Cold-pressed juice retains more nutrients and enzymes due to its slow extraction process, preserving the juice's natural flavors and health benefits. Centrifugal juice, produced quickly by high-speed spinning, tends to oxidize faster, resulting in less nutrient retention and a shorter shelf life. Choosing cold-pressed juice ensures a fresher, more nutrient-dense beverage ideal for health-conscious consumers.
Table of Comparison
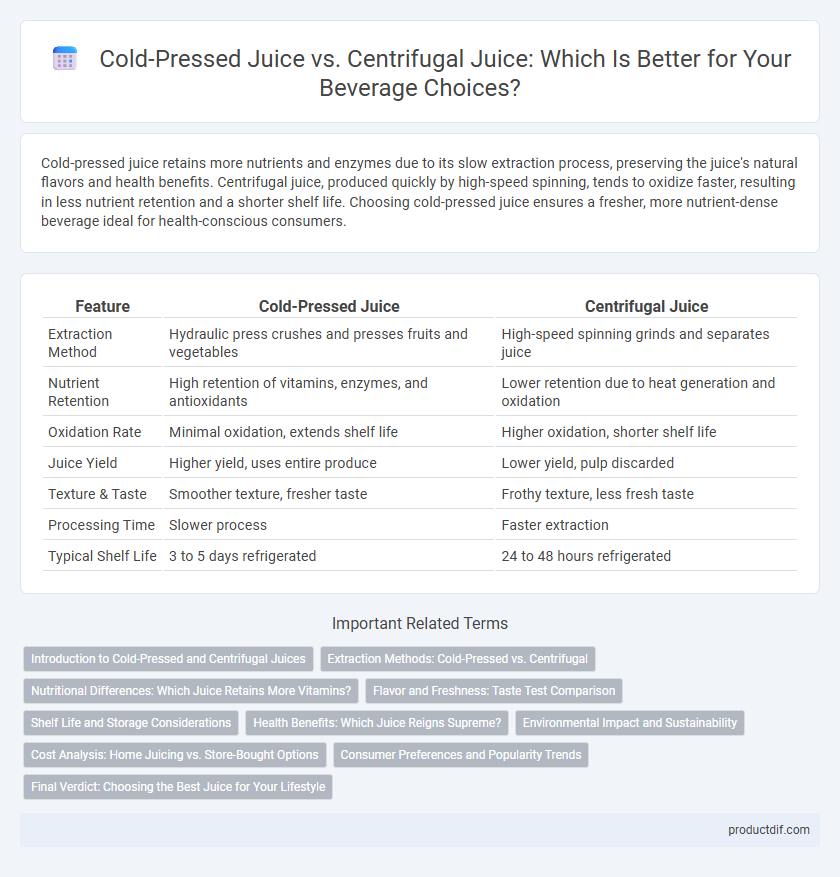
| Feature | Cold-Pressed Juice | Centrifugal Juice |
|---|---|---|
| Extraction Method | Hydraulic press crushes and presses fruits and vegetables | High-speed spinning grinds and separates juice |
| Nutrient Retention | High retention of vitamins, enzymes, and antioxidants | Lower retention due to heat generation and oxidation |
| Oxidation Rate | Minimal oxidation, extends shelf life | Higher oxidation, shorter shelf life |
| Juice Yield | Higher yield, uses entire produce | Lower yield, pulp discarded |
| Texture & Taste | Smoother texture, fresher taste | Frothy texture, less fresh taste |
| Processing Time | Slower process | Faster extraction |
| Typical Shelf Life | 3 to 5 days refrigerated | 24 to 48 hours refrigerated |
Introduction to Cold-Pressed and Centrifugal Juices
Cold-pressed juice is extracted using a hydraulic press that slowly crushes fruits and vegetables to preserve nutrients and enzymes, resulting in a nutrient-dense and fresh-tasting beverage. Centrifugal juice is produced by shredding ingredients at high speed with a spinning blade, which generates heat and causes oxidation, potentially reducing vitamin content and shelf life. Consumers seeking maximum nutritional benefits often prefer cold-pressed juice for its higher retention of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants compared to centrifugal juice.
