Borosciliate glassware pet is known for its exceptional thermal resistance and durability, making it ideal for applications requiring frequent temperature changes and chemical stability. In contrast, soda-lime glassware pet is more affordable and commonly used for everyday containers but lacks the heat tolerance and strength of borosilicate. Choosing borosilicate over soda-lime enhances the lifespan and safety of glassware pet products in demanding environments.
Table of Comparison
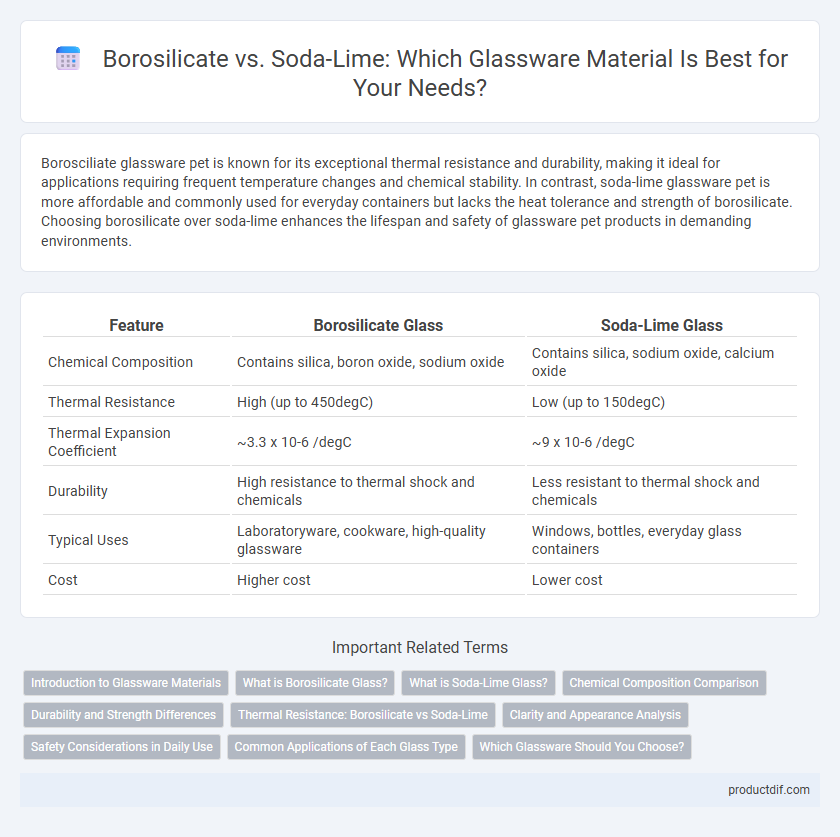
| Feature | Borosilicate Glass | Soda-Lime Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Contains silica, boron oxide, sodium oxide | Contains silica, sodium oxide, calcium oxide |
| Thermal Resistance | High (up to 450degC) | Low (up to 150degC) |
| Thermal Expansion Coefficient | ~3.3 x 10-6 /degC | ~9 x 10-6 /degC |
| Durability | High resistance to thermal shock and chemicals | Less resistant to thermal shock and chemicals |
| Typical Uses | Laboratoryware, cookware, high-quality glassware | Windows, bottles, everyday glass containers |
| Cost | Higher cost | Lower cost |
Introduction to Glassware Materials
Borossilicate glassware contains approximately 80% silica and 13% boron oxide, providing superior thermal resistance and durability compared to soda-lime glass, which is primarily composed of silica, sodium oxide, and calcium oxide. Borosilicate's low thermal expansion coefficient makes it ideal for laboratory and cookware applications, while soda-lime glass is favored for everyday containers and windows due to its lower cost and ease of manufacture. Understanding these material properties is essential for selecting the appropriate glassware based on thermal stability, chemical resistance, and application requirements.
What is Borosilicate Glass?
