Hot fill involves heating beverages to high temperatures before filling to ensure microbial safety and shelf stability, often used for juices and teas with moderate acid levels. Aseptic fill sterilizes both the product and packaging separately before filling in a sterile environment, enabling longer shelf life without preservatives, commonly applied for dairy and low-acid beverages. Choosing between hot fill and aseptic fill depends on factors like product acidity, desired shelf life, and packaging type.
Table of Comparison
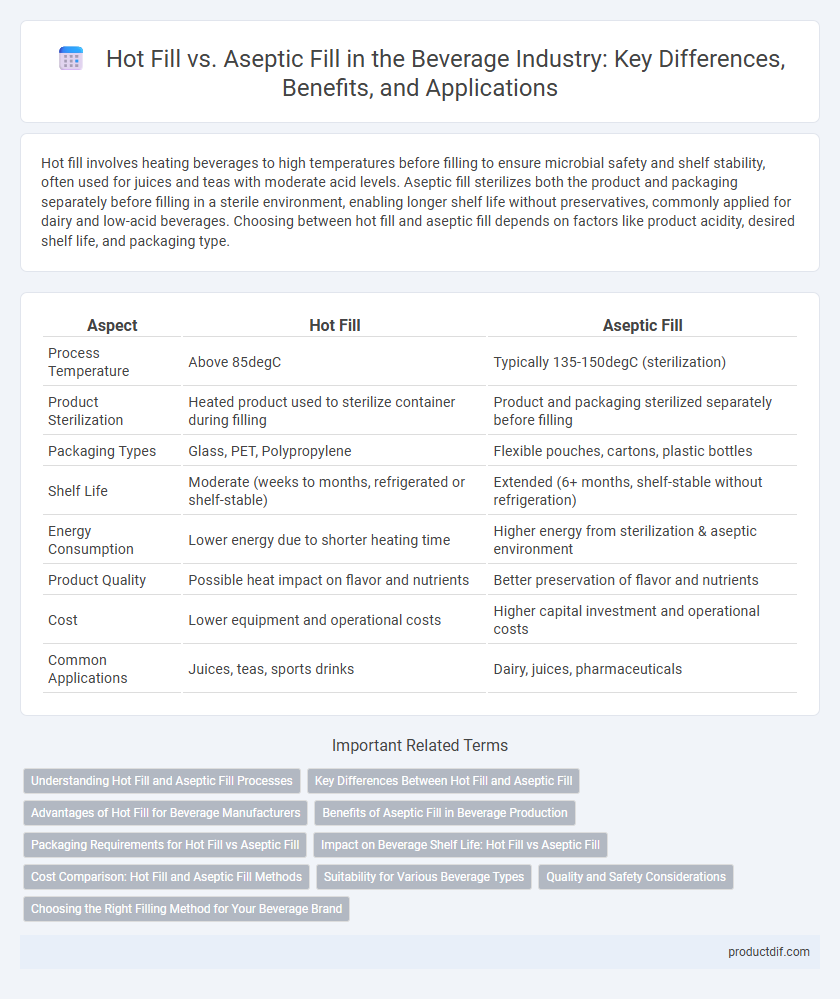
| Aspect | Hot Fill | Aseptic Fill |
|---|---|---|
| Process Temperature | Above 85degC | Typically 135-150degC (sterilization) |
| Product Sterilization | Heated product used to sterilize container during filling | Product and packaging sterilized separately before filling |
| Packaging Types | Glass, PET, Polypropylene | Flexible pouches, cartons, plastic bottles |
| Shelf Life | Moderate (weeks to months, refrigerated or shelf-stable) | Extended (6+ months, shelf-stable without refrigeration) |
| Energy Consumption | Lower energy due to shorter heating time | Higher energy from sterilization & aseptic environment |
| Product Quality | Possible heat impact on flavor and nutrients | Better preservation of flavor and nutrients |
| Cost | Lower equipment and operational costs | Higher capital investment and operational costs |
| Common Applications | Juices, teas, sports drinks | Dairy, juices, pharmaceuticals |
Understanding Hot Fill and Aseptic Fill Processes
Hot fill involves heating the beverage to a high temperature (usually around 85-95degC) before filling it into containers to ensure microbial safety and extend shelf life without refrigeration. Aseptic fill combines sterilized beverage and sterilized packaging in a sterile environment, allowing products to remain shelf-stable for long periods without preservatives or refrigeration. Understanding these processes helps manufacturers choose the best method based on product type, shelf life requirements, and cost-efficiency.
