Hydroponics offers precise nutrient control and faster plant growth compared to traditional soil cultivation, making it ideal for limited spaces and controlled environments. Soil cultivation promotes natural microbial activity and supports a diverse ecosystem, enhancing plant resilience and flavor complexity. Choosing between hydroponics and soil depends on factors such as resource availability, crop type, and desired yield quality.
Table of Comparison
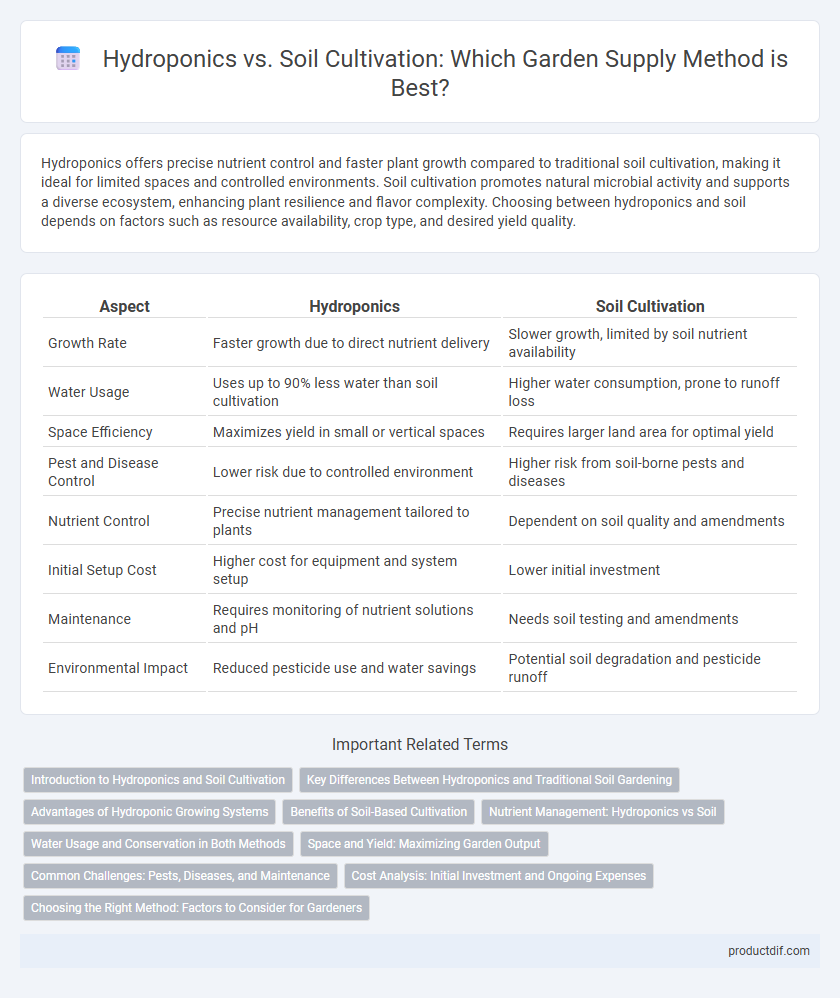
| Aspect | Hydroponics | Soil Cultivation |
|---|---|---|
| Growth Rate | Faster growth due to direct nutrient delivery | Slower growth, limited by soil nutrient availability |
| Water Usage | Uses up to 90% less water than soil cultivation | Higher water consumption, prone to runoff loss |
| Space Efficiency | Maximizes yield in small or vertical spaces | Requires larger land area for optimal yield |
| Pest and Disease Control | Lower risk due to controlled environment | Higher risk from soil-borne pests and diseases |
| Nutrient Control | Precise nutrient management tailored to plants | Dependent on soil quality and amendments |
| Initial Setup Cost | Higher cost for equipment and system setup | Lower initial investment |
| Maintenance | Requires monitoring of nutrient solutions and pH | Needs soil testing and amendments |
| Environmental Impact | Reduced pesticide use and water savings | Potential soil degradation and pesticide runoff |
Introduction to Hydroponics and Soil Cultivation
Hydroponics is a soil-free cultivation method where plants grow in nutrient-rich water solutions, enabling faster growth and higher yields in controlled environments. Soil cultivation relies on traditional earth medium, providing natural nutrients and microbial activity essential for plant health and ecosystem balance. Both methods offer unique benefits, with hydroponics excelling in space efficiency and soil cultivation supporting biodiversity and long-term sustainability.
