Insecticidal soap effectively targets soft-bodied insects by disrupting their cell membranes, providing a fast-acting, low-toxicity option for garden pest control. Neem oil offers a broader spectrum approach by interfering with pest feeding and reproduction, making it ideal for managing a wide range of insects and fungal issues while promoting plant health. Choosing between insecticidal soap and neem oil depends on the specific pest problem and the desired level of environmental impact and plant safety.
Table of Comparison
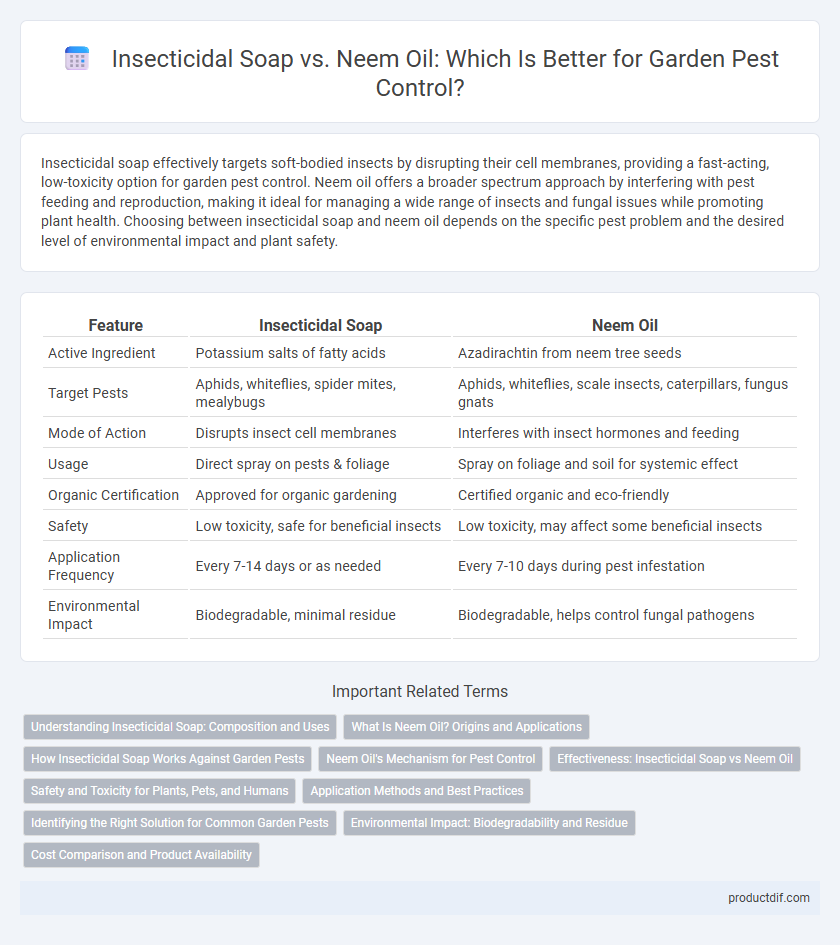
| Feature | Insecticidal Soap | Neem Oil |
|---|---|---|
| Active Ingredient | Potassium salts of fatty acids | Azadirachtin from neem tree seeds |
| Target Pests | Aphids, whiteflies, spider mites, mealybugs | Aphids, whiteflies, scale insects, caterpillars, fungus gnats |
| Mode of Action | Disrupts insect cell membranes | Interferes with insect hormones and feeding |
| Usage | Direct spray on pests & foliage | Spray on foliage and soil for systemic effect |
| Organic Certification | Approved for organic gardening | Certified organic and eco-friendly |
| Safety | Low toxicity, safe for beneficial insects | Low toxicity, may affect some beneficial insects |
| Application Frequency | Every 7-14 days or as needed | Every 7-10 days during pest infestation |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, minimal residue | Biodegradable, helps control fungal pathogens |
Understanding Insecticidal Soap: Composition and Uses
Insecticidal soap is composed primarily of potassium salts of fatty acids derived from plants, making it a biodegradable and eco-friendly solution for managing soft-bodied insects like aphids, whiteflies, and spider mites. This soap works by breaking down the insect's cell membranes, causing dehydration and death without harming beneficial insects or plants. Commonly used in organic gardening, insecticidal soap is effective for direct contact application and requires thorough coverage of affected plant areas for optimal pest control.
