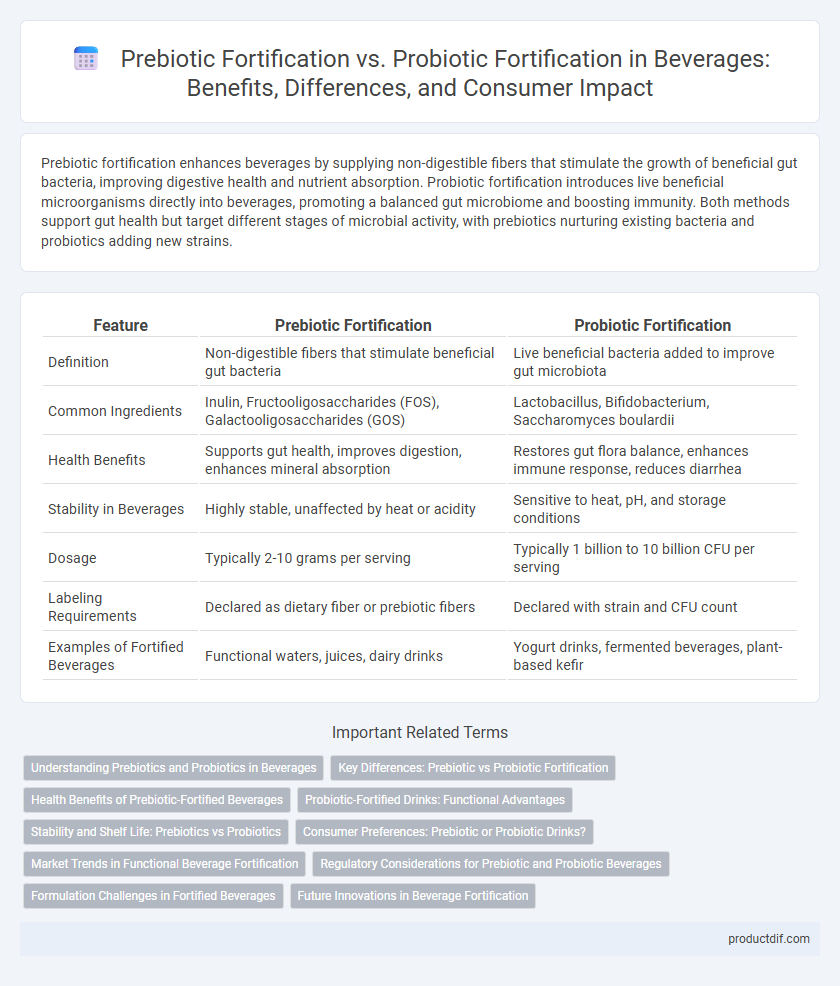
Prebiotic fortification enhances beverages by supplying non-digestible fibers that stimulate the growth of beneficial gut bacteria, improving digestive health and nutrient absorption. Probiotic fortification introduces live beneficial microorganisms directly into beverages, promoting a balanced gut microbiome and boosting immunity. Both methods support gut health but target different stages of microbial activity, with prebiotics nurturing existing bacteria and probiotics adding new strains.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Prebiotic Fortification | Probiotic Fortification |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Non-digestible fibers that stimulate beneficial gut bacteria | Live beneficial bacteria added to improve gut microbiota |
| Common Ingredients | Inulin, Fructooligosaccharides (FOS), Galactooligosaccharides (GOS) | Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium, Saccharomyces boulardii |
| Health Benefits | Supports gut health, improves digestion, enhances mineral absorption | Restores gut flora balance, enhances immune response, reduces diarrhea |
| Stability in Beverages | Highly stable, unaffected by heat or acidity | Sensitive to heat, pH, and storage conditions |
| Dosage | Typically 2-10 grams per serving | Typically 1 billion to 10 billion CFU per serving |
| Labeling Requirements | Declared as dietary fiber or prebiotic fibers | Declared with strain and CFU count |
| Examples of Fortified Beverages | Functional waters, juices, dairy drinks | Yogurt drinks, fermented beverages, plant-based kefir |
Understanding Prebiotics and Probiotics in Beverages
Prebiotic fortification in beverages involves adding non-digestible fibers that selectively stimulate the growth of beneficial gut bacteria, enhancing digestive health and nutrient absorption. Probiotic fortification introduces live beneficial microorganisms, such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium strains, which actively colonize the gut to improve microbiome balance and immune function. Understanding the distinct roles of prebiotics as food for microbes and probiotics as live bacteria is crucial for developing functional beverages that support gut health effectively.
Key Differences: Prebiotic vs Probiotic Fortification
Prebiotic fortification in beverages involves adding non-digestible fibers that selectively stimulate the growth of beneficial gut bacteria, enhancing digestive health and immune function. Probiotic fortification introduces live beneficial microorganisms directly into the beverage, promoting a balanced gut microbiota through colonization. Key differences lie in their mechanisms: prebiotics serve as food for existing microbes, while probiotics supply live bacteria to the digestive system.
Health Benefits of Prebiotic-Fortified Beverages
Prebiotic-fortified beverages enhance gut health by promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria such as Bifidobacteria and Lactobacilli, which improve digestion and boost immune function. Unlike probiotic fortification, prebiotics serve as dietary fibers that resist digestion and selectively stimulate the activity of advantageous microbiota, leading to improved bowel regularity and reduced inflammation. These beverages also support mineral absorption, particularly calcium and magnesium, contributing to better bone health and overall metabolic balance.
Probiotic-Fortified Drinks: Functional Advantages
Probiotic-fortified drinks enhance gut health by delivering live beneficial microorganisms that balance the intestinal microbiota and improve digestive function. These beverages support immune system modulation and may reduce symptoms of gastrointestinal disorders such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). Compared to prebiotic fortification, probiotic drinks offer the advantage of immediate microbial colonization, providing direct health benefits and promoting overall wellness.
Stability and Shelf Life: Prebiotics vs Probiotics
Prebiotic fortification offers superior stability and longer shelf life compared to probiotic fortification due to the non-living nature of prebiotics, which resist degradation during processing and storage. Probiotics require specific conditions such as controlled temperature and moisture to maintain viability, often resulting in reduced shelf life and potential loss of efficacy over time. Consequently, beverages fortified with prebiotics provide a more consistent functional benefit and longer-lasting nutritional value.
Consumer Preferences: Prebiotic or Probiotic Drinks?
Consumer preferences in the beverage industry show a growing demand for prebiotic drinks due to their digestive health benefits and ability to promote beneficial gut bacteria without introducing live cultures. Probiotic drinks remain popular for their direct provision of live microorganisms that support gut flora balance and immune health. Market trends indicate a shift toward prebiotic fortification as consumers seek longer shelf life and functional benefits with fewer dietary restrictions.
Market Trends in Functional Beverage Fortification
Prebiotic fortification in functional beverages is gaining significant traction due to its ability to selectively nourish beneficial gut bacteria, promoting digestive health and enhancing immune function. Probiotic fortification remains popular, especially in dairy-based beverages, leveraging live microorganisms to improve gut microbiota balance and overall wellness. Market trends indicate a growing consumer preference for prebiotic ingredients such as inulin and fructooligosaccharides, driven by increased awareness of gut health and the demand for clean-label, shelf-stable products.
Regulatory Considerations for Prebiotic and Probiotic Beverages
Regulatory considerations for prebiotic and probiotic beverages focus on ingredient approval, health claims, and labeling requirements set by agencies such as the FDA and EFSA. Prebiotic fortification must demonstrate safety and efficacy of fibers like inulin and oligosaccharides, while probiotic beverages require strain-specific evidence supporting viability and health benefits. Compliance with microbial limits, shelf-life stability, and accurate quantification of active microorganisms are critical factors for market authorization and consumer trust.
Formulation Challenges in Fortified Beverages
Prebiotic fortification in beverages faces formulation challenges such as maintaining stability and solubility of dietary fibers without compromising taste or texture, while probiotic fortification requires careful control of microbial viability during processing and shelf life. Both fortifications demand precise pH and temperature management to preserve functional efficacy and sensory quality. Optimizing delivery systems like microencapsulation can enhance stability and bioavailability in fortified beverages.
Future Innovations in Beverage Fortification
Future innovations in beverage fortification emphasize the integration of prebiotic and probiotic compounds to enhance gut health and immunity. Advances in microencapsulation technology enable the stable delivery of live probiotic strains alongside prebiotic fibers, improving shelf life and bioavailability. Emerging trends include personalized beverage formulations tailored to individual microbiome profiles, promoting targeted digestive benefits and overall wellness.
Prebiotic Fortification vs Probiotic Fortification Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com