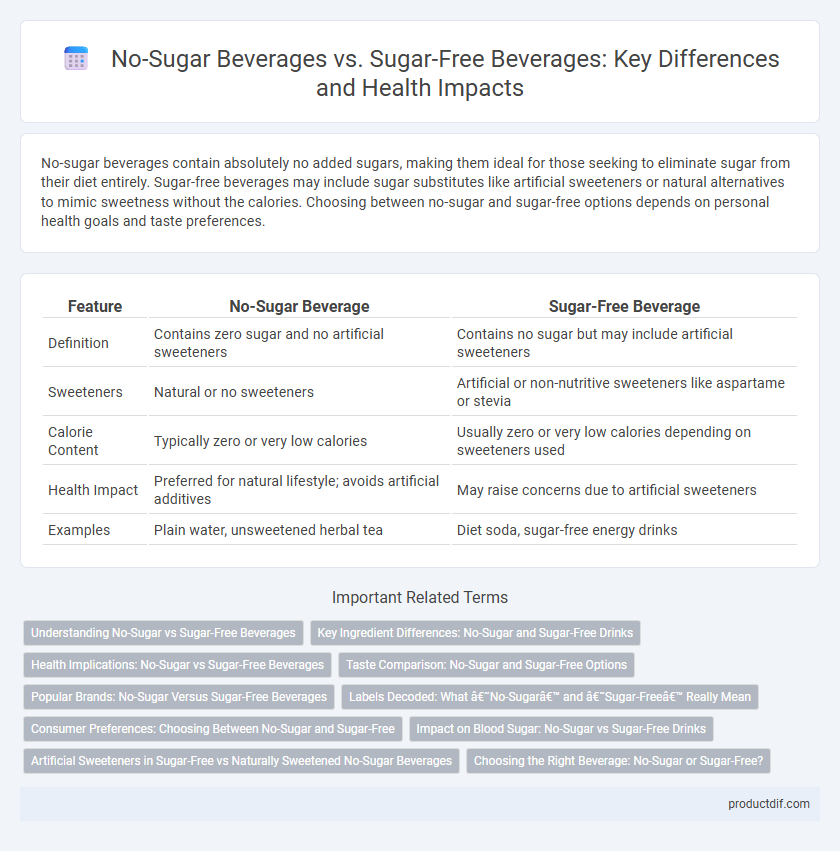
| Feature | No-Sugar Beverage | Sugar-Free Beverage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Contains zero sugar and no artificial sweeteners | Contains no sugar but may include artificial sweeteners |
| Sweeteners | Natural or no sweeteners | Artificial or non-nutritive sweeteners like aspartame or stevia |
| Calorie Content | Typically zero or very low calories | Usually zero or very low calories depending on sweeteners used |
| Health Impact | Preferred for natural lifestyle; avoids artificial additives | May raise concerns due to artificial sweeteners |
| Examples | Plain water, unsweetened herbal tea | Diet soda, sugar-free energy drinks |
Understanding No-Sugar vs Sugar-Free Beverages
No-sugar beverages contain no added sugars and typically rely on natural ingredients without artificial sweeteners, catering to those seeking to avoid all forms of sugar. Sugar-free beverages, often sweetened with artificial or non-nutritive sweeteners like aspartame or stevia, provide sweetness without calories or blood sugar impact. Understanding the difference helps consumers make informed choices based on dietary needs, health goals, and taste preferences in the beverage market.
Key Ingredient Differences: No-Sugar and Sugar-Free Drinks
No-sugar beverages contain naturally occurring or minimal sugars without added sweeteners, relying on ingredients like fruit juice or natural extracts for flavor. Sugar-free beverages replace sugar with artificial or natural non-caloric sweeteners such as stevia, sucralose, or erythritol to maintain sweetness without calories. Key ingredient differences impact taste profiles, calorie content, and metabolic responses, making the choice important for dietary preferences and health goals.
