Hydroponics and aquaponics are innovative soil-free gardening methods that optimize plant growth through nutrient-rich water solutions. Hydroponics uses mineral nutrient solutions in water, allowing precise control over plant nutrition and faster growth rates. Aquaponics integrates fish farming with hydroponic cultivation, creating a sustainable ecosystem where fish waste provides natural fertilizers for plants, reducing environmental impact and water usage.
Table of Comparison
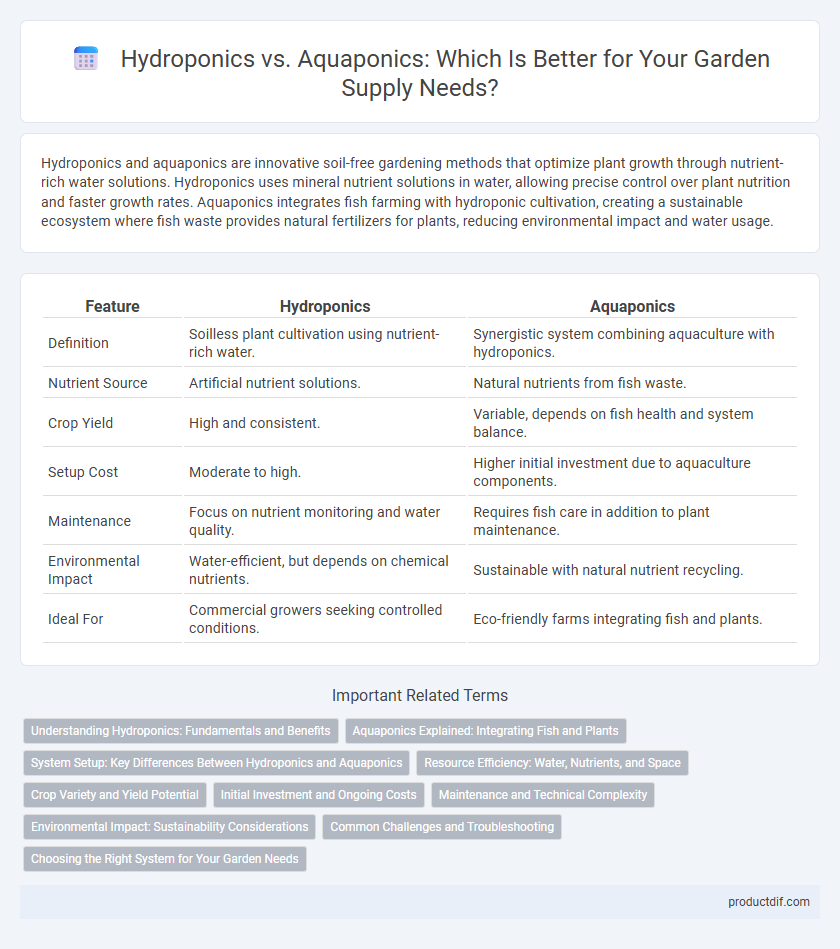
| Feature | Hydroponics | Aquaponics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Soilless plant cultivation using nutrient-rich water. | Synergistic system combining aquaculture with hydroponics. |
| Nutrient Source | Artificial nutrient solutions. | Natural nutrients from fish waste. |
| Crop Yield | High and consistent. | Variable, depends on fish health and system balance. |
| Setup Cost | Moderate to high. | Higher initial investment due to aquaculture components. |
| Maintenance | Focus on nutrient monitoring and water quality. | Requires fish care in addition to plant maintenance. |
| Environmental Impact | Water-efficient, but depends on chemical nutrients. | Sustainable with natural nutrient recycling. |
| Ideal For | Commercial growers seeking controlled conditions. | Eco-friendly farms integrating fish and plants. |
Understanding Hydroponics: Fundamentals and Benefits
Hydroponics is a soil-free gardening method where plants grow in nutrient-rich water solutions, optimizing space and water usage while promoting faster growth rates compared to traditional soil gardening. This technique allows precise control over nutrient delivery, minimizing pest risks and enhancing plant health and yield. Hydroponic systems are ideal for growing leafy greens, herbs, and certain fruits, making them highly efficient for both commercial and home garden supply applications.
