Potting mix is specifically formulated for container plants, offering lightweight drainage and aeration properties essential for root health, while garden soil is denser and better suited for in-ground planting due to its natural composition and nutrient content. Potting mix typically contains organic matter, peat moss, and perlite or vermiculite to improve moisture retention and airflow, unlike garden soil which may include heavier clay and minerals. Choosing the correct medium enhances plant growth, as potting mix prevents waterlogging in pots and garden soil provides structural support and nutrients in open ground.
Table of Comparison
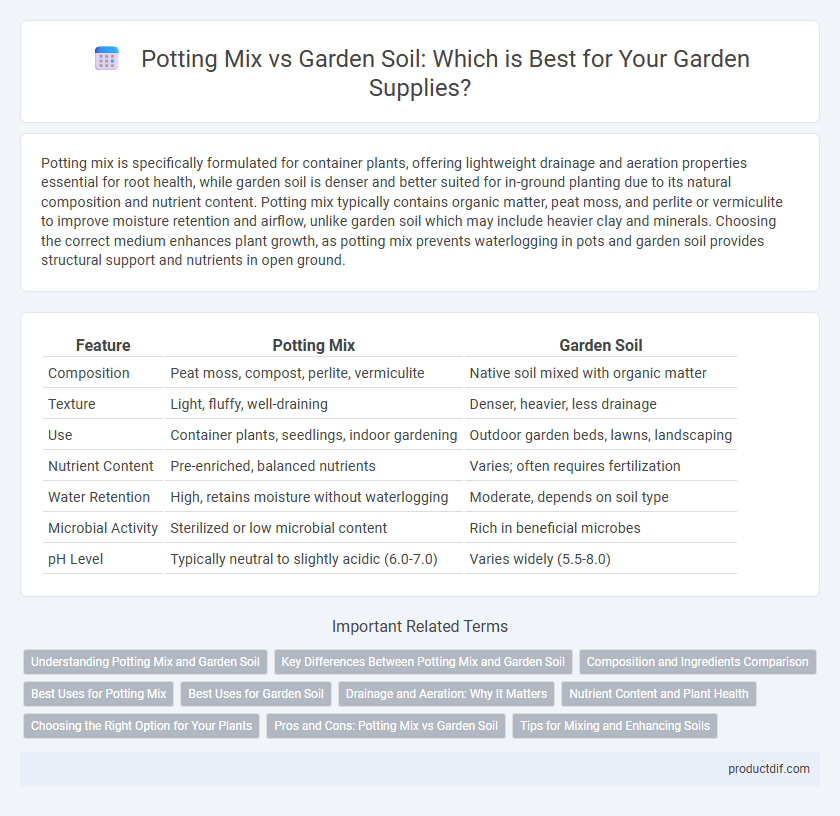
| Feature | Potting Mix | Garden Soil |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Peat moss, compost, perlite, vermiculite | Native soil mixed with organic matter |
| Texture | Light, fluffy, well-draining | Denser, heavier, less drainage |
| Use | Container plants, seedlings, indoor gardening | Outdoor garden beds, lawns, landscaping |
| Nutrient Content | Pre-enriched, balanced nutrients | Varies; often requires fertilization |
| Water Retention | High, retains moisture without waterlogging | Moderate, depends on soil type |
| Microbial Activity | Sterilized or low microbial content | Rich in beneficial microbes |
| pH Level | Typically neutral to slightly acidic (6.0-7.0) | Varies widely (5.5-8.0) |
Understanding Potting Mix and Garden Soil
Potting mix is a lightweight, sterile growing medium designed for container gardening, composed of peat moss, perlite, vermiculite, and organic matter to ensure excellent drainage and aeration. Garden soil, on the other hand, consists of natural soil blended with compost and minerals, optimized for in-ground planting with a denser texture that retains more moisture. Understanding the specific uses and composition of potting mix versus garden soil is key to promoting healthy plant growth and preventing issues like root rot or poor nutrient uptake.
