Borosilicate glassware pet is known for its superior durability and resistance to thermal shock compared to soda-lime glass, making it ideal for high-temperature applications. Soda-lime glass, while more affordable and widely available, is less resistant to chemical corrosion and temperature fluctuations. Choosing borosilicate ensures longer-lasting performance and greater safety for pet-related glass containers.
Table of Comparison
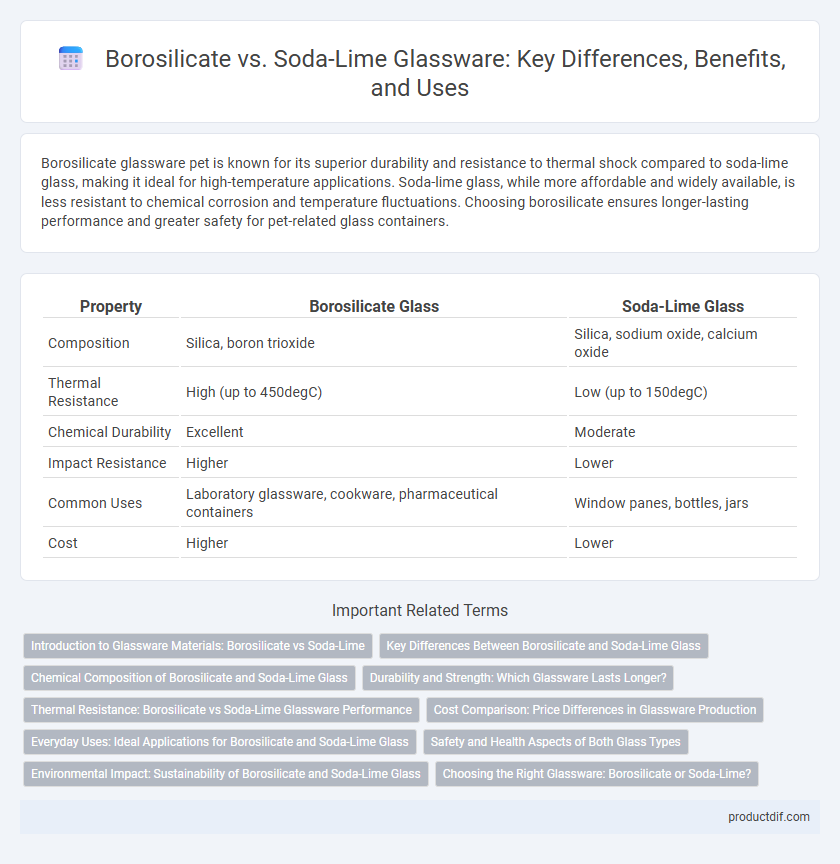
| Property | Borosilicate Glass | Soda-Lime Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Silica, boron trioxide | Silica, sodium oxide, calcium oxide |
| Thermal Resistance | High (up to 450degC) | Low (up to 150degC) |
| Chemical Durability | Excellent | Moderate |
| Impact Resistance | Higher | Lower |
| Common Uses | Laboratory glassware, cookware, pharmaceutical containers | Window panes, bottles, jars |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Introduction to Glassware Materials: Borosilicate vs Soda-Lime
Borosilicate glass, composed of silica and boron trioxide, offers superior thermal resistance and chemical durability compared to soda-lime glass, which primarily consists of silica, soda, and lime. Soda-lime glass is widely used for everyday glassware due to its cost-effectiveness and ease of manufacture, yet it is more prone to thermal shock and chemical corrosion. Laboratory and high-performance glassware favor borosilicate for its robustness under rapid temperature changes and exposure to harsh chemicals.
Key Differences Between Borosilicate and Soda-Lime Glass
Borosilicate glass offers superior thermal resistance and chemical durability compared to soda-lime glass, making it ideal for laboratory and cookware applications. Soda-lime glass is more affordable and widely used in everyday items like windows and bottles but is less resistant to temperature fluctuations and chemical corrosion. The distinct composition of borosilicate glass, with added boron oxide, reduces thermal expansion, enhancing its strength and longevity.