Aquaponics Explained: Integrating Fish and Plants
Aquaponics combines fish farming and hydroponic plant cultivation in a symbiotic environment where fish waste provides essential nutrients for plant growth, eliminating the need for chemical fertilizers. This sustainable system promotes water conservation by recirculating water between the fish tanks and grow beds, enhancing resource efficiency. Aquaponics supports diverse plant varieties, such as leafy greens and herbs, while producing protein-rich fish, creating an integrated ecosystem ideal for urban gardening and commercial agriculture.
System Setup: Key Differences Between Hydroponics and Aquaponics
Hydroponics relies on a soil-free system using nutrient-rich water solutions circulated through plant roots, requiring pumps, reservoirs, and grow trays for setup. Aquaponics integrates fish tanks with plant beds, where fish waste provides natural nutrients processed by bacteria before reaching plants, necessitating additional components like biofilters and aeration systems. The complexity of aquaponics setup is higher due to the need to balance aquatic life and plant health, whereas hydroponics is more straightforward and focused solely on nutrient delivery and water management.
Resource Efficiency: Water, Nutrients, and Space
Hydroponics uses up to 90% less water than traditional soil gardening by recycling nutrient solutions, while aquaponics integrates fish waste as natural fertilizer, optimizing nutrient cycling with minimal external input. Both systems maximize space efficiency by enabling vertical farming and higher crop density, but aquaponics requires more water to sustain aquatic life, balancing resource use differently than hydroponics. The synergy of water recirculation and efficient nutrient delivery in these methods ensures sustainable growth with reduced environmental impact.
Crop Variety and Yield Potential
Hydroponics allows precise control over nutrient delivery, supporting a wider variety of crops including leafy greens, herbs, and fruiting plants, often achieving faster growth rates and higher yields per square foot. Aquaponics combines fish farming with crop cultivation, favoring leafy greens and herbs while producing both protein and vegetables, but the nutrient balance can limit crop variety and yield consistency compared to hydroponics. Crop diversity and yield potential in hydroponics typically surpass aquaponics due to optimized nutrient management and fewer biological dependencies.
Initial Investment and Ongoing Costs
Hydroponic systems generally require a lower initial investment compared to aquaponics, as they involve fewer components such as fish tanks and water filtration systems. Ongoing costs for hydroponics mainly include nutrient solutions, electricity, and water, whereas aquaponics incurs additional expenses related to fish feed, fish care, and more complex system maintenance. Choosing between hydroponics and aquaponics depends on budget constraints and willingness to manage biological elements alongside plant production.
Maintenance and Technical Complexity
Hydroponics systems require regular nutrient solution monitoring and precise pH adjustments, demanding consistent maintenance to ensure optimal plant growth. Aquaponics setups combine fish and plant care, involving complex biological balance management, which increases technical complexity due to balancing water quality for both aquatic life and plants. Maintenance in aquaponics is more intricate, requiring expertise in fish health, water chemistry, and system mechanics compared to the more controlled nutrient management in hydroponics.
Environmental Impact: Sustainability Considerations
Hydroponics uses nutrient-rich water solutions to grow plants without soil, reducing water usage by up to 90% compared to traditional agriculture and minimizing land degradation. Aquaponics combines hydroponic plant cultivation with fish farming, creating a closed-loop system that recycles nutrients and waste, decreasing the need for synthetic fertilizers and lowering water pollution. Both methods promote sustainable agriculture by conserving resources, but aquaponics offers enhanced biodiversity benefits and more efficient nutrient cycling.
Common Challenges and Troubleshooting
Hydroponics and aquaponics systems both face common challenges such as nutrient imbalance, water quality management, and pest control. Troubleshooting often involves monitoring pH levels closely, ensuring proper oxygenation, and preventing root diseases like root rot. Regular system maintenance and biofilter cleaning are essential to sustain healthy plant growth and fish well-being in aquaponics.
Choosing the Right System for Your Garden Needs
Hydroponics utilizes nutrient-rich water solutions to grow plants without soil, offering precise control over nutrient delivery and faster plant growth. Aquaponics combines hydroponics with aquaculture, using fish waste to naturally fertilize plants, creating a sustainable ecosystem that reduces water usage and waste. Selecting the right system depends on factors like space, budget, desired crop types, and commitment to maintaining aquatic life.
Hydroponics vs Aquaponics Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com