Active suspension systems use sensors and actuators to continuously adjust the suspension settings, providing superior ride comfort and improved handling. Passive suspension relies on fixed springs and dampers, offering a simpler and less expensive setup but with limited adaptability to changing road conditions. Active suspension enhances vehicle stability and reduces body roll, making it ideal for performance and luxury vehicles.
Table of Comparison
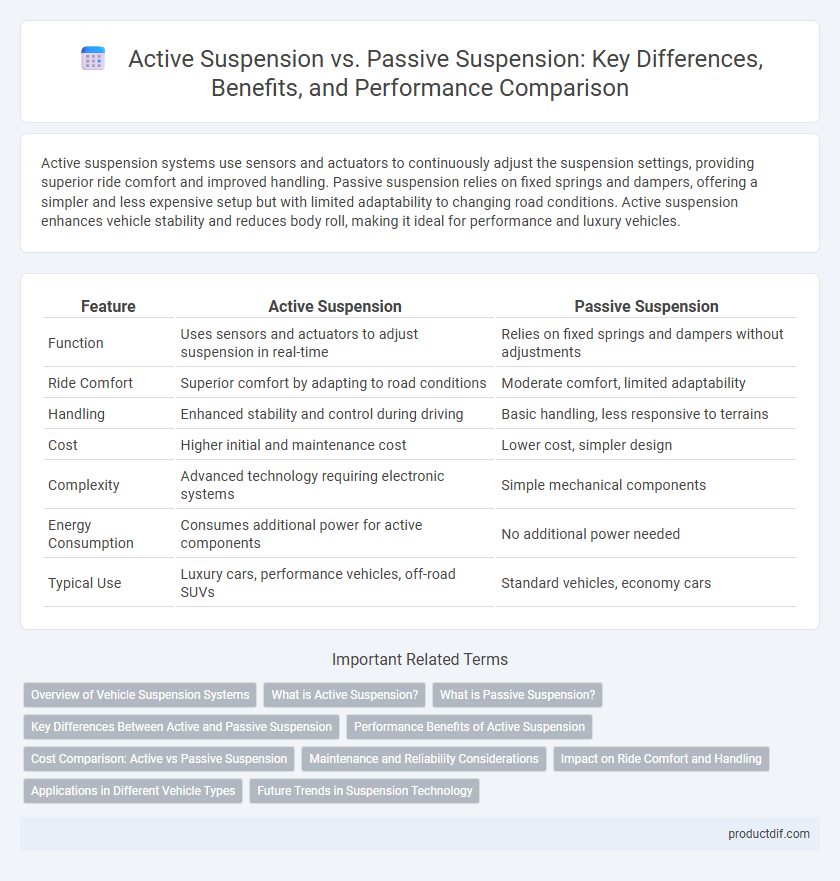
| Feature | Active Suspension | Passive Suspension |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Uses sensors and actuators to adjust suspension in real-time | Relies on fixed springs and dampers without adjustments |
| Ride Comfort | Superior comfort by adapting to road conditions | Moderate comfort, limited adaptability |
| Handling | Enhanced stability and control during driving | Basic handling, less responsive to terrains |
| Cost | Higher initial and maintenance cost | Lower cost, simpler design |
| Complexity | Advanced technology requiring electronic systems | Simple mechanical components |
| Energy Consumption | Consumes additional power for active components | No additional power needed |
| Typical Use | Luxury cars, performance vehicles, off-road SUVs | Standard vehicles, economy cars |
Overview of Vehicle Suspension Systems
Vehicle suspension systems are designed to enhance ride comfort and handling by managing the interaction between the chassis and the road surface. Active suspension uses sensors, actuators, and control units to adjust damping and stiffness in real time, providing improved stability and responsiveness. Passive suspension relies on fixed springs and dampers, offering simplicity and cost-effectiveness but less adaptability to varying driving conditions.
What is Active Suspension?
Active suspension is a vehicle suspension system that uses sensors, actuators, and a control unit to continuously adjust the suspension settings in real-time, enhancing ride comfort and handling stability. Unlike passive suspension, which relies on fixed springs and dampers, active suspension adapts to varying road conditions by actively controlling the movement of each wheel. This technology improves vehicle dynamics, reduces body roll, and maintains optimal tire contact with the road for safer driving performance.
What is Passive Suspension?
Passive suspension relies on fixed springs and shock absorbers to absorb road shocks without external control or adjustment. It provides basic ride comfort and vehicle stability by mechanically dampening vibrations through components such as coil springs, leaf springs, and hydraulic shock absorbers. While cost-effective and simple, passive suspension systems cannot adapt to changing road conditions in real-time like active suspension systems.
Key Differences Between Active and Passive Suspension
Active suspension systems use sensors and actuators to continuously adjust the damping and stiffness, providing improved ride comfort and vehicle handling compared to passive suspension, which relies on fixed springs and dampers without real-time adjustments. Active suspension enhances stability by responding dynamically to road conditions and driving inputs, while passive suspension often results in a compromise between comfort and control due to its static nature. The complexity and cost of active suspension are higher, but the technology significantly reduces body roll, pitch, and vibrations, optimizing overall vehicle performance.
Performance Benefits of Active Suspension
Active suspension systems enhance vehicle performance by continuously adjusting the damping and spring rates in real-time, resulting in improved handling, stability, and ride comfort. By using sensors and electronic controls, active suspension minimizes body roll, pitch, and vibrations, offering superior traction and control compared to passive suspension systems. This technology optimizes tire contact with the road, enabling better cornering capabilities and increased safety during dynamic driving conditions.
Cost Comparison: Active vs Passive Suspension
Active suspension systems generally incur higher initial costs due to advanced sensors, actuators, and electronic control units, whereas passive suspension relies on simpler mechanical components, resulting in lower upfront expenses. Maintenance costs for active suspension tend to be greater because of the complexity and potential electronic failures, while passive suspension offers more affordable upkeep and greater durability over time. The total cost of ownership for active suspension can be significantly higher despite performance benefits, making passive suspension a cost-effective choice for budget-conscious vehicle owners.
Maintenance and Reliability Considerations
Active suspension systems require more frequent maintenance due to their complex electronic components and hydraulic mechanisms, which may lead to higher repair costs over time. Passive suspension systems offer greater reliability with simpler mechanical parts, resulting in lower maintenance demands and longer service intervals. Choosing between the two depends on balancing the advanced performance benefits of active suspension against the proven durability and ease of upkeep found in passive suspension.
Impact on Ride Comfort and Handling
Active suspension systems use sensors and actuators to constantly adjust damping and stiffness, significantly enhancing ride comfort by reducing vibrations and body roll. Passive suspension relies on fixed components like springs and dampers, limiting its ability to adapt to varying road conditions and often resulting in a compromise between comfort and handling. Vehicles equipped with active suspension demonstrate superior handling precision and stability, especially during cornering and uneven terrain, by dynamically optimizing suspension performance.
Applications in Different Vehicle Types
Active suspension systems, featuring electronic sensors and actuators, are extensively used in luxury cars and high-performance sports vehicles to provide superior ride comfort and handling precision. Passive suspension systems, relying on fixed springs and dampers, are commonly found in economy cars, trucks, and off-road vehicles due to their simplicity, reliability, and cost-effectiveness. Commercial vehicles and buses often employ semi-active suspension to balance comfort and load adaptability across diverse driving conditions.
Future Trends in Suspension Technology
Future trends in suspension technology emphasize adaptive and predictive systems that enhance ride comfort, handling, and safety by continuously adjusting to road conditions using sensors and AI algorithms. Active suspension systems, capable of real-time adjustments, outperform passive suspensions by reducing body roll and improving vehicle stability. Integration with autonomous driving technologies and electric vehicles accelerates the development of smart, energy-efficient suspension solutions that optimize performance and passenger experience.
Active Suspension vs Passive Suspension Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com