Chemical Composition of Borosilicate and Soda-Lime Glass
Borosilicate glass contains approximately 80% silica (SiO2) and 12-13% boron oxide (B2O3), which enhances its thermal resistance and chemical durability. Soda-lime glass typically consists of 70-75% silica, 12-15% sodium oxide (Na2O), and 5-10% calcium oxide (CaO), making it more prone to thermal shock and chemical corrosion compared to borosilicate. The differing chemical compositions result in borosilicate glass being preferred for laboratory and high-heat applications, while soda-lime is commonly used in everyday glassware due to its cost-effectiveness.
Durability and Strength: Which Glassware Lasts Longer?
Borosilicate glassware offers superior durability and strength due to its resistance to thermal shock and chemical corrosion, making it ideal for laboratory and kitchen use. Soda-lime glass, while more affordable, is more prone to breakage and less resistant to temperature fluctuations, reducing its overall lifespan. For long-lasting glassware, borosilicate significantly outperforms soda-lime in durability and strength.
Thermal Resistance: Borosilicate vs Soda-Lime Glassware Performance
Borosilicate glassware offers superior thermal resistance compared to soda-lime glass, withstanding temperatures up to 500degC without deformation or cracking. Soda-lime glass typically endures temperatures up to 250degC but is prone to thermal shock due to its lower expansion coefficient. This makes borosilicate the preferred choice for laboratory and high-heat applications requiring durability and reliability under rapid temperature changes.
Cost Comparison: Price Differences in Glassware Production
Borosilicate glassware generally commands higher prices due to its superior thermal resistance and chemical durability, which require more expensive raw materials like boron oxide and a complex manufacturing process. In contrast, soda-lime glass is more cost-effective to produce, benefiting from abundant raw materials such as silica, soda ash, and limestone, making it the preferred choice for mass-market glassware. Despite the higher initial cost, borosilicate's longevity and resistance to thermal shock often provide better value in specialized laboratory and culinary applications.
Everyday Uses: Ideal Applications for Borosilicate and Soda-Lime Glass
Borosilicate glass is ideal for laboratory equipment, cookware, and high-temperature applications due to its superior thermal resistance and durability. Soda-lime glass is commonly used in windows, bottles, and jars, favored for its cost-effectiveness and ease of manufacturing. Each type's unique chemical composition determines its suitability for specific everyday uses, with borosilicate excelling under thermal stress and soda-lime preferred for standard consumer products.
Safety and Health Aspects of Both Glass Types
Borosilicate glass offers superior thermal resistance and chemical durability, reducing the risk of breakage and leaching harmful substances into food or beverages compared to soda-lime glass. Soda-lime glass, commonly used in everyday drinkware, contains higher amounts of sodium oxide which may weaken its structural integrity under rapid temperature changes, posing a safety concern. Borosilicate's low thermal expansion and inert composition make it a safer choice for laboratory and kitchen use, minimizing exposure to potentially hazardous contaminants.
Environmental Impact: Sustainability of Borosilicate and Soda-Lime Glass
Borosilicate glass offers superior durability and thermal resistance, reducing the need for frequent replacements and lowering waste generation compared to soda-lime glass. Soda-lime glass, although more energy-efficient to produce, tends to have a shorter lifespan and higher breakage rates, contributing to increased environmental burden. Recycling rates for soda-lime glass are generally higher, but the extended usability of borosilicate glass supports long-term sustainability by minimizing resource consumption.
Choosing the Right Glassware: Borosilicate or Soda-Lime?
Borosilicate glassware offers superior thermal resistance and chemical durability, making it ideal for laboratory and high-heat applications, while soda-lime glass is more affordable and commonly used for everyday drinkware and containers. Choosing between borosilicate and soda-lime depends on the need for heat resistance, chemical stability, and budget constraints. Borosilicate withstands rapid temperature changes up to 450degC, whereas soda-lime glass is prone to cracking under thermal stress but excels in cost-effectiveness for routine use.
Borosilicate vs Soda-Lime Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com