Key Differences Between Hydroponics and Traditional Soil Gardening
Hydroponics uses nutrient-rich water solutions to grow plants without soil, allowing for faster growth and higher yields compared to traditional soil gardening, which relies on natural soil nutrients and microbial activity. Hydroponic systems offer precise control over environmental factors like pH, nutrient concentration, and water delivery, reducing the risk of pests and diseases common in soil cultivation. Soil gardening supports beneficial ecosystems and organic matter, enhancing plant resilience but requiring more space and longer growth cycles.
Advantages of Hydroponic Growing Systems
Hydroponic growing systems offer superior water efficiency, using up to 90% less water than traditional soil cultivation by recirculating nutrient solutions directly to plant roots. These systems enable faster plant growth and higher yields by delivering precise nutrient control and optimal oxygen levels, minimizing nutrient loss. Additionally, hydroponics reduces the risk of soil-borne diseases and pests, promoting healthier plants and decreasing the need for pesticides.
Benefits of Soil-Based Cultivation
Soil-based cultivation enhances plant growth by providing natural nutrients, beneficial microbes, and organic matter that improve soil structure and water retention. This method supports biodiversity and fosters stronger root systems, which leads to improved plant resilience and higher-quality yields. Soil cultivation also reduces dependency on synthetic inputs, promoting sustainable and eco-friendly gardening practices.
Nutrient Management: Hydroponics vs Soil
Hydroponics allows precise control over nutrient delivery by directly supplying water-soluble fertilizers to plant roots, resulting in faster growth and higher nutrient efficiency compared to soil cultivation. Soil cultivation relies on organic matter and microbial activity to release nutrients gradually, often requiring regular soil testing and amendments to maintain optimal fertility. Nutrient management in hydroponics reduces waste and environmental impact, while soil cultivation supports biodiversity and enhances natural nutrient cycling.
Water Usage and Conservation in Both Methods
Hydroponics systems use up to 90% less water than traditional soil cultivation by recycling nutrient solutions, reducing water waste significantly. Soil cultivation typically requires more frequent watering due to evaporation and runoff, leading to higher water consumption. Efficient water management in hydroponics supports sustainable gardening practices by conserving precious water resources.
Space and Yield: Maximizing Garden Output
Hydroponics systems enable gardeners to maximize yield in limited spaces by allowing plants to grow vertically and closer together without soil constraints. Soil cultivation requires more area for root expansion, often resulting in lower density planting and reduced output per square foot. Optimizing garden output depends on choosing hydroponic setups for compact environments and high-yield production.
Common Challenges: Pests, Diseases, and Maintenance
Hydroponics and soil cultivation both face common challenges such as pest infestations, disease outbreaks, and ongoing maintenance demands, but hydroponic systems often require more precise monitoring of nutrient levels and water quality to prevent root diseases. Soil cultivation struggles with soil-borne pests and diseases like nematodes and fungi, which can be mitigated through crop rotation and organic amendments. Maintenance in hydroponics includes frequent system checks and cleaning to avoid algae growth and equipment failure, while soil cultivation relies heavily on tilling, weeding, and soil fertility management.
Cost Analysis: Initial Investment and Ongoing Expenses
Hydroponics systems typically demand a higher initial investment due to the cost of specialized equipment like pumps, grow trays, and nutrient solutions, while soil cultivation requires basic tools and soil preparation with lower upfront costs. Ongoing expenses for hydroponics include electricity for lighting and water circulation, alongside nutrient replenishment, whereas soil cultivation incurs costs for fertilizers, pest control, and potential soil amendments. Over time, hydroponics can offer higher efficiency and reduced water usage, potentially offsetting some operational costs compared to traditional soil gardening.
Choosing the Right Method: Factors to Consider for Gardeners
Hydroponics offers precise nutrient control and faster growth, ideal for limited spaces and water conservation, while soil cultivation supports natural microbial activity and offers ease of setup for traditional gardeners. Consider factors such as available space, budget, plant types, and environmental conditions when choosing between hydroponics and soil cultivation. Assessing maintenance requirements and desired crop yields helps gardeners select the most effective growing method.
Hydroponics vs Soil Cultivation Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com