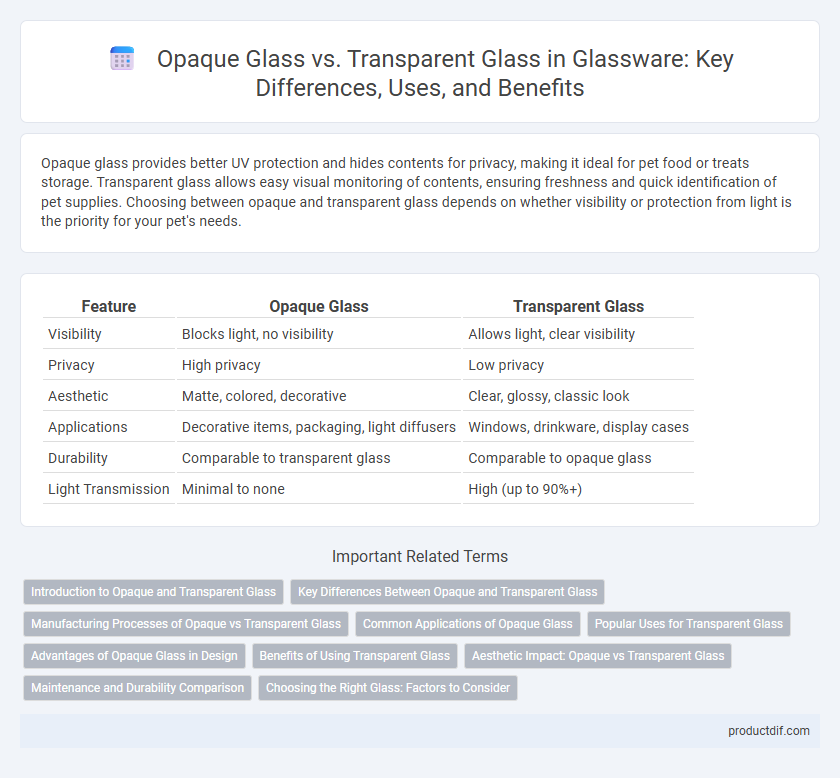
Opaque glass provides better UV protection and hides contents for privacy, making it ideal for pet food or treats storage. Transparent glass allows easy visual monitoring of contents, ensuring freshness and quick identification of pet supplies. Choosing between opaque and transparent glass depends on whether visibility or protection from light is the priority for your pet's needs.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Opaque Glass | Transparent Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Visibility | Blocks light, no visibility | Allows light, clear visibility |
| Privacy | High privacy | Low privacy |
| Aesthetic | Matte, colored, decorative | Clear, glossy, classic look |
| Applications | Decorative items, packaging, light diffusers | Windows, drinkware, display cases |
| Durability | Comparable to transparent glass | Comparable to opaque glass |
| Light Transmission | Minimal to none | High (up to 90%+) |
Introduction to Opaque and Transparent Glass
Opaque glass blocks light transmission due to its dense composition or coating, making it ideal for privacy and decorative purposes. Transparent glass allows nearly full light passage, providing clear visibility while serving functional roles in windows, lenses, and display cases. Both types of glass leverage unique physical properties to meet specific architectural and industrial needs.
Key Differences Between Opaque and Transparent Glass
Opaque glass blocks light transmission, providing privacy and heat insulation, whereas transparent glass allows light to pass through clearly, enhancing visibility and natural illumination. Opaque glass often contains additives or coatings that prevent light penetration, making it suitable for decorative or functional applications requiring concealment. Transparent glass, typically made from purified silica, emphasizes clarity and optical quality, ideal for windows, display cases, and lenses.
Manufacturing Processes of Opaque vs Transparent Glass
Opaque glass is produced by incorporating specific metal oxides or other additives during the molten stage, which block light transmission and create a solid, non-transparent appearance. In contrast, transparent glass manufacturing involves careful control of raw materials and melting conditions to minimize impurities and crystallization, resulting in clear, unobstructed glass. The cooling and annealing processes for both types vary to optimize structural integrity and final optical properties specific to opaque or transparent glass.
Common Applications of Opaque Glass
Opaque glass is commonly used in applications requiring privacy and light control, such as bathroom windows, decorative panels, and glass doors. Its ability to block light while maintaining durability makes it ideal for architectural features and interior design elements in homes and commercial spaces. Opaque glass is also popular in the production of glassware like bottles and jars where contents need protection from light exposure.
Popular Uses for Transparent Glass
Transparent glass is widely used in architectural applications such as windows, skylights, and glass doors, offering natural light and visibility while maintaining energy efficiency. It is essential in automotive manufacturing for windshields and windows, providing safety and clear vision for drivers. In consumer products, transparent glass is favored for drinkware, display cases, and electronic screens due to its clarity and aesthetic appeal.
Advantages of Opaque Glass in Design
Opaque glass offers superior protection against light, preserving the integrity of light-sensitive contents such as perfumes and pharmaceuticals. Its ability to provide a sleek, modern aesthetic enhances product differentiation and brand identity in retail environments. The versatility in color and texture options allows designers to create visually striking packaging that stands out on shelves.
Benefits of Using Transparent Glass
Transparent glass offers superior clarity, allowing optimal light transmission and visibility, which enhances aesthetic appeal and user experience. It aids in monitoring contents without opening containers, improving convenience and safety in applications like food storage and laboratory use. Its ability to showcase colors and textures makes it ideal for display purposes in retail and interior design.
Aesthetic Impact: Opaque vs Transparent Glass
Opaque glass creates a bold aesthetic impact by offering solid color and blocking light, enhancing privacy and adding a sense of mystery to interior designs. Transparent glass, on the other hand, maximizes natural light flow and visual connection between spaces, contributing to an open, airy, and modern ambiance. The choice between opaque and transparent glass significantly influences spatial perception and design mood through light manipulation and visual accessibility.
Maintenance and Durability Comparison
Opaque glass requires less frequent cleaning than transparent glass because it hides smudges, fingerprints, and stains better, reducing visible wear over time. Transparent glass demands more regular maintenance to preserve clarity, as scratches and dirt are more noticeable and can weaken its aesthetic appeal. In terms of durability, both types offer similar resistance to breakage, but opaque glass can better conceal minor imperfections and surface damage that might otherwise affect transparent glass's visual quality.
Choosing the Right Glass: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right glassware involves considering the transparency level, where opaque glass offers privacy and better light protection, ideal for storing sensitive liquids like medications or oils. Transparent glass allows easy visibility of contents, making it preferred for showcasing beverages or decorative items. Factors like light sensitivity, aesthetic preference, and usage purpose should guide the selection between opaque and transparent glass.
Opaque glass vs Transparent glass Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com