Key Differences Between Hot Fill and Aseptic Fill
Hot fill involves filling beverages at temperatures typically between 85degC to 95degC to ensure microbial safety and shelf stability, primarily used for juices and teas. Aseptic fill sterilizes both the product and packaging separately before filling in a sterile environment, allowing for extended shelf life without refrigeration, commonly applied in dairy and liquid nutrition products. The key difference lies in the packaging requirements and processing temperatures, with hot fill requiring heat-resistant containers while aseptic fill allows flexible packaging options due to separate sterilization.
Advantages of Hot Fill for Beverage Manufacturers
Hot fill technology offers beverage manufacturers enhanced microbial safety by utilizing high temperatures to eliminate contaminants, extending product shelf life without preservatives. It enables packaging in flexible containers such as PET bottles, which reduces material costs and environmental impact compared to aseptic cartons. The process also simplifies production lines by eliminating the need for sterile environments, reducing capital expenditure and maintenance requirements.
Benefits of Aseptic Fill in Beverage Production
Aseptic fill technology extends the shelf life of beverages without the need for preservatives, maintaining product freshness and nutritional quality. It allows for efficient packaging of a wide range of beverage types, including juices and dairy alternatives, under sterile conditions that minimize contamination risks. This method also reduces energy consumption compared to hot fill, contributing to more sustainable beverage production.
Packaging Requirements for Hot Fill vs Aseptic Fill
Hot fill packaging requires containers made from heat-resistant materials such as PET or glass to withstand temperatures typically above 85degC, ensuring product stability and microbial safety during filling and cooling. Aseptic fill packaging demands sterile, hermetically sealed containers, often multi-layered cartons or barrier-coated bottles, to maintain product sterility without heat exposure. Both methods mandate precise sealing technologies, but aseptic fill prioritizes sterile environments and materials that prevent microbial ingress without the need for thermal pasteurization.
Impact on Beverage Shelf Life: Hot Fill vs Aseptic Fill
Hot fill processes use high temperatures to sterilize beverages and containers, extending shelf life by eliminating microbial contamination but potentially altering flavor and nutrient profiles. Aseptic fill combines sterilized products and containers in a sterile environment, preserving sensory qualities and nutritional value while achieving longer shelf stability without refrigeration. Shelf life impact depends on beverage type, packaging material, and storage conditions, with aseptic fill generally offering superior shelf longevity.
Cost Comparison: Hot Fill and Aseptic Fill Methods
Hot fill packaging incurs higher energy costs due to the need for heating beverages to 85-95degC for sterilization, while aseptic fill methods require sophisticated, costly equipment but reduce energy consumption by filling products in a sterile environment without heat. Aseptic filling typically offers lower overall operational costs through longer shelf life and reduced preservative use, though initial capital investment is significantly higher compared to hot fill systems. Cost efficiency between the two methods depends on production volume, product type, and desired shelf stability, with aseptic fill favored for high-value, long shelf-life products.
Suitability for Various Beverage Types
Hot fill is ideal for acidic beverages such as juices and teas due to its ability to eliminate harmful microorganisms through high-temperature processing, ensuring product safety without preservatives. Aseptic fill suits low-acid beverages like milk and plant-based drinks by sterilizing both product and packaging separately, preserving flavor and nutrients with extended shelf life. Both methods cater to different beverage pH levels and nutritional stability requirements, optimizing packaging and quality maintenance.
Quality and Safety Considerations
Hot fill processes use high temperatures to sterilize both the beverage and container, effectively killing pathogens and extending shelf life without preservatives, ensuring product safety and maintaining beverage quality. Aseptic fill techniques sterilize the product and packaging separately before filling in a sterile environment, preserving flavor integrity and nutritional value while minimizing contamination risks. Both methods prioritize quality and safety but differ in thermal exposure, impacting the beverage's sensory properties and shelf stability.
Choosing the Right Filling Method for Your Beverage Brand
Hot Fill ensures extended shelf life for acidic beverages by using heat to sterilize both product and packaging, ideal for fruit juices and teas. Aseptic Fill involves sterilizing liquid and packaging separately before filling, preserving flavor and nutrients, suitable for dairy and sensitive drinks. Selecting the right method depends on product pH, sensitivity to heat, shelf life requirements, and packaging materials to maintain quality and safety.
Hot Fill vs Aseptic Fill Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com