Slow-release fertilizer provides nutrients gradually over time, reducing the risk of burning plants and minimizing frequent applications. Liquid fertilizer delivers nutrients quickly, offering immediate feeding but requiring more frequent use to maintain nutrient levels. Choosing between them depends on plant type and growth stage, with slow-release ideal for steady nourishment and liquid best for quick nutrient boosts.
Table of Comparison
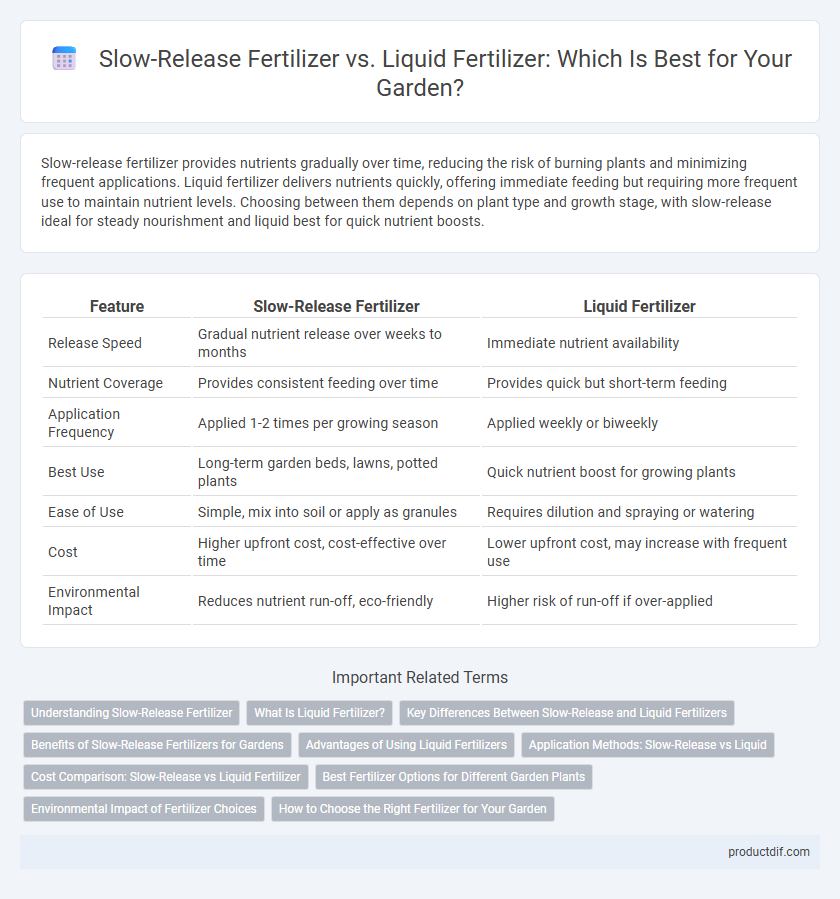
| Feature | Slow-Release Fertilizer | Liquid Fertilizer |
|---|---|---|
| Release Speed | Gradual nutrient release over weeks to months | Immediate nutrient availability |
| Nutrient Coverage | Provides consistent feeding over time | Provides quick but short-term feeding |
| Application Frequency | Applied 1-2 times per growing season | Applied weekly or biweekly |
| Best Use | Long-term garden beds, lawns, potted plants | Quick nutrient boost for growing plants |
| Ease of Use | Simple, mix into soil or apply as granules | Requires dilution and spraying or watering |
| Cost | Higher upfront cost, cost-effective over time | Lower upfront cost, may increase with frequent use |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces nutrient run-off, eco-friendly | Higher risk of run-off if over-applied |
Understanding Slow-Release Fertilizer
Slow-release fertilizer gradually delivers nutrients to plants over an extended period, minimizing nutrient loss and reducing the frequency of application compared to liquid fertilizer. Its controlled nutrient release enhances root development and improves soil health by maintaining consistent nutrient availability. This makes slow-release fertilizer ideal for sustained plant growth and reduced environmental impact in garden supply management.
