Native plants are adapted to the local climate and soil, requiring less water and maintenance while supporting local wildlife and pollinators. Exotic plants can add unique colors and textures but may become invasive, outcompeting native species and disrupting ecosystems. Choosing native plants promotes biodiversity and sustainability in garden supply planning.
Table of Comparison
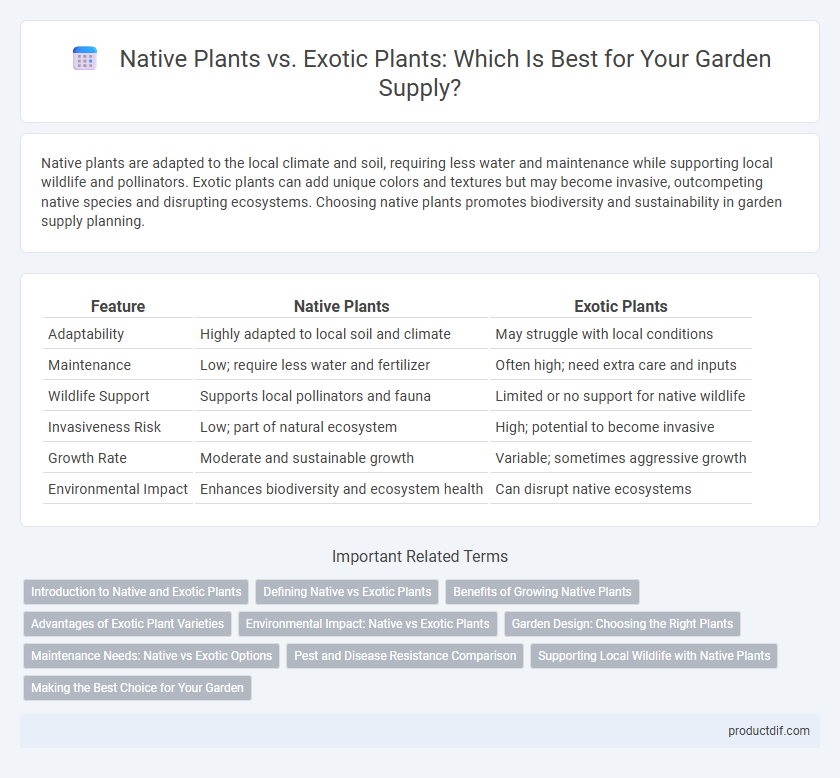
| Feature | Native Plants | Exotic Plants |
|---|---|---|
| Adaptability | Highly adapted to local soil and climate | May struggle with local conditions |
| Maintenance | Low; require less water and fertilizer | Often high; need extra care and inputs |
| Wildlife Support | Supports local pollinators and fauna | Limited or no support for native wildlife |
| Invasiveness Risk | Low; part of natural ecosystem | High; potential to become invasive |
| Growth Rate | Moderate and sustainable growth | Variable; sometimes aggressive growth |
| Environmental Impact | Enhances biodiversity and ecosystem health | Can disrupt native ecosystems |
Introduction to Native and Exotic Plants
Native plants are species that have evolved naturally in a specific region, adapted to local soil, climate, and wildlife, promoting biodiversity and ecosystem stability. Exotic plants, introduced from other regions or countries, can offer aesthetic variety and crop potential but may risk disrupting native ecosystems if invasive. Understanding the differences between native and exotic plants is crucial for gardeners aiming to support local habitats while exploring diverse garden designs.
Defining Native vs Exotic Plants
Native plants naturally occur in a specific region or ecosystem without human intervention, often supporting local wildlife and maintaining ecological balance. Exotic plants, also known as non-native or invasive species, are introduced from other regions and can sometimes disrupt native habitats by competing for resources. Understanding the difference between native and exotic plants is crucial for effective garden supply choices that promote biodiversity and sustainable landscaping.
Benefits of Growing Native Plants
Native plants enhance local biodiversity by providing essential habitats and food sources for native pollinators and wildlife. They require less water, fertilizer, and maintenance since they are adapted to regional soil and climate conditions. Incorporating native plants into gardens promotes ecological balance and supports sustainable landscaping practices.
Advantages of Exotic Plant Varieties
Exotic plant varieties offer unique aesthetic appeal and enhanced biodiversity by introducing new colors, textures, and flowering times to gardens. These plants often demonstrate increased resistance to local pests and diseases, reducing the need for chemical treatments and lowering maintenance efforts. Many exotic species can thrive in diverse environmental conditions, contributing to more resilient and adaptable garden ecosystems.
Environmental Impact: Native vs Exotic Plants
Native plants support local ecosystems by providing food and habitat for indigenous wildlife, promoting biodiversity and soil health. Exotic plants often compete with native species, leading to habitat disruption, reduced biodiversity, and sometimes the spread of invasive species that alter ecosystem balance. Choosing native plants helps maintain ecological stability and reduces the environmental impact associated with water use, pesticide application, and soil erosion.
Garden Design: Choosing the Right Plants
Selecting native plants for garden design enhances local biodiversity and ensures better adaptability to soil and climate conditions, reducing maintenance and irrigation needs. Exotic plants offer unique aesthetic appeal and diversity but may require more care and pose risks of invasiveness, disrupting local ecosystems. Balancing native and exotic species allows gardeners to create visually striking landscapes while promoting ecological stability and sustainability.
Maintenance Needs: Native vs Exotic Options
Native plants require significantly less maintenance compared to exotic plants due to their natural adaptation to local soil, climate, and pests. Exotic plants often demand more frequent watering, fertilizing, and pest control, increasing overall garden upkeep. Choosing native species promotes sustainable gardening by reducing resource consumption and minimizing chemical interventions.
Pest and Disease Resistance Comparison
Native plants exhibit higher pest and disease resistance due to their evolutionary adaptation to local conditions, reducing the need for chemical interventions in gardens. Exotic plants often lack this resilience, making them more susceptible to infestations and diseases that local pests and pathogens can exploit. Selecting native species enhances sustainable garden management by promoting ecological balance and minimizing pest-related damage.
Supporting Local Wildlife with Native Plants
Native plants provide essential habitat and food sources for local wildlife, promoting biodiversity and ecosystem health. They are well-adapted to the climate and soil conditions, reducing the need for additional water and fertilizers. In contrast, exotic plants often fail to support native insects and birds, potentially disrupting local ecological balance.
Making the Best Choice for Your Garden
Selecting native plants enhances garden resilience by supporting local ecosystems and requiring less maintenance due to their adaptation to regional soil and climate conditions. Exotic plants can offer unique colors and textures but may demand more water, fertilizer, and pest control, potentially disrupting local biodiversity. Prioritizing native species ensures sustainability, conserves resources, and promotes pollinator health for a thriving garden environment.
Native plants vs Exotic plants Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com