Organic fertilizer enriches soil health by improving its structure and promoting beneficial microbial activity, making it a sustainable choice for long-term gardening. Synthetic fertilizer provides nutrients quickly and in precise amounts, which can boost plant growth rapidly but may harm soil quality and lead to nutrient runoff. Choosing between organic and synthetic fertilizer depends on balancing immediate plant needs with environmental impact and soil vitality.
Table of Comparison
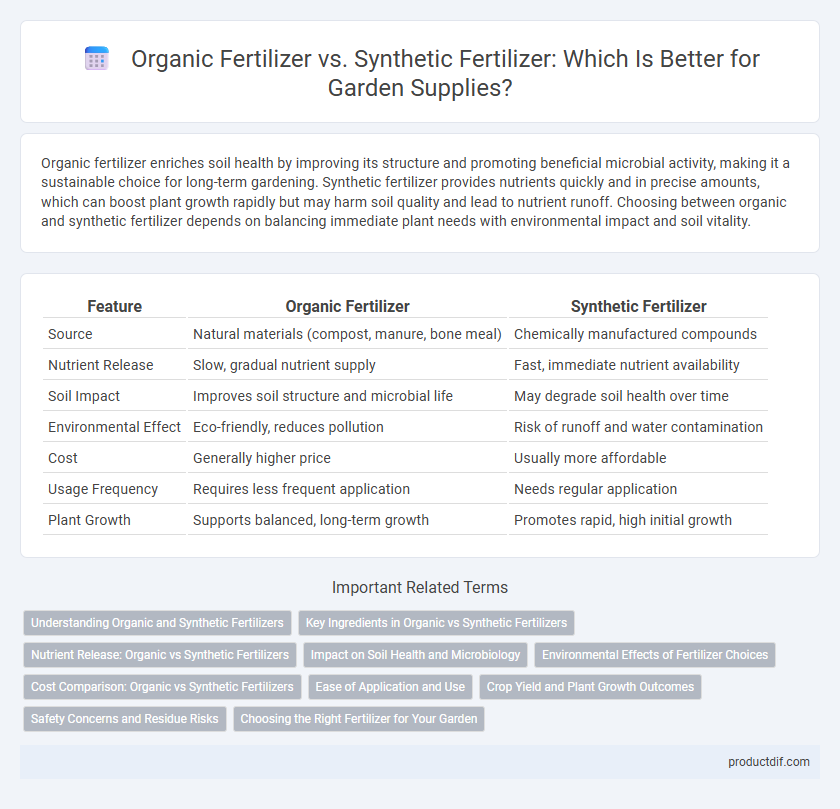
| Feature | Organic Fertilizer | Synthetic Fertilizer |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Natural materials (compost, manure, bone meal) | Chemically manufactured compounds |
| Nutrient Release | Slow, gradual nutrient supply | Fast, immediate nutrient availability |
| Soil Impact | Improves soil structure and microbial life | May degrade soil health over time |
| Environmental Effect | Eco-friendly, reduces pollution | Risk of runoff and water contamination |
| Cost | Generally higher price | Usually more affordable |
| Usage Frequency | Requires less frequent application | Needs regular application |
| Plant Growth | Supports balanced, long-term growth | Promotes rapid, high initial growth |
Understanding Organic and Synthetic Fertilizers
Organic fertilizers are derived from natural materials such as compost, manure, and bone meal, providing essential nutrients that improve soil structure and promote microbial activity. Synthetic fertilizers consist of chemically manufactured compounds that deliver concentrated nutrients quickly but may risk soil degradation and nutrient runoff. Understanding the benefits and limitations of both types enables gardeners to make informed decisions tailored to plant needs and environmental impact.
Key Ingredients in Organic vs Synthetic Fertilizers
Organic fertilizers contain natural ingredients such as composted manure, bone meal, and seaweed, which release nutrients slowly and improve soil health by enhancing microbial activity. Synthetic fertilizers typically include concentrated chemical compounds like ammonium nitrate, urea, and superphosphate, designed for rapid nutrient availability and precise nutrient ratios. The key difference lies in organic fertilizers providing a broad spectrum of micronutrients and organic matter, while synthetic fertilizers offer specific, readily available macronutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium.
Nutrient Release: Organic vs Synthetic Fertilizers
Organic fertilizers release nutrients slowly as microbes break down natural materials, providing a steady supply of essential elements like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium over time. Synthetic fertilizers deliver nutrients in a readily available form, resulting in faster plant uptake but increased risk of nutrient runoff and leaching. Understanding the nutrient release patterns helps gardeners select the best fertilizer type for crop needs and soil health.
Impact on Soil Health and Microbiology
Organic fertilizer enhances soil health by promoting beneficial microbial activity and improving soil structure through natural nutrient cycling. Synthetic fertilizers provide immediate nutrient availability but can disrupt soil microbiology, reducing microbial diversity and long-term soil fertility. Sustainable garden management prioritizes organic inputs to maintain robust soil ecosystems and ensure nutrient balance.
Environmental Effects of Fertilizer Choices
Organic fertilizers improve soil health by enhancing microbial activity and reducing chemical runoff, which helps in maintaining biodiversity and preventing water pollution. Synthetic fertilizers often lead to nutrient leaching and greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to soil degradation and environmental imbalance. Choosing organic options supports sustainable gardening practices and minimizes long-term ecological damage.
Cost Comparison: Organic vs Synthetic Fertilizers
Organic fertilizers typically have higher upfront costs due to natural ingredient sourcing and slower nutrient release, but they improve soil health and reduce long-term expenses. Synthetic fertilizers offer lower initial prices and faster nutrient availability, but may lead to soil degradation and increased dependency on chemical inputs over time. Evaluating total cost-effectiveness requires considering both immediate expenses and lasting impacts on soil productivity.
Ease of Application and Use
Organic fertilizer typically requires less frequent application due to its slow nutrient release, making it easier for gardeners to manage over time. Synthetic fertilizer offers precise nutrient formulations and quick results but often demands careful measuring and more frequent use to avoid over-fertilization. Ease of application varies with the gardener's knowledge, as organic options may need composting or spreading, while synthetic types often come in ready-to-use granular or liquid forms.
Crop Yield and Plant Growth Outcomes
Organic fertilizers enhance soil structure and microbial activity, leading to sustainable nutrient release that improves crop yield over time and promotes healthier, more resilient plant growth. Synthetic fertilizers provide immediate nutrient availability, resulting in rapid crop growth and higher initial yields but may cause soil degradation and reduced long-term fertility. Balancing organic and synthetic inputs can optimize plant growth outcomes and maintain soil vitality for consistent crop production.
Safety Concerns and Residue Risks
Organic fertilizer offers enhanced safety by minimizing chemical residues and reducing the risk of soil and water contamination commonly associated with synthetic fertilizers. Synthetic fertilizers pose greater residue risks due to their concentrated chemical compounds, which may accumulate in crops and negatively impact human health. Choosing organic options supports sustainable gardening practices while ensuring safer produce free from harmful synthetic residues.
Choosing the Right Fertilizer for Your Garden
Organic fertilizer enhances soil health by providing essential nutrients and promoting microbial activity, making it ideal for long-term garden sustainability. Synthetic fertilizer delivers nutrients in concentrated forms for rapid plant growth but may lead to soil degradation over time. Selecting the right fertilizer depends on soil condition, plant needs, and environmental impact considerations to optimize garden productivity and health.
Organic fertilizer vs Synthetic fertilizer Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com