Biodegradable mulch offers an eco-friendly alternative to plastic mulch by naturally breaking down into the soil, reducing waste and environmental impact. It enhances soil health by improving moisture retention and temperature regulation without leaving harmful residues. Plastic mulch, while effective for weed control and moisture conservation, often contributes to long-term pollution and disposal challenges.
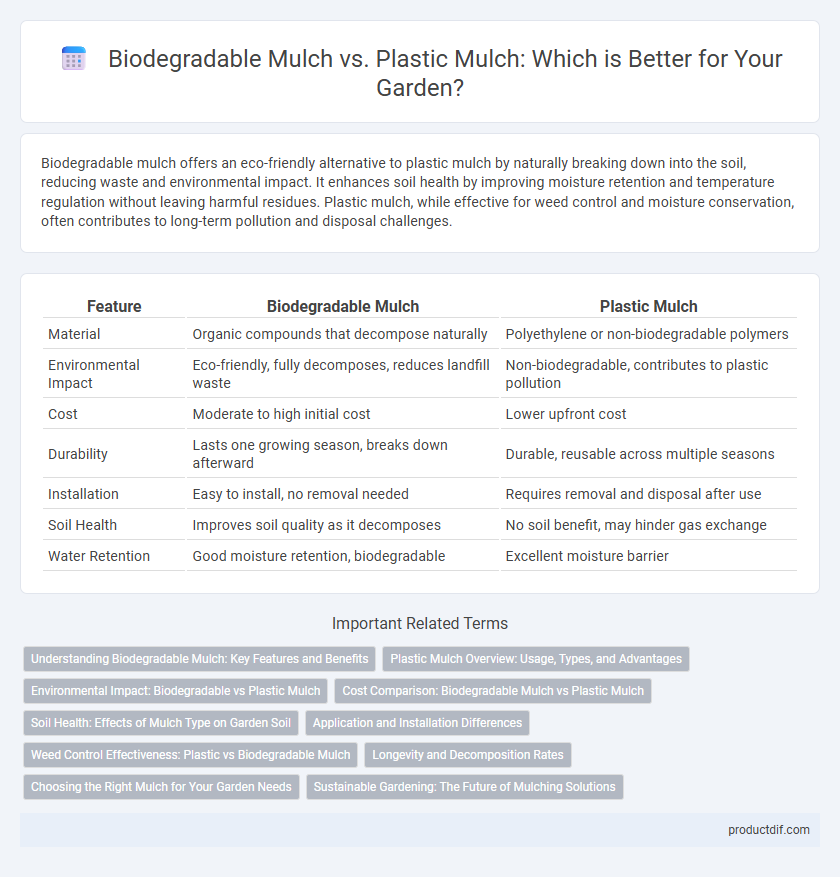
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Biodegradable Mulch | Plastic Mulch |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Organic compounds that decompose naturally | Polyethylene or non-biodegradable polymers |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, fully decomposes, reduces landfill waste | Non-biodegradable, contributes to plastic pollution |
| Cost | Moderate to high initial cost | Lower upfront cost |
| Durability | Lasts one growing season, breaks down afterward | Durable, reusable across multiple seasons |
| Installation | Easy to install, no removal needed | Requires removal and disposal after use |
| Soil Health | Improves soil quality as it decomposes | No soil benefit, may hinder gas exchange |
| Water Retention | Good moisture retention, biodegradable | Excellent moisture barrier |
Understanding Biodegradable Mulch: Key Features and Benefits
Biodegradable mulch is made from natural materials that decompose into the soil, reducing plastic waste and eliminating the need for removal after the growing season. It enhances soil moisture retention, suppresses weeds effectively, and improves soil health by adding organic matter as it breaks down. Unlike plastic mulch, biodegradable mulch supports sustainable gardening practices by minimizing environmental impact and promoting soil biodiversity.