Borosilicate glass is a type of glass characterized by its low thermal expansion and high resistance to thermal shock, making it ideal for laboratory glassware and cookware. Composed primarily of silica and boron trioxide, it maintains stability under extreme temperature changes compared to soda-lime glass, which has higher thermal expansion and is more prone to cracking. Borosilicate glass's durability and chemical resistance make it a preferred choice for scientific applications and high-quality drinkware.
What is Soda-Lime Glass?
Soda-lime glass is the most common type of glass used worldwide, composed primarily of silica (SiO2), sodium oxide (Na2O), and calcium oxide (CaO). It offers cost-effectiveness and ease of manufacture but lacks the thermal resistance and durability of borosilicate glass. Soda-lime glass is widely used for everyday items such as windows, bottles, and glassware that do not require high heat resistance.
Chemical Composition Comparison
Borosiilicate glass consists primarily of silica (SiO2) and boron trioxide (B2O3), providing enhanced thermal resistance and chemical durability. Soda-lime glass is mainly composed of silica, sodium oxide (Na2O), and calcium oxide (CaO), which makes it more susceptible to chemical corrosion and thermal shock. The boron content in borosilicate glass reduces its coefficient of thermal expansion, distinguishing its chemical stability from the more reactive soda-lime variant.
Durability and Strength Differences
Borosilicate glass offers superior durability and thermal resistance compared to soda-lime glass, making it ideal for laboratory and high-temperature applications. Its low thermal expansion coefficient minimizes the risk of cracking under sudden temperature changes, whereas soda-lime glass is more prone to breakage under thermal stress. Soda-lime glass, although less durable, is commonly used for everyday items due to its lower production cost and sufficient strength for non-extreme conditions.
Thermal Resistance: Borosilicate vs Soda-Lime
Borosilicate glass exhibits superior thermal resistance compared to soda-lime glass, with a low coefficient of thermal expansion around 3.3 x 10^-6 /degC, allowing it to withstand rapid temperature changes without cracking. Soda-lime glass has a higher coefficient near 9 x 10^-6 /degC, making it more susceptible to thermal shock and less ideal for high-temperature applications. This thermal durability makes borosilicate glass the preferred choice for laboratory glassware, cookware, and heat-resistant bottles.
Clarity and Appearance Analysis
Borosciliate glass exhibits superior clarity and brilliance compared to soda-lime glass, attributed to its higher purity and fewer impurities that cause haze or discoloration. The low thermal expansion coefficient of borosilicate ensures minimal stress-induced distortions, enhancing optical clarity and consistent appearance over time. Soda-lime glass, while more economical, often contains higher iron content, leading to a noticeable greenish tint that reduces transparency and visual appeal.
Safety Considerations in Daily Use
Boronsilicate glass offers superior thermal resistance and minimizes the risk of breakage under rapid temperature changes, making it safer for everyday kitchen use compared to soda-lime glass. Soda-lime glass, while more affordable and widely available, is more prone to cracking or shattering when exposed to extreme heat or sudden temperature fluctuations. Choosing borosilicate glassware enhances safety for cooking, storing hot liquids, and repeated thermal stress scenarios.
Common Applications of Each Glass Type
Borosiilicate glass is commonly used in laboratory equipment, cookware, and high-end glassware due to its excellent thermal resistance and durability. Soda-lime glass is widely utilized in everyday applications such as window panes, bottles, and jars because of its affordability and ease of manufacturing. Each glass type's unique properties make borosilicate ideal for high-temperature and chemical-resistant uses, while soda-lime suits general-purpose packaging and construction needs.
Which Glassware Should You Choose?
Borosiilicate glassware offers superior thermal resistance and durability, making it ideal for laboratory and high-heat applications, whereas soda-lime glassware is more affordable and sufficient for everyday use such as beverage containers and decorative items. Choosing borosilicate glass ensures resistance to thermal shock and chemical corrosion, while soda-lime glass prioritizes cost-effectiveness and availability. The decision depends on the need for heat resistance, durability, and budget constraints in glassware selection.
Borosciliate vs Soda-Lime Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com