Health Implications: No-Sugar vs Sugar-Free Beverages
No-sugar beverages contain no added sugars and may still have natural sweeteners or sugar alcohols, while sugar-free beverages are formulated to have zero sugars, often using artificial sweeteners. Both options aim to reduce calorie intake and manage blood glucose levels, but sugar-free drinks may pose concerns due to artificial sweeteners linked to potential metabolic effects. Choosing between no-sugar and sugar-free beverages involves considering individual health conditions, such as diabetes or weight management goals, ensuring a balanced intake without relying on excessive artificial additives.
Taste Comparison: No-Sugar and Sugar-Free Options
No-sugar beverages maintain the natural taste of the drink by eliminating added sugars, resulting in a cleaner, often less sweet flavor profile that appeals to health-conscious consumers. Sugar-free beverages use artificial or non-nutritive sweeteners to replicate sweetness, offering a sweet taste similar to sugary drinks but with fewer or no calories. Taste preferences vary, with no-sugar options favored for authenticity and sugar-free choices preferred for sweetness without the calorie load.
Popular Brands: No-Sugar Versus Sugar-Free Beverages
Popular no-sugar beverages like Zevia and LaCroix emphasize natural ingredients without any added sweeteners, appealing to health-conscious consumers seeking zero-calorie options. Sugar-free beverages such as Diet Coke and Pepsi Max contain artificial sweeteners like aspartame or sucralose, offering the taste of traditional sodas without sugar but with some processed additives. Market trends show increasing demand for no-sugar brands due to rising awareness of artificial sweetener effects, while sugar-free options remain popular for those prioritizing flavor similarity to regular sodas.
Labels Decoded: What ‘No-Sugar’ and ‘Sugar-Free’ Really Mean
"No-Sugar" beverages contain no added sugars but may include natural sugars found in ingredients like fruit juice, whereas "Sugar-Free" drinks have little to no sugars, often replaced with artificial or non-nutritive sweeteners. Labels like "No-Sugar" indicate zero added sugars according to FDA guidelines, while "Sugar-Free" must contain less than 0.5 grams of sugars per serving, making both options suitable for sugar-conscious consumers. Understanding these definitions helps buyers make informed choices based on dietary needs and sugar intake goals.
Consumer Preferences: Choosing Between No-Sugar and Sugar-Free
Consumer preferences between no-sugar and sugar-free beverages hinge on ingredient transparency and taste expectations, with no-sugar options typically containing natural sweeteners or no sweeteners at all, appealing to those seeking cleaner labels. Sugar-free beverages often use artificial or non-nutritive sweeteners, attracting consumers focused on calorie control without sacrificing sweetness. Market trends reveal a rising demand for no-sugar beverages due to increasing health consciousness and skepticism towards artificial additives, influencing purchasing decisions significantly.
Impact on Blood Sugar: No-Sugar vs Sugar-Free Drinks
No-sugar beverages contain no added sugars but may include natural sugars, influencing blood sugar levels differently than sugar-free drinks, which use artificial or non-nutritive sweeteners that typically have minimal impact on glycemic response. Studies show sugar-free beverages can help maintain stable blood glucose levels, making them preferable for individuals managing diabetes or insulin sensitivity. However, the metabolic effects of artificial sweeteners remain under investigation, highlighting the importance of individual response monitoring.
Artificial Sweeteners in Sugar-Free vs Naturally Sweetened No-Sugar Beverages
Sugar-free beverages typically contain artificial sweeteners such as aspartame, sucralose, or stevia, which provide sweetness without adding calories, making them a popular choice for calorie-conscious consumers. In contrast, no-sugar beverages are naturally sweetened using ingredients like fruit extracts, monk fruit, or erythritol, offering a more natural alternative without compromising on taste. Understanding the differences in sweetener types helps consumers make informed decisions based on health preferences and dietary restrictions.
Choosing the Right Beverage: No-Sugar or Sugar-Free?
Choosing the right beverage between no-sugar and sugar-free options depends on ingredient awareness and health goals. No-sugar beverages contain no added sugars but may have natural sugars, while sugar-free beverages use artificial sweeteners or sugar substitutes to eliminate all sugars. Understanding labels and personal dietary needs ensures optimal hydration without unwanted calories or sugar intake.
No-Sugar Beverage vs Sugar-Free Beverage Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com