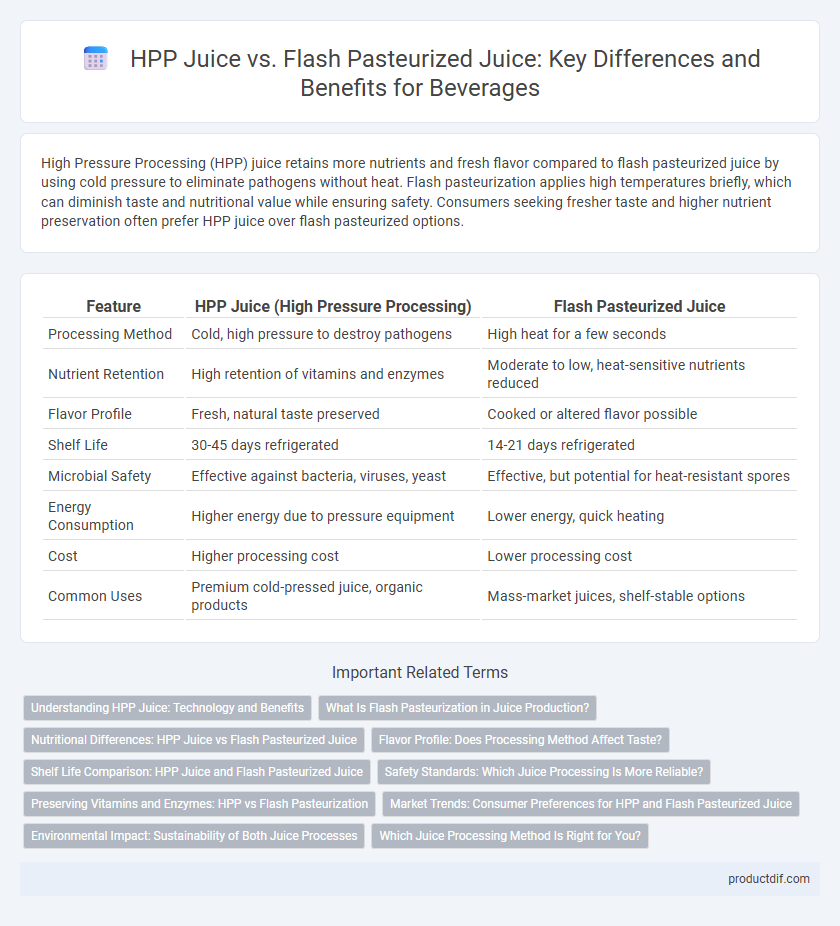
High Pressure Processing (HPP) juice retains more nutrients and fresh flavor compared to flash pasteurized juice by using cold pressure to eliminate pathogens without heat. Flash pasteurization applies high temperatures briefly, which can diminish taste and nutritional value while ensuring safety. Consumers seeking fresher taste and higher nutrient preservation often prefer HPP juice over flash pasteurized options.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | HPP Juice (High Pressure Processing) | Flash Pasteurized Juice |
|---|---|---|
| Processing Method | Cold, high pressure to destroy pathogens | High heat for a few seconds |
| Nutrient Retention | High retention of vitamins and enzymes | Moderate to low, heat-sensitive nutrients reduced |
| Flavor Profile | Fresh, natural taste preserved | Cooked or altered flavor possible |
| Shelf Life | 30-45 days refrigerated | 14-21 days refrigerated |
| Microbial Safety | Effective against bacteria, viruses, yeast | Effective, but potential for heat-resistant spores |
| Energy Consumption | Higher energy due to pressure equipment | Lower energy, quick heating |
| Cost | Higher processing cost | Lower processing cost |
| Common Uses | Premium cold-pressed juice, organic products | Mass-market juices, shelf-stable options |
Understanding HPP Juice: Technology and Benefits
HPP juice, or High Pressure Processing juice, uses intense pressure to eliminate pathogens and extend shelf life without compromising nutritional value or flavor, unlike flash pasteurized juice which relies on heat. The technology preserves vitamins, enzymes, and antioxidants, maintaining a fresher taste and higher nutrient retention. This method also supports clean label marketing by reducing the need for preservatives.
What Is Flash Pasteurization in Juice Production?
