Fabric sourcing involves selecting high-quality raw materials like cotton, silk, or synthetic fibers, essential for ensuring durability, comfort, and aesthetic appeal in apparel. Garment sourcing focuses on procuring finished products ready for retail, emphasizing factors such as production timelines, cost efficiency, and adherence to design specifications. Understanding the distinction between fabric and garment sourcing helps apparel businesses optimize supply chain management and maintain consistent product quality.
Table of Comparison
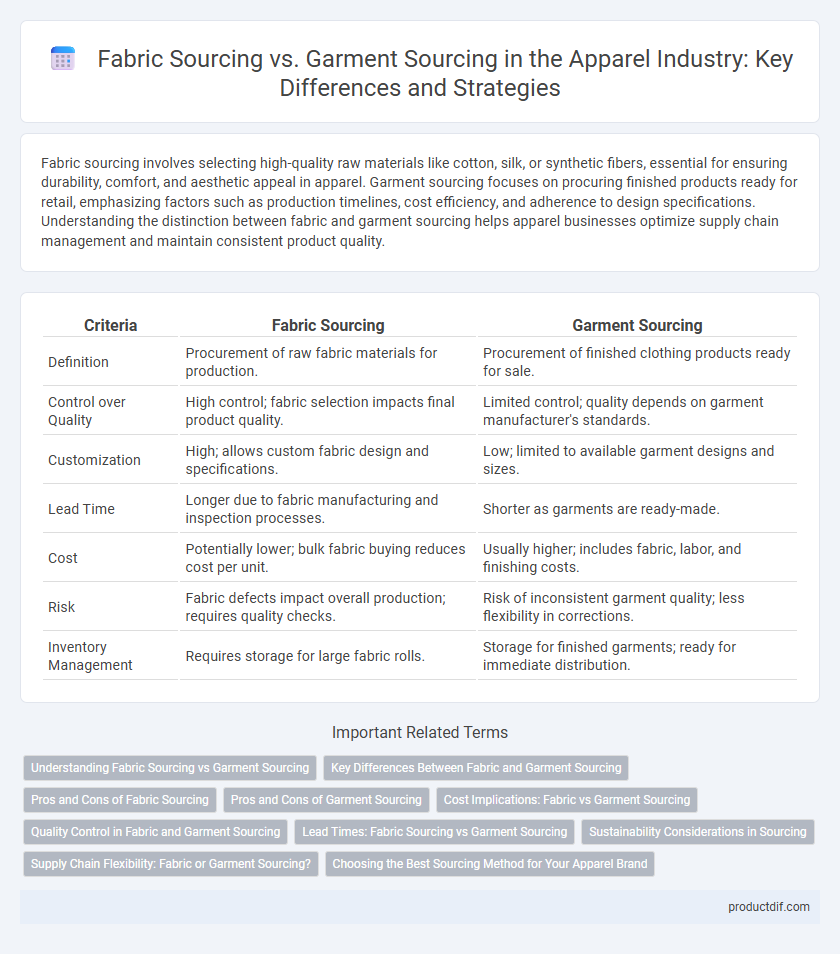
| Criteria | Fabric Sourcing | Garment Sourcing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Procurement of raw fabric materials for production. | Procurement of finished clothing products ready for sale. |
| Control over Quality | High control; fabric selection impacts final product quality. | Limited control; quality depends on garment manufacturer's standards. |
| Customization | High; allows custom fabric design and specifications. | Low; limited to available garment designs and sizes. |
| Lead Time | Longer due to fabric manufacturing and inspection processes. | Shorter as garments are ready-made. |
| Cost | Potentially lower; bulk fabric buying reduces cost per unit. | Usually higher; includes fabric, labor, and finishing costs. |
| Risk | Fabric defects impact overall production; requires quality checks. | Risk of inconsistent garment quality; less flexibility in corrections. |
| Inventory Management | Requires storage for large fabric rolls. | Storage for finished garments; ready for immediate distribution. |
Understanding Fabric Sourcing vs Garment Sourcing
Fabric sourcing involves procuring raw materials like cotton, silk, or synthetic fibers essential for textile production, whereas garment sourcing focuses on acquiring finished clothing items for retail or distribution. Understanding the distinction helps optimize supply chains by addressing fabric quality, cost, and lead times separately from garment manufacturing, assembly, and logistics. Efficient fabric sourcing impacts textile performance and customization, while garment sourcing emphasizes production efficiency, design fidelity, and market readiness.