What Is Neem Oil? Origins and Applications
Neem oil, extracted from the seeds of the Azadirachta indica tree native to India and Southeast Asia, serves as a natural insecticide and fungicide in garden supply. Rich in azadirachtin, this bioactive compound disrupts insect growth and feeding, making neem oil effective against pests such as aphids, whiteflies, and spider mites. Its applications extend to organic farming, pest control in vegetable gardens, and as a preventative treatment for fungal diseases like powdery mildew.
How Insecticidal Soap Works Against Garden Pests
Insecticidal soap works by breaking down the outer protective layer of soft-bodied garden pests like aphids, whiteflies, and spider mites, causing dehydration and death. It targets the pest's cell membranes directly, making it effective without harming most beneficial insects or plants. This mode of action helps gardeners control infestations while maintaining a healthy garden ecosystem.
Neem Oil's Mechanism for Pest Control
Neem oil controls pests by disrupting the feeding, growth, and reproduction of various insects due to its active compound azadirachtin, which acts as an antifeedant and growth regulator. It interferes with the hormone systems of insects, leading to molting disruption and reduced egg-laying, effectively reducing pest populations over time. This natural botanical insecticide targets a broad spectrum of garden pests while being biodegradable and safe for beneficial insects when used as directed.
Effectiveness: Insecticidal Soap vs Neem Oil
Insecticidal soap effectively targets soft-bodied insects such as aphids, whiteflies, and spider mites by disrupting their cell membranes on direct contact. Neem oil operates both as an insecticide and a fungicide, interfering with insect hormone systems to reduce feeding and reproduction, making it effective against a broader range of pests including scale, mealybugs, and fungal diseases. Neem oil offers longer residual protection compared to insecticidal soap, which requires more frequent applications for sustained control.
Safety and Toxicity for Plants, Pets, and Humans
Insecticidal soap and neem oil are popular garden supplies known for low toxicity and safety to plants, pets, and humans when used as directed; insecticidal soap works by disrupting insect cell membranes while neem oil acts as a natural pesticide and fungicide derived from the neem tree. Both treatments minimize chemical residue and degrade quickly, reducing environmental impact and risk to beneficial insects like bees and ladybugs. Neem oil may cause mild phytotoxicity on sensitive plants if applied in hot conditions, whereas insecticidal soap is generally safer but can damage delicate foliage if overused.
Application Methods and Best Practices
Insecticidal soap is typically applied as a direct spray to the foliage, targeting soft-bodied insects through contact, while neem oil is often diluted and sprayed broadly, affecting pests both on contact and systemically through plant absorption. Best practices for insecticidal soap include avoiding application during peak sunlight to prevent leaf burn and ensuring thorough coverage for effective pest control. Neem oil application benefits from consistent treatment every 7-14 days and is most effective when applied during early morning or late evening to maximize absorption and minimize plant stress.
Identifying the Right Solution for Common Garden Pests
Insecticidal soap effectively targets soft-bodied pests like aphids and spider mites by disrupting their cell membranes without harming beneficial insects, making it ideal for quick pest control. Neem oil acts as a repellent and growth disruptor for a broad spectrum of insects including whiteflies and scales, while also providing antifungal properties that protect plants from diseases. Choosing between insecticidal soap and neem oil depends on the type of pests present, plant sensitivity, and whether organic antifungal benefits are desired for overall garden health.
Environmental Impact: Biodegradability and Residue
Insecticidal soap is highly biodegradable, breaking down quickly in the environment with minimal residue, making it a safer choice for beneficial insects and soil health. Neem oil, derived from the neem tree, also biodegrades naturally but can leave some residue that persists longer, potentially affecting non-target organisms if overused. Both options reduce chemical pollution compared to synthetic pesticides, but insecticidal soap generally offers a lower environmental footprint due to its rapid degradation.
Cost Comparison and Product Availability
Insecticidal soap typically costs between $8 and $15 per quart, making it an affordable option for small to medium-sized gardens, while neem oil ranges from $10 to $20 per quart due to its multi-purpose uses. Both products are widely available at garden centers, home improvement stores, and online retailers, but neem oil is often found in organic and specialty gardening sections. The choice between the two often depends on budget constraints and the desired spectrum of pest control benefits.
Insecticidal Soap vs Neem Oil Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com