Flash pasteurization in juice production involves rapidly heating the juice to temperatures between 71degC and 74degC for 15 to 30 seconds, effectively killing pathogens while preserving flavor and nutrients. This method contrasts with High Pressure Processing (HPP), which uses intense pressure rather than heat to extend shelf life and maintain fresh taste. Flash pasteurized juices often have a shorter shelf life and slightly altered sensory profiles compared to HPP juices, making process selection critical depending on product goals.
Nutritional Differences: HPP Juice vs Flash Pasteurized Juice
HPP juice retains higher levels of vitamins C and B due to its cold-press process, preserving more antioxidants compared to flash pasteurized juice, which undergoes heat treatment that can degrade sensitive nutrients. Enzymatic activity and natural flavors remain more intact in HPP juice, resulting in a fresher taste and nutrient profile. Flash pasteurization extends shelf life but often reduces nutritional value, particularly impacts heat-sensitive compounds like polyphenols and enzymes.
Flavor Profile: Does Processing Method Affect Taste?
High Pressure Processing (HPP) juice retains more of the fresh fruit's natural flavor, aroma, and vibrant taste due to minimal heat exposure, preserving sensitive volatile compounds. In contrast, flash pasteurization uses high temperatures briefly, which can slightly diminish freshness and alter delicate flavor notes by causing thermal degradation. Consumers seeking a crisp, fresh flavor typically prefer HPP juice for its closer-to-fresh taste profile compared to flash pasteurized options.
Shelf Life Comparison: HPP Juice and Flash Pasteurized Juice
HPP juice typically boasts a longer shelf life of up to 45 days when refrigerated, compared to flash pasteurized juice, which usually lasts around 14 to 21 days due to the heat treatment process. High Pressure Processing preserves more nutrients and flavor by inactivating spoilage microbes without heat, enhancing shelf stability without compromising quality. Flash pasteurization employs high temperatures for a few seconds, reducing microbial load but potentially affecting taste and nutrient retention, resulting in a shorter refrigerated shelf life.
Safety Standards: Which Juice Processing Is More Reliable?
High Pressure Processing (HPP) juice maintains higher levels of nutrients and freshness by using extreme pressure to eliminate pathogens without heat, ensuring safer consumption while retaining flavor. Flash pasteurization applies high heat briefly to kill harmful microorganisms but may degrade vitamins and alter taste profiles. Despite both meeting strict safety standards, HPP is often considered more reliable for preserving juice quality alongside effective microbial control.
Preserving Vitamins and Enzymes: HPP vs Flash Pasteurization
HPP juice retains higher levels of vitamins and enzymes by using high pressure to inactivate pathogens without heat, preserving nutritional quality. Flash pasteurization involves brief exposure to high temperatures, which can degrade sensitive vitamins and enzymes. Studies show HPP-treated juice maintains superior antioxidant activity and enzyme function compared to flash pasteurized alternatives.
Market Trends: Consumer Preferences for HPP and Flash Pasteurized Juice
HPP juice is gaining market share due to its appeal to health-conscious consumers seeking fresher taste and higher nutrient retention compared to flash pasteurized juice. Flash pasteurized juice remains popular for its longer shelf life and cost-effectiveness, maintaining strong presence in mass retail channels. Current market trends show a growing preference for premium, minimally processed beverages, driving increased demand for HPP juice in urban and specialty markets.
Environmental Impact: Sustainability of Both Juice Processes
HPP juice processing uses high pressure instead of heat, significantly reducing energy consumption and preserving more nutrients, making it a more sustainable choice compared to flash pasteurization which relies on high temperatures and continuous energy input. Wastewater and carbon emissions from flash pasteurization are typically higher due to thermal treatment, whereas HPP systems produce less thermal waste and enable longer shelf life without preservatives, reducing overall food waste. The adoption of HPP technology aligns with growing consumer demand for eco-friendly beverages by minimizing environmental footprint throughout the juice production cycle.
Which Juice Processing Method Is Right for You?
High Pressure Processing (HPP) juice retains more natural nutrients and flavor due to its cold pasteurization, making it ideal for consumers seeking freshness and extended shelf life without additives. Flash pasteurized juice undergoes high heat treatment for a shorter time, effectively killing pathogens while slightly altering taste and reducing some heat-sensitive vitamins. Choosing the right method depends on priorities like nutrient preservation, flavor retention, shelf stability, and production costs.
HPP Juice vs Flash Pasteurized Juice Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com