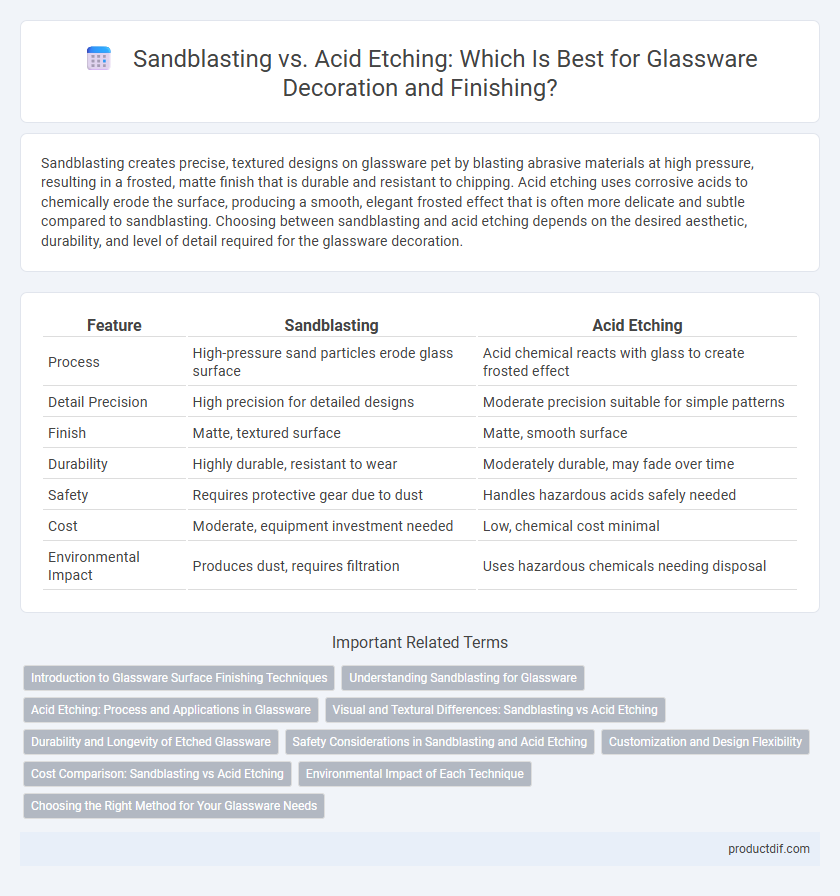
Sandblasting creates precise, textured designs on glassware pet by blasting abrasive materials at high pressure, resulting in a frosted, matte finish that is durable and resistant to chipping. Acid etching uses corrosive acids to chemically erode the surface, producing a smooth, elegant frosted effect that is often more delicate and subtle compared to sandblasting. Choosing between sandblasting and acid etching depends on the desired aesthetic, durability, and level of detail required for the glassware decoration.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Sandblasting | Acid Etching |
|---|---|---|
| Process | High-pressure sand particles erode glass surface | Acid chemical reacts with glass to create frosted effect |
| Detail Precision | High precision for detailed designs | Moderate precision suitable for simple patterns |
| Finish | Matte, textured surface | Matte, smooth surface |
| Durability | Highly durable, resistant to wear | Moderately durable, may fade over time |
| Safety | Requires protective gear due to dust | Handles hazardous acids safely needed |
| Cost | Moderate, equipment investment needed | Low, chemical cost minimal |
| Environmental Impact | Produces dust, requires filtration | Uses hazardous chemicals needing disposal |
Introduction to Glassware Surface Finishing Techniques
Sandblasting and acid etching are two prominent glassware surface finishing techniques that enhance texture and visual appeal by creating frosted or matte effects. Sandblasting uses high-pressure abrasive particles to mechanically abrade the glass surface, offering precise and customizable patterns with a durable finish. Acid etching involves chemical treatment with hydrofluoric acid to produce consistent, smooth frosted areas, ideal for delicate designs and uniform surface opacity.