Key Differences Between Potting Mix and Garden Soil
Potting mix is specifically formulated for container gardening, featuring lightweight components like peat moss, perlite, and vermiculite to ensure excellent drainage and aeration, while garden soil is denser, often containing natural soil with organic matter suitable for in-ground planting. Potting mix is sterile and free from weed seeds and pathogens, making it ideal for indoor and container plants, whereas garden soil can harbor pests and requires amendments for optimal growth. Key differences lie in texture, nutrient content, and usage, where potting mix prioritizes moisture retention and root health in confined spaces, and garden soil supports plants rooted directly in the earth.
Composition and Ingredients Comparison
Potting mix typically consists of a blend of peat moss, vermiculite, perlite, and composted bark, designed to provide excellent drainage and aeration for container plants. Garden soil combines native soil with organic matter such as compost, sand, and clay, offering a denser composition suited for in-ground planting. The key difference lies in potting mix's lightweight, sterile formula ideal for potted plants, whereas garden soil contains natural microorganisms and nutrients for outdoor garden beds.
Best Uses for Potting Mix
Potting mix is specially formulated for container gardening, offering excellent drainage, aeration, and moisture retention that supports healthy root development in potted plants. It typically contains peat moss, perlite, and vermiculite, which create a lightweight medium ideal for indoor plants, seedlings, and annuals. Unlike garden soil, potting mix minimizes compaction and provides a sterile environment, reducing the risk of pests and diseases in containers.
Best Uses for Garden Soil
Garden soil is ideal for outdoor planting beds and landscaping projects because it contains a natural blend of sand, silt, clay, and organic matter that supports native plant growth. It enhances soil structure, promotes drainage, and provides essential nutrients for established trees, shrubs, and perennials. Unlike potting mix, garden soil is best suited for in-ground applications rather than container gardening.
Drainage and Aeration: Why It Matters
Potting mix offers superior drainage and aeration compared to garden soil, essential for healthy root development and preventing waterlogged conditions. Its lightweight composition includes materials like peat moss, perlite, and vermiculite that create air pockets, promoting oxygen flow to roots. In contrast, garden soil is denser and can compact easily, leading to poor drainage and reduced aeration, which may hinder plant growth and increase the risk of root diseases.
Nutrient Content and Plant Health
Potting mix contains a balanced blend of nutrients, organic matter, and aeration components designed to promote rapid root growth and overall plant health in container gardening. Garden soil, often denser and less nutrient-rich, may lack the ideal structure and essential nutrients required for potted plants, potentially leading to poor drainage and root compaction. Choosing potting mix over garden soil ensures optimized nutrient availability and enhanced aeration, vital for healthy, thriving container plants.
Choosing the Right Option for Your Plants
Potting mix offers a lightweight, well-draining medium enriched with nutrients and organic matter, ideal for container plants and seedlings. Garden soil contains heavier minerals and natural microorganisms, making it suitable for in-ground planting where soil structure supports root growth. Selecting the right option depends on plant type, container use, and desired moisture retention, ensuring optimal growth and health.
Pros and Cons: Potting Mix vs Garden Soil
Potting mix offers excellent drainage and aeration, making it ideal for container gardening, but it often lacks the nutrients found in garden soil. Garden soil provides natural fertility and structure suitable for in-ground planting, yet it can be dense and poorly draining in pots. Choosing between potting mix and garden soil depends on the specific plant needs and growing environment, balancing moisture retention with nutrient availability.
Tips for Mixing and Enhancing Soils
Combine potting mix with garden soil to improve aeration and drainage, aiming for a ratio of three parts potting mix to one part garden soil for optimal plant growth. Enrich the mixture with organic matter such as compost or aged manure to boost nutrient content and microbial activity. Regularly test soil pH and adjust with lime or sulfur to create the ideal environment for nutrient uptake.
Potting mix vs Garden soil Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com