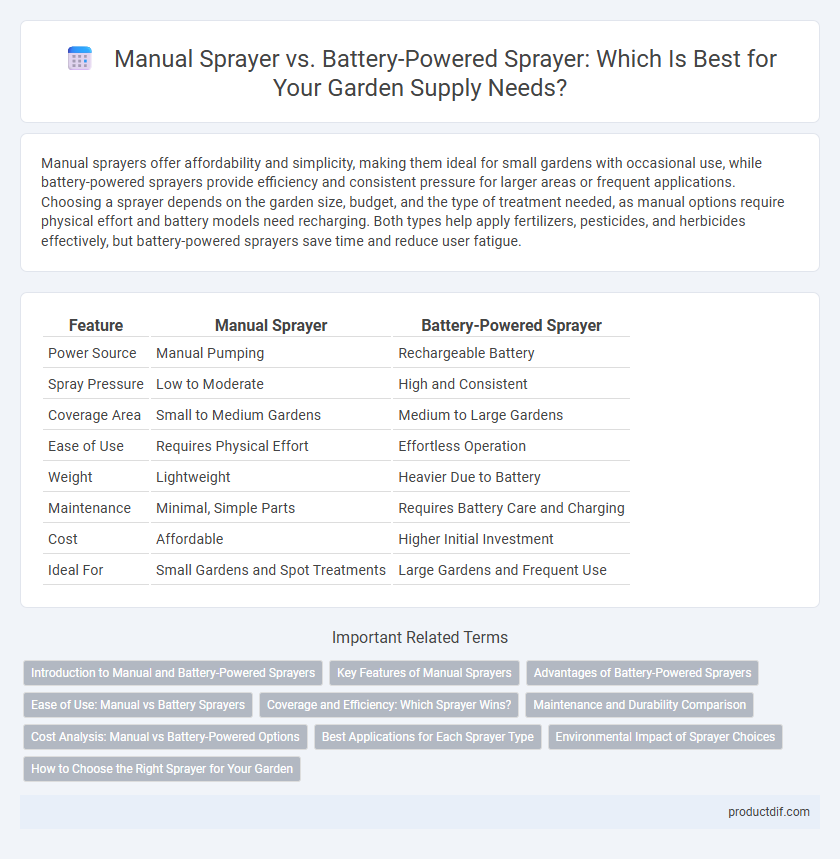
Manual sprayers offer affordability and simplicity, making them ideal for small gardens with occasional use, while battery-powered sprayers provide efficiency and consistent pressure for larger areas or frequent applications. Choosing a sprayer depends on the garden size, budget, and the type of treatment needed, as manual options require physical effort and battery models need recharging. Both types help apply fertilizers, pesticides, and herbicides effectively, but battery-powered sprayers save time and reduce user fatigue.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Manual Sprayer | Battery-Powered Sprayer |
|---|---|---|
| Power Source | Manual Pumping | Rechargeable Battery |
| Spray Pressure | Low to Moderate | High and Consistent |
| Coverage Area | Small to Medium Gardens | Medium to Large Gardens |
| Ease of Use | Requires Physical Effort | Effortless Operation |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier Due to Battery |
| Maintenance | Minimal, Simple Parts | Requires Battery Care and Charging |
| Cost | Affordable | Higher Initial Investment |
| Ideal For | Small Gardens and Spot Treatments | Large Gardens and Frequent Use |
Introduction to Manual and Battery-Powered Sprayers
Manual sprayers operate through hand-pump pressure, offering precise control for small to medium garden tasks with minimal maintenance and no reliance on power sources. Battery-powered sprayers feature rechargeable batteries that provide consistent pressure and longer spray durations, ideal for larger gardens and frequent use. Choosing between them depends on garden size, spray frequency, and the need for portability versus convenience in application.
Key Features of Manual Sprayers
Manual sprayers boast simplicity with no reliance on batteries or electricity, making them lightweight and easy to maintain. Their compact design and adjustable nozzles enable precise application of herbicides, pesticides, and fertilizers. Ideal for small to medium gardens, manual sprayers offer cost-effective, eco-friendly pest and plant care solutions.
Advantages of Battery-Powered Sprayers
Battery-powered sprayers offer increased efficiency and ease of use compared to manual sprayers, allowing gardeners to cover larger areas with less physical effort. These sprayers provide consistent pressure and even spray patterns, improving the application of fertilizers, pesticides, and herbicides. Their rechargeable batteries ensure longer operational times, reducing downtime and enhancing productivity in garden maintenance tasks.
Ease of Use: Manual vs Battery Sprayers
Manual sprayers require physical pumping to build pressure, demanding consistent effort that can cause user fatigue during extended use. Battery-powered sprayers feature electric pumps that maintain constant pressure with minimal manual intervention, significantly reducing physical strain and increasing efficiency. Ergonomic designs in battery models also enhance comfort and usability, making them preferable for larger gardens or frequent applications.
Coverage and Efficiency: Which Sprayer Wins?
Manual sprayers provide precise control for small garden areas but require consistent physical effort, limiting coverage and efficiency over time. Battery-powered sprayers offer expansive coverage with adjustable pressure settings, reducing fatigue and increasing application speed for large-scale gardening tasks. Efficiency gains with battery-powered models result from uniform spray patterns and faster operation, making them ideal for extensive garden maintenance.
Maintenance and Durability Comparison
Manual sprayers require regular cleaning after each use to prevent nozzle clogging and maintain optimal pressure, while battery-powered sprayers demand battery care and occasional motor inspection to ensure longevity. The durability of manual sprayers often depends on the tank and seal materials, typically lasting longer due to fewer electronic components, whereas battery-powered models may face wear in electrical parts but offer more consistent spray performance. Choosing between them involves weighing the simplicity and low maintenance of manual sprayers against the advanced features and maintenance needs of battery-powered alternatives.
Cost Analysis: Manual vs Battery-Powered Options
Manual sprayers typically cost between $20 and $50, offering affordability with minimal maintenance expenses but requiring physical effort for operation. Battery-powered sprayers range from $80 to $200, with higher upfront costs offset by increased efficiency and reduced labor over time. Evaluating long-term investment includes considering battery replacement costs and energy usage against manual sprayer durability and ease of repair.
Best Applications for Each Sprayer Type
Manual sprayers excel in small garden areas or spot treatments where precision and control are essential, especially for applying herbicides or insecticides on individual plants. Battery-powered sprayers are ideal for larger gardens or commercial landscapes, providing efficient coverage with less physical effort, suitable for widespread fertilizing and pest control. Choosing the right sprayer depends on garden size, frequency of use, and the need for portability versus coverage speed.
Environmental Impact of Sprayer Choices
Manual sprayers produce zero emissions during operation, making them an eco-friendly choice for garden care. Battery-powered sprayers, while more efficient and less physically demanding, rely on electricity that may come from non-renewable energy sources and require battery disposal, raising environmental concerns. Selecting a manual sprayer reduces carbon footprint and prevents chemical leakage linked to battery waste, promoting sustainable gardening practices.
How to Choose the Right Sprayer for Your Garden
Choosing the right sprayer for your garden depends on the garden size and spraying frequency. Manual sprayers are ideal for small gardens and light tasks due to their affordability and low maintenance. Battery-powered sprayers offer greater efficiency and coverage for larger areas, reducing physical strain with rechargeable lithium-ion batteries.
Manual sprayer vs Battery-powered sprayer Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com