Key Differences Between Fabric and Garment Sourcing
Fabric sourcing involves obtaining raw textile materials such as cotton, silk, or polyester directly from mills or suppliers, emphasizing quality, fiber content, and production capabilities. Garment sourcing refers to procuring finished clothing products, prioritizing factors like design, fit, compliance with apparel standards, and branding consistency. The key differences lie in the supply chain stage, with fabric sourcing concentrating on material characteristics and fabric development, while garment sourcing focuses on end-product manufacturing and distribution logistics.
Pros and Cons of Fabric Sourcing
Fabric sourcing allows brands greater control over quality, customization, and fabric choice, enabling the use of unique or proprietary materials that differentiate their products. It can enhance supply chain flexibility and reduce costs by eliminating middlemen, but requires significant expertise in textile selection, longer lead times, and higher inventory risks. Conversely, garment sourcing simplifies production management by outsourcing the entire apparel creation, though it may limit control over fabric quality and design details.
Pros and Cons of Garment Sourcing
Garment sourcing offers the advantage of reduced lead times and simplified supply chain management by procuring fully finished apparel directly from manufacturers. This approach minimizes the need for in-house production expertise and capital investments in machinery or labor. However, garment sourcing may limit customization options, increase costs per unit, and reduce control over quality compared to fabric sourcing and in-house garment production.
Cost Implications: Fabric vs Garment Sourcing
Fabric sourcing often involves lower initial costs due to bulk purchasing and direct supplier relationships, enabling greater control over material quality and customization. Garment sourcing can lead to higher expenses as it includes manufacturing, labor, and finishing costs, but may reduce overall lead time and operational complexity. Evaluating cost implications requires balancing fabric price volatility against production overheads inherent in garment sourcing.
Quality Control in Fabric and Garment Sourcing
Fabric sourcing emphasizes strict quality control measures including fiber composition verification, colorfastness testing, and durability assessments to ensure raw materials meet production standards. Garment sourcing involves comprehensive inspections such as stitching accuracy, fit conformity, and final product durability to guarantee finished apparel aligns with design specifications. Both processes integrate stringent quality checkpoints to minimize defects and uphold overall product excellence in the apparel supply chain.
Lead Times: Fabric Sourcing vs Garment Sourcing
Fabric sourcing typically involves longer lead times due to dyeing, weaving, and quality inspections, which can extend production schedules by several weeks. Garment sourcing often shortens lead times since finished products are procured directly, bypassing initial fabric processing stages. Efficient coordination between fabric and garment sourcing is crucial to optimize overall supply chain timelines in apparel manufacturing.
Sustainability Considerations in Sourcing
Fabric sourcing emphasizes the sustainability of raw materials, prioritizing organic, recycled, and low-impact fibers to reduce environmental footprints. Garment sourcing focuses on entire production cycles, including ethical labor practices, water usage, and carbon emissions associated with manufacturing processes. Both approaches require rigorous supply chain transparency to ensure adherence to sustainability certifications such as GOTS, OEKO-TEX, and Fair Trade.
Supply Chain Flexibility: Fabric or Garment Sourcing?
Fabric sourcing offers greater supply chain flexibility by allowing apparel brands to customize designs and switch garment manufacturers without dependency on a single supplier. Garment sourcing streamlines production but can limit adaptability due to fixed styles and reliance on specific factories. Choosing fabric sourcing enhances responsiveness to market trends and reduces risks associated with supply disruptions.
Choosing the Best Sourcing Method for Your Apparel Brand
Evaluating fabric sourcing versus garment sourcing depends on your brand's control over quality, customization, and production timelines. Fabric sourcing allows for greater design flexibility and unique material selection, ideal for brands prioritizing originality, while garment sourcing offers faster turnaround and cost efficiency by purchasing ready-made products. Choosing the best sourcing method requires balancing factors like supply chain complexity, minimum order quantities, and brand identity to optimize both creativity and operational efficiency.
Fabric sourcing vs Garment sourcing Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com