Plastic Mulch Overview: Usage, Types, and Advantages
Plastic mulch is widely used in gardening and agriculture for its durability and effectiveness in weed suppression, soil temperature regulation, and moisture retention. Common types include polyethylene, which comes in various colors like black, clear, and reflective, each tailored to specific crop needs. Advantages of plastic mulch encompass enhanced crop yield, improved soil structure, and reduced need for herbicides, making it a preferred choice despite environmental concerns.
Environmental Impact: Biodegradable vs Plastic Mulch
Biodegradable mulch decomposes naturally, reducing plastic waste and minimizing soil pollution compared to traditional plastic mulch, which contributes to long-term environmental contamination and landfill accumulation. The use of biodegradable mulch enhances soil health by allowing organic matter to integrate into the ground, promoting microbial activity and reducing carbon footprint in gardening practices. Plastic mulch often leads to microplastic buildup in soil, posing risks to ecosystems and water quality, whereas biodegradable options support sustainable agriculture and promote ecological balance.
Cost Comparison: Biodegradable Mulch vs Plastic Mulch
Biodegradable mulch generally has a higher upfront cost compared to plastic mulch, but it eliminates disposal expenses since it decomposes naturally in the soil. Plastic mulch often requires additional labor and fees for removal and recycling, increasing total long-term costs. Considering lifecycle expenses, biodegradable mulch can offer greater economic efficiency despite its initial price.
Soil Health: Effects of Mulch Type on Garden Soil
Biodegradable mulch improves soil health by breaking down naturally, enriching the soil with organic matter and enhancing microbial activity, whereas plastic mulch can create a barrier that restricts water infiltration and gas exchange, potentially harming soil structure. The decomposition of biodegradable mulch supports nutrient cycling and reduces the risk of soil contamination. In contrast, plastic mulch often requires removal and disposal, which may lead to soil compaction and long-term degradation of soil quality.
Application and Installation Differences
Biodegradable mulch decomposes naturally after application, eliminating the need for removal and reducing labor costs, making it ideal for sustainable gardening practices. Plastic mulch requires manual installation with stakes or staples and must be removed at the end of the season to prevent environmental waste. Biodegradable mulch offers a simpler, eco-friendly installation process that supports soil health, while plastic mulch provides longer-lasting weed control but demands more intensive cleanup.
Weed Control Effectiveness: Plastic vs Biodegradable Mulch
Plastic mulch provides superior weed control by creating a durable barrier that blocks sunlight and prevents weed growth more effectively than biodegradable mulch. Biodegradable mulch, while environmentally friendly, may break down prematurely, reducing its ability to suppress weeds over the entire growing season. Gardeners seeking maximum weed control often prefer plastic mulch for its long-lasting, consistent performance in maintaining weed-free soil.
Longevity and Decomposition Rates
Biodegradable mulch typically lasts one to three growing seasons, breaking down naturally within six to 12 months through microbial activity, which enriches soil health without leaving residue. Plastic mulch, while durable for multiple seasons, can persist in the environment for decades, contributing to plastic pollution unless properly collected and recycled. Choosing biodegradable mulch supports sustainable gardening by aligning longevity with environmental decomposition rates, reducing long-term waste impact.
Choosing the Right Mulch for Your Garden Needs
Biodegradable mulch offers eco-friendly benefits by naturally breaking down and enriching soil, making it ideal for sustainable gardening practices, whereas plastic mulch provides superior weed control and moisture retention but requires removal and disposal. Selecting the right mulch depends on your garden's environmental priorities, crop type, and maintenance capabilities. Consider soil health, cost-effectiveness, and long-term impact when deciding between biodegradable and plastic mulch for optimal growth and sustainability.
Sustainable Gardening: The Future of Mulching Solutions
Biodegradable mulch made from natural materials like cornstarch and cellulose breaks down into the soil, enhancing soil health without leaving harmful residues, making it a sustainable choice for eco-conscious gardeners. Plastic mulch, while effective at weed control and moisture retention, contributes to long-term environmental pollution as it does not decompose and requires disposal. Sustainable gardening increasingly favors biodegradable mulch as a future-forward mulching solution that supports soil ecology and reduces plastic waste in gardens.
Biodegradable mulch vs Plastic mulch Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com