Understanding Sandblasting for Glassware
Sandblasting for glassware involves propelling fine abrasive particles at high velocity to create intricate, frosted designs with precise control over depth and texture. This technique offers superior durability and scratch resistance compared to acid etching, which relies on chemical reactions to produce surface patterns. Sandblasted glassware provides a more consistent matte finish, making it ideal for decorative and functional applications requiring long-lasting visual appeal.
Acid Etching: Process and Applications in Glassware
Acid etching in glassware involves using hydrofluoric acid or similar chemicals to create a frosted, opaque surface by selectively removing layers of glass. This process allows for precise, intricate designs and durable finishes suitable for decorative items, drinkware, and architectural glass. Acid etching is preferred over sandblasting for achieving finer detail and a consistent matte texture without abrasive residue.
Visual and Textural Differences: Sandblasting vs Acid Etching
Sandblasting produces a uniformly frosted, opaque surface on glassware with a slightly rough texture that diffuses light softly, creating a matte finish. Acid etching results in a smoother, more delicate frosted appearance with finer detail and less surface abrasion, offering a subtle translucence compared to the harsher effect of sandblasting. These visual and textural differences influence the tactile experience and aesthetic appeal, making sandblasted glassware feel coarser and acid-etched glassware smoother to the touch.
Durability and Longevity of Etched Glassware
Sandblasted glassware offers enhanced durability due to the depth and texture of the etched design, which resists wear and maintains clarity over time. Acid etching creates a smoother, more delicate surface that can be less resistant to scratches and environmental damage, potentially reducing the longevity of the glassware. For long-lasting, durable etched glass, sandblasting is the preferred technique, especially in high-use or commercial settings.
Safety Considerations in Sandblasting and Acid Etching
Sandblasting requires comprehensive protective gear including respirators, gloves, and eye protection to prevent inhalation of silica dust and exposure to abrasive particles, which pose significant respiratory and skin hazards. Acid etching involves handling strong acids like hydrofluoric or hydrochloric acid, necessitating the use of acid-resistant gloves, goggles, and ventilation systems to avoid chemical burns and harmful fume inhalation. Proper training and adherence to safety protocols in both methods are critical to minimize risks associated with airborne particles in sandblasting and corrosive chemicals in acid etching.
Customization and Design Flexibility
Sandblasting offers superior customization and design flexibility by allowing precise control over depth and texture, enabling intricate patterns and multi-layered effects on glassware surfaces. Acid etching provides a uniform, frosted finish with less detail variation, which suits simpler or repetitive designs but limits artistic complexity. Choosing between these methods depends on the desired level of detail and tactile dimension in the final glassware customization.
Cost Comparison: Sandblasting vs Acid Etching
Sandblasting typically incurs higher initial equipment costs but offers lower ongoing operational expenses compared to acid etching, which requires costly chemicals and stringent waste disposal measures. Acid etching involves repeated chemical purchases and safety equipment, leading to increased variable costs over time. Overall, sandblasting tends to provide a more cost-effective solution for large-scale or frequent glassware customization projects.
Environmental Impact of Each Technique
Sandblasting glassware consumes significant amounts of compressed air and abrasive materials, which can generate airborne silica dust harmful to both workers and the environment. Acid etching involves hazardous chemicals such as hydrofluoric or hydrochloric acid, posing risks of chemical spills and toxic waste requiring careful disposal to prevent water contamination. Choosing between these techniques depends on balancing the environmental impact of abrasive particulate pollution versus chemical waste management.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Glassware Needs
Sandblasting offers precise and durable designs on glassware by using high-pressure abrasive materials, ideal for complex patterns and deep etching. Acid etching provides a smooth, frosted finish suited for subtle, elegant decorations but requires careful handling due to the use of hazardous chemicals. Selecting between sandblasting and acid etching depends on the desired design detail, durability, and safety considerations for your specific glassware project.
Sandblasting vs Acid etching Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com