What Is Liquid Fertilizer?
Liquid fertilizer is a water-soluble nutrient solution commonly used in gardens to provide immediate nourishment to plants. It delivers essential macro and micronutrients directly to the root zone or foliage, ensuring rapid absorption and quick growth response. Gardeners often choose liquid fertilizer for its ease of application and ability to correct nutrient deficiencies promptly.
Key Differences Between Slow-Release and Liquid Fertilizers
Slow-release fertilizers gradually supply nutrients over weeks or months, minimizing leaching and reducing the frequency of application, making them ideal for long-term plant health. Liquid fertilizers provide immediate nutrient availability, promoting rapid growth and quick correction of nutrient deficiencies but require frequent reapplication due to faster nutrient depletion. The choice between slow-release and liquid fertilizers depends on plant type, growth stage, and desired speed of nutrient uptake in gardening and agricultural practices.
Benefits of Slow-Release Fertilizers for Gardens
Slow-release fertilizers provide a steady supply of nutrients over an extended period, reducing the risk of nutrient leaching and minimizing the need for frequent reapplication. These fertilizers enhance root development and promote sustained plant growth by delivering essential elements like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium gradually. Their controlled nutrient release improves soil health and water efficiency, making them ideal for maintaining long-term garden productivity.
Advantages of Using Liquid Fertilizers
Liquid fertilizers offer immediate nutrient availability to plants, promoting rapid growth and quick recovery from nutrient deficiencies. Their ease of application allows for precise nutrient delivery through foliar feeding or irrigation systems, enhancing efficiency and reducing waste. This method supports better nutrient uptake, especially in container gardening and hydroponics, ensuring optimal plant health and productivity.
Application Methods: Slow-Release vs Liquid
Slow-release fertilizers are typically applied directly to the soil, releasing nutrients gradually over weeks or months, reducing the frequency of application and minimizing nutrient runoff. Liquid fertilizers are usually applied via foliar spray or irrigation systems, providing quick nutrient absorption but requiring more frequent applications to maintain optimal nutrient levels. Understanding these application methods helps gardeners choose the best fertilizer type for their plants' immediate and long-term nutritional needs.
Cost Comparison: Slow-Release vs Liquid Fertilizer
Slow-release fertilizer typically has a higher upfront cost than liquid fertilizer but offers long-term savings by reducing application frequency and nutrient loss. Liquid fertilizer is generally less expensive initially but requires more frequent applications, increasing labor and overall costs. Evaluating cost-efficiency depends on garden size, crop type, and nutrient requirements, with slow-release fertilizers often proving more economical over time for sustained nutrient delivery.
Best Fertilizer Options for Different Garden Plants
Slow-release fertilizer offers a steady nutrient supply over time, ideal for perennials, shrubs, and established trees requiring consistent growth support. Liquid fertilizer provides immediate nutrient availability, perfect for fast-growing vegetables, annuals, and container plants needing quick nourishment. Choosing the best fertilizer depends on plant type, growth stage, and soil conditions to optimize nutrient uptake and garden health.
Environmental Impact of Fertilizer Choices
Slow-release fertilizers reduce nutrient runoff by gradually releasing nutrients, minimizing water pollution and soil degradation compared to liquid fertilizers, which can leach quickly into waterways. Liquid fertilizers, while providing immediate nutrient availability, often contribute to higher rates of nitrogen and phosphorus leaching, increasing the risk of eutrophication in aquatic ecosystems. Choosing slow-release options supports sustainable gardening by enhancing nutrient efficiency and protecting surrounding environments from harmful chemical exposure.
How to Choose the Right Fertilizer for Your Garden
Selecting the right fertilizer depends on your garden's specific needs and growth stage. Slow-release fertilizers provide a steady supply of nutrients over time, ideal for long-term plants and reducing the risk of nutrient burn. Liquid fertilizers deliver quick nutrient absorption, making them suitable for fast-growing plants or correcting nutrient deficiencies rapidly.
Slow-release fertilizer vs Liquid fertilizer Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com