Extraction Methods: Cold-Pressed vs. Centrifugal
Cold-pressed juice is extracted using a hydraulic press that slowly crushes fruits and vegetables, preserving more nutrients and enzymes due to minimal heat generation. Centrifugal juice is produced by grating produce at high speed and spinning it to separate juice from pulp, which introduces heat and oxidation, potentially reducing nutrient content. The cold-press method yields a higher-quality juice with a richer flavor profile and longer shelf life compared to the faster, but nutrient-compromising, centrifugal process.
Nutritional Differences: Which Juice Retains More Vitamins?
Cold-pressed juice retains significantly more vitamins, especially vitamin C and B-complex vitamins, due to its gentle extraction process that minimizes heat and oxidation. In contrast, centrifugal juice extraction generates heat and incorporates air, leading to faster nutrient degradation and reduced antioxidant levels. Studies indicate that cold-pressed juice can preserve up to 30% more nutrients than centrifugal methods, making it a superior choice for maximizing vitamin intake.
Flavor and Freshness: Taste Test Comparison
Cold-pressed juice retains more nutrients and natural enzymes due to its slow extraction process, resulting in a rich, vibrant flavor and fresher taste compared to centrifugal juice. Centrifugal juice often experiences oxidation and heat buildup during fast spinning, which can lead to a diluted flavor and reduced freshness. Taste tests consistently show cold-pressed juices have a smoother texture and a more pronounced, natural fruit or vegetable flavor profile.
Shelf Life and Storage Considerations
Cold-pressed juice retains nutrients longer due to minimal oxidation during extraction, offering a shelf life of up to 3-5 days when refrigerated between 32-38degF (0-3degC). Centrifugal juice, exposed to higher heat and oxygen levels, typically lasts 24-48 hours under refrigeration before nutrient degradation and spoilage occur. Proper storage in airtight, opaque containers slows oxidation and microbial growth, extending freshness for both juice types.
Health Benefits: Which Juice Reigns Supreme?
Cold-pressed juice retains more nutrients and enzymes due to its low-heat extraction method, preserving vitamins like C and antioxidants that support immune health and skin vitality. Centrifugal juice, processed rapidly with high-speed blades, tends to generate heat that can degrade sensitive nutrients, resulting in lower levels of fiber and antioxidants. For maximum health benefits, cold-pressed juice offers superior nutrient density and enzymatic activity essential for detoxification and digestion.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Cold-pressed juice production uses a hydraulic press that requires less energy compared to centrifugal juicers, resulting in a lower carbon footprint. The process preserves more nutrients and generates less waste by efficiently extracting juice, contributing to sustainable consumption. Centrifugal juicers often produce more pulp waste and consume higher electricity, making cold-pressed juice a more eco-friendly choice.
Cost Analysis: Home Juicing vs. Store-Bought Options
Cold-pressed juice machines typically cost between $200 and $500, delivering higher nutrient retention but slower extraction compared to centrifugal juicers priced around $50 to $150, which offer faster juice output with increased oxidation. Homemade cold-pressed juice reduces expenses over time, with per-serving costs averaging $2 to $4, contrasting with store-bought cold-pressed juices that range from $5 to $10 per bottle. Consumers should evaluate initial appliance investment, maintenance expenses, and price per serving to determine cost-effectiveness between home juicing and purchasing pre-made juices.
Consumer Preferences and Popularity Trends
Cold-pressed juice has surged in consumer popularity due to its perceived higher nutritional value and fresher taste, as it retains more vitamins and enzymes through gentle extraction. Centrifugal juice remains favored for its quick preparation and affordability, attracting consumers seeking convenience and lower cost. Market trends indicate a growing preference for cold-pressed options among health-conscious buyers, driving expansion in specialty juice bars and premium retail segments.
Final Verdict: Choosing the Best Juice for Your Lifestyle
Cold-pressed juice retains higher nutrient density and antioxidants due to its low-heat extraction process, making it ideal for health-conscious individuals seeking maximum vitamin and enzyme benefits. Centrifugal juice is faster to produce and offers convenience but may have reduced nutrient levels and shorter shelf life due to oxidation. Choosing the best juice depends on balancing convenience with nutritional value, where cold-pressed juice suits wellness-focused lifestyles, while centrifugal juice fits busy routines demanding quick refreshment.
Cold-Pressed Juice vs Centrifugal Juice Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com