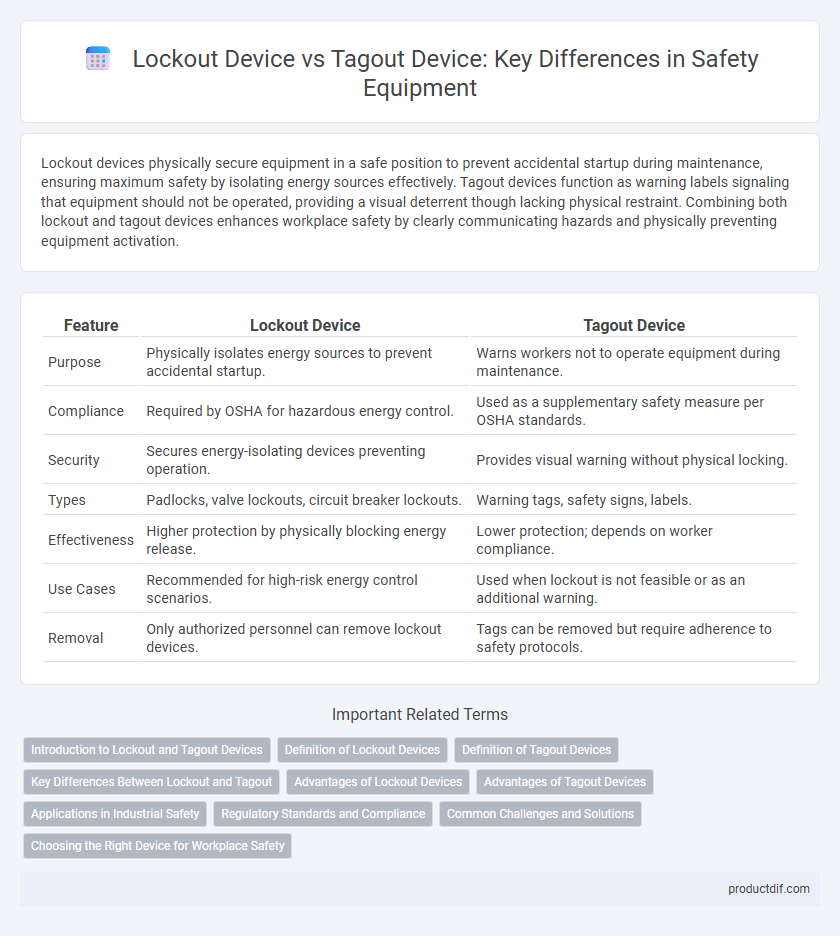
Lockout devices physically secure equipment in a safe position to prevent accidental startup during maintenance, ensuring maximum safety by isolating energy sources effectively. Tagout devices function as warning labels signaling that equipment should not be operated, providing a visual deterrent though lacking physical restraint. Combining both lockout and tagout devices enhances workplace safety by clearly communicating hazards and physically preventing equipment activation.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Lockout Device | Tagout Device |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Physically isolates energy sources to prevent accidental startup. | Warns workers not to operate equipment during maintenance. |
| Compliance | Required by OSHA for hazardous energy control. | Used as a supplementary safety measure per OSHA standards. |
| Security | Secures energy-isolating devices preventing operation. | Provides visual warning without physical locking. |
| Types | Padlocks, valve lockouts, circuit breaker lockouts. | Warning tags, safety signs, labels. |
| Effectiveness | Higher protection by physically blocking energy release. | Lower protection; depends on worker compliance. |
| Use Cases | Recommended for high-risk energy control scenarios. | Used when lockout is not feasible or as an additional warning. |
| Removal | Only authorized personnel can remove lockout devices. | Tags can be removed but require adherence to safety protocols. |
Introduction to Lockout and Tagout Devices
Lockout devices physically prevent machines from being energized during maintenance, providing a secure mechanical barrier to hazardous energy sources. Tagout devices serve as warning labels, alerting personnel that equipment is being serviced but do not provide a physical restraint. Combining lockout and tagout devices enhances safety by ensuring both physical prevention and clear communication of energy control measures.
Definition of Lockout Devices
Lockout devices are physical mechanisms designed to isolate energy sources by preventing machinery or equipment from being powered on during maintenance or repair. These devices typically include padlocks, circuit breaker locks, and valve covers that secure switches or valves in the off position to ensure worker safety. Lockout devices are crucial in controlling hazardous energy and complying with OSHA regulations for workplace safety.
Definition of Tagout Devices
Tagout devices are safety tools used to visually indicate that specific equipment or machinery is locked out and should not be operated until maintenance or servicing is complete. Unlike lockout devices, which physically prevent machinery from being activated, tagout devices serve as warning tags to inform workers of potential hazards. These devices are crucial for OSHA compliance and help reduce workplace accidents by clearly communicating lockout status.
Key Differences Between Lockout and Tagout
Lockout devices physically isolate energy sources by securing switches or valves to prevent accidental activation during maintenance, ensuring employee safety. Tagout devices use warning tags to signal that equipment should not be operated but do not provide physical restraint, relying on employee compliance. Lockout offers a more reliable method for energy control by physically blocking operation, whereas tagout serves as a cautionary notice without physically preventing equipment use.
Advantages of Lockout Devices
Lockout devices provide a physical barrier that effectively prevents the accidental energization of machinery, enhancing workplace safety during maintenance. Their secure locking mechanism ensures only authorized personnel can restore power, reducing risks of injury and equipment damage. Unlike tagout devices, lockout systems offer a more visible and reliable control method in hazardous energy isolation.
Advantages of Tagout Devices
Tagout devices offer clear visual warnings by prominently displaying hazard information, reducing the risk of accidental equipment activation during maintenance. Their flexibility allows workers to communicate specific instructions and safety status without physically restraining the energy source. Tagout devices are easy to implement in complex systems where physical lockout is impractical, enhancing communication and overall workplace safety.
Applications in Industrial Safety
Lockout devices physically isolate energy sources to prevent accidental machine activation, ensuring worker safety during maintenance in industrial settings. Tagout devices serve as prominent warning labels indicating that equipment must not be operated until the tag is removed by authorized personnel. Together, lockout and tagout procedures form a critical part of energy control protocols in manufacturing plants, construction sites, and maintenance operations.
Regulatory Standards and Compliance
Lockout devices physically isolate energy sources to ensure machinery cannot be powered during maintenance, complying with OSHA standard 29 CFR 1910.147 for controlling hazardous energy. Tagout devices serve as warning labels but do not provide physical restraint, requiring additional measures to meet OSHA and ANSI safety regulations effectively. Compliance with these standards mandates proper training, documentation, and implementation of either device to prevent accidental equipment startup and ensure worker safety.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Lockout devices physically secure energy-isolating devices to prevent accidental activation, while tagout devices serve as warning tags that alert workers to potential hazards. Common challenges include tagout devices being easily bypassed or ignored, increasing the risk of accidental machine start-up, whereas lockout devices may cause delays if not standardized across equipment. Implementing rigorous training programs and combining lockout and tagout procedures enhances compliance, reduces unauthorized access, and improves overall workplace safety.
Choosing the Right Device for Workplace Safety
Selecting the appropriate lockout or tagout device depends on the specific hazards and equipment types present in the workplace to ensure maximum safety. Lockout devices physically prevent machinery from powering on by securing energy isolating devices, while tagout devices serve as warning labels indicating that equipment should not be operated. Employing lockout devices is generally preferred for higher-risk situations where accidental startup could cause injury, whereas tagout devices may be used when physical locking is impractical but visibility of a safety warning is crucial.
lockout